Workspace ONE UEM Management Modes
Overview
An organization’s device deployment can become complex. Some devices might be corporate-owned, some employee-owned. Some users may not be full-time, such as contractors or temp workers, and may report to multiple organizations. And depending on the industry, different levels of security might be required.
Regardless of the type of employee or device, the technology should be transparent and not hinder productivity or the employee experience.
The Workspace ONE platform provides flexibility to support the ever-changing device management needs of an organization as devices and use cases evolve, and the ability to provide a consistent onboarding experience across device makes, models, or employee personas.
Purpose of This Guide
Workspace ONE Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) provides several modes to manage devices with varying levels of control for the administrator and privacy for the user. This document will introduce you to the options and uses for each mode.
Audience
This document is intended for IT administrators and product evaluators who are familiar with Workspace ONE UEM. Knowledge of other technologies, such as Omnissa Access and Omnissa Intelligence, is also helpful.
Management Mode Terminology
To cover a variety of use cases, Workspace ONE provides four general options for device management.
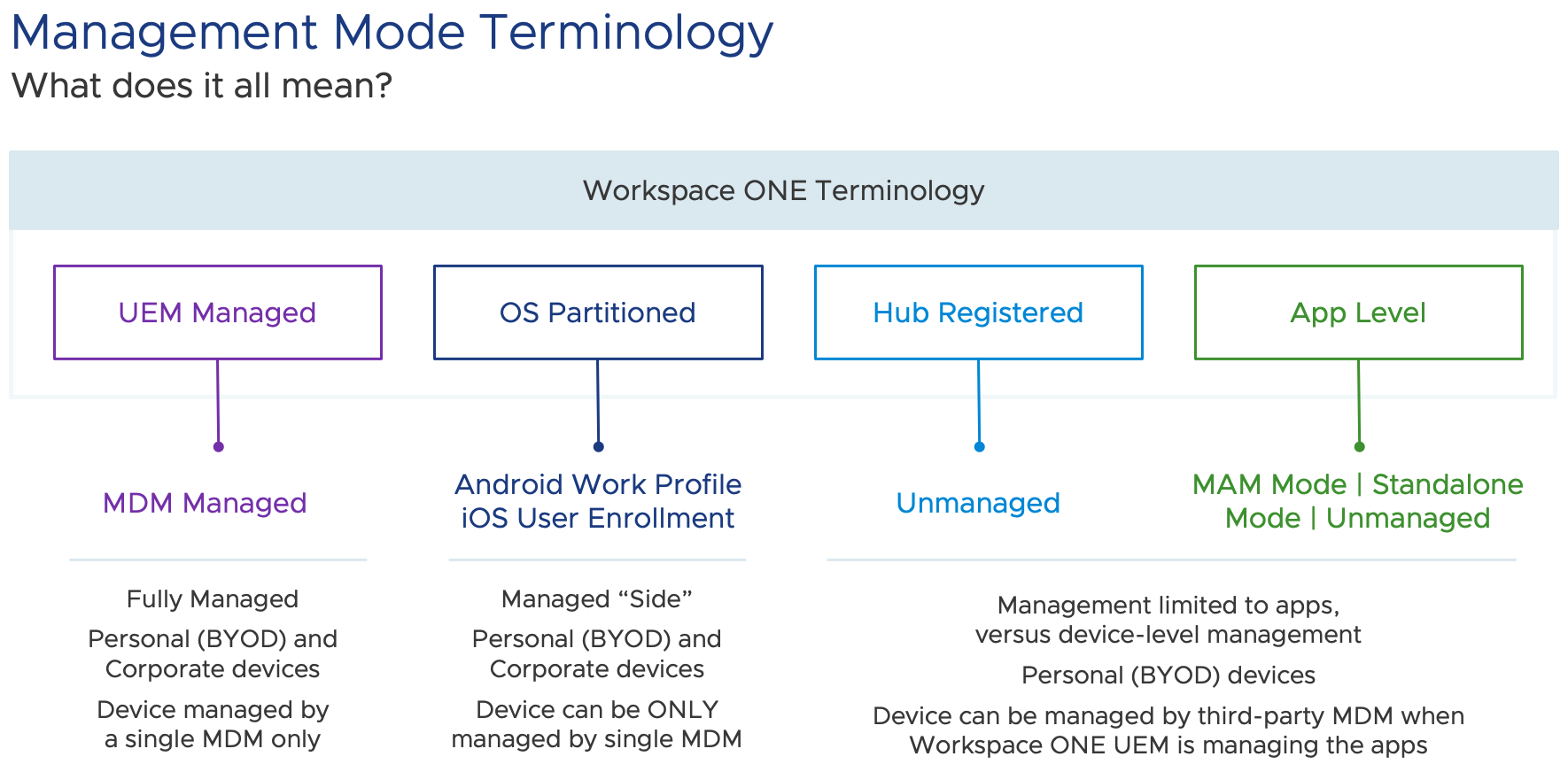
Figure 1: Terminology found in the Workspace ONE UEM admin console mapped to industry terms
UEM Managed
UEM managed, or device-level management, requires the user to enroll the device into management to access any work applications or resources. Enrollment involves downloading a management, or MDM, profile to the device and then Workspace ONE UEM utilizes APIs built into the device operating system to manage aspects of the device and to query data. This method provides the most control for the administrator, including full policies and restrictions, attestation and compliance, conditional access to internal resources, and device remediation.
Most of the time UEM Managed is used for corporate-owned devices; however, many organizations in regulated industries require this level of management even for employee-owned devices. Other terms you might hear are “MDM managed”, “fully managed” or “device-level management.” Note that fully MDM managed devices are managed by a single MDM provider only. In addition, any device listed as “UEM Managed” in the Workspace ONE UEM admin console consumes a UEM device license.
OS Partitioned
The OS partitioned option is provided by the device operating system and is enabled using Workspace ONE UEM, also known as Work Profile for Android or iOS User Enrollment. OS partitioned separates work and personal apps and data to enable administrators to maintain control of the work side of the device, but also provides a private, or personal side. Note that in the Workspace ONE admin console, you will see OS partitioned devices labeled as “UEM Managed” mode, as UEM will be managing only the resources within the partitioned area and this option will also consume a UEM device license.
Hub Registered Mode
Hub Registered mode allows users to log into Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub, the employee-facing digital workspace, and access applications without full, device-level management or an MDM profile. In other words, the device is registered with the UEM console, not managed by the UEM console. The admin can only retrieve limited information about the device and therefore Hub Registered mode provides privacy for the user and is a great option for BYOD, temp or contract workers and any other situations where a user needs quick access to select corporate resources, but the device does not need to be fully managed. Hub Registered devices do still consume a UEM device license since lightweight management can take place.
Note: UEM admins can import a list of device serial numbers into the Workspace ONE UEM console to pre-approve specific devices for UEM enrollment. You will see these devices listed as “Pre-enrollment Registration Record”. Although these devices are shown in the Device List, they have not been enrolled yet and therefore do not consume a UEM device license, and should not be confused with Hub Registered devices which do consume a UEM device license.
App Level Management
App Level management utilizes the Workspace ONE productivity apps, such as Workspace ONE Boxer, Workspace ONE Content, and Workspace ONE Tunnel, in a stand-alone mode without device-level management or Hub Registered mode. For example, a doctor or contractor may work with two or more organizations, and it is not practical to constantly enroll and unenroll his or her device. So, if the doctor or contractor needs email access only, using Workspace ONE Boxer alone may suffice. You may also hear MAM, which stands for Mobile Application Management, or “standalone mode”. App Level managed devices will consume a UEM device license.
Management Mode Comparison
Let’s review some of the major differences between the Workspace ONE UEM management modes.
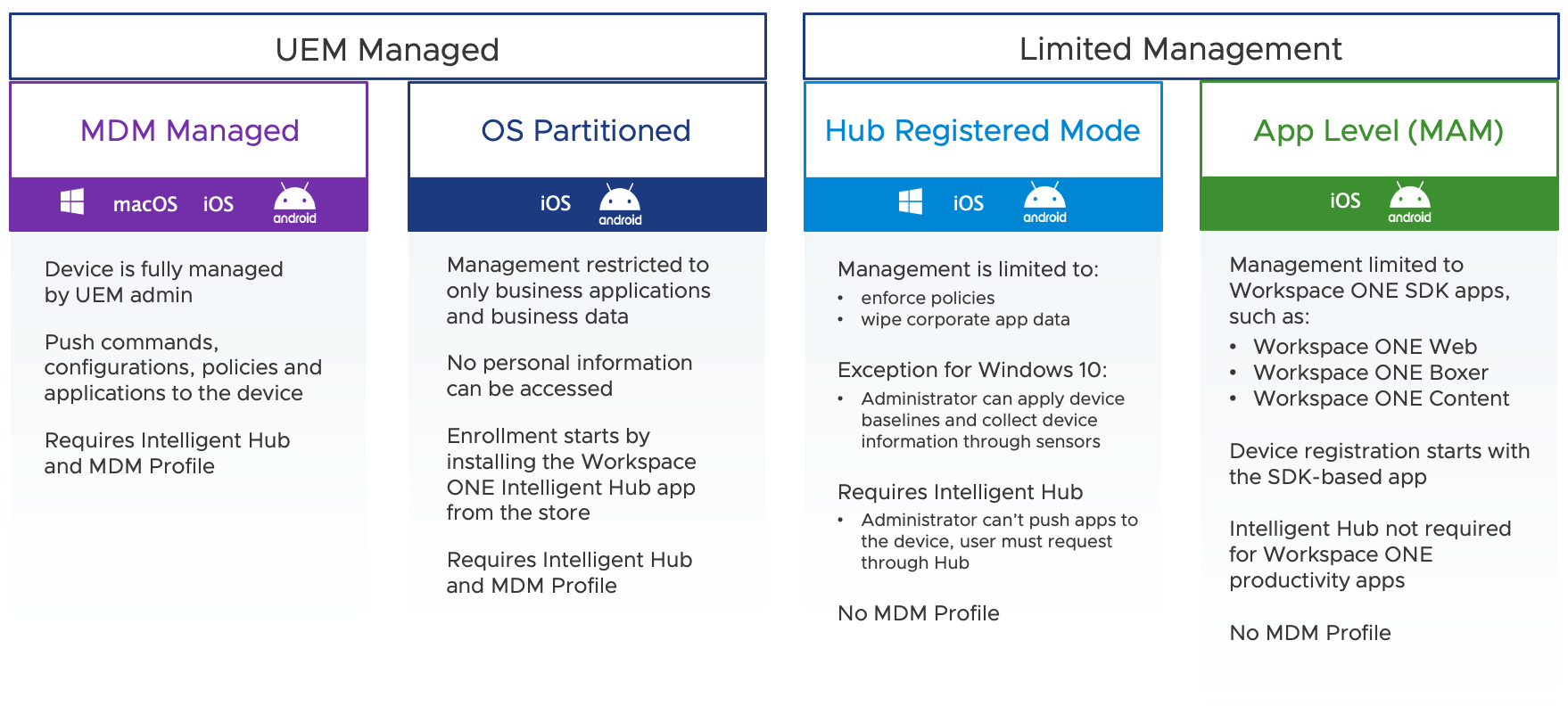
Figure 2: Device management mode comparison
Each one of these management modes has various levels of control for the administrator. UEM Managed will have the most options for administrators to configure and secure devices. Hub Registered mode has fewer management options, and therefore the control switches over to the end user. For example, in Hub Registered mode, the admin cannot push applications to the device, but instead, the user can access the corporate app catalog and download apps as needed. Essentially, any actions are controlled by the end user. Although Hub Registered mode will then have limited access to corporate resources.
In addition to all modes considered “enrolled” and consuming a device license, all these management modes support jailbreak detection for iOS and device rooting detection for Android. Administrators can also enable Workspace ONE Mobile Threat Defense for advanced mobile threat security within Intelligent Hub for iOS and Android and deploy Workspace ONE Assist to remotely troubleshoot devices in real-time, highlight items onscreen, record remote sessions for training purposes, and much more.
Note that Workspace ONE UEM supports Hub Registered mode for Windows 10, iOS, and Android and that the desktop functionality differs from mobile platforms due to the differences in the operating system.
And to clarify App Level management, or MAM, the Workspace ONE Productivity Apps, such as Boxer, Web, Content, and Tunnel, can be used in a stand-alone mode without requiring Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub on the device. Policies and restrictions, such as data loss prevention (DLP), can still be configured for the app even though the device is not fully managed. Also, note that internally developed apps that include the Workspace ONE SDK still require the Intelligent Hub app to register the device in the UEM console.
If you are not already familiar, let’s cover Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub in a little more detail.
What is Intelligent Hub?
Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub is the employee-facing digital workspace application that not only contains the agent that makes device management possible but also includes many other services to improve employee experience, such as a unified app catalog supporting SaaS, native, web and virtual apps, access to links and resources, people search and provides advanced mobile threat defense.
To learn more about Intelligent Hub, check out the Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub page.
How do these management modes look from the admin perspective?
Within the device List View in the Workspace ONE UEM admin console, you will see either UEM Managed, Hub Registered, or App Level. As mentioned earlier, OS Partitioned is still UEM managed, so will have that label in the console.
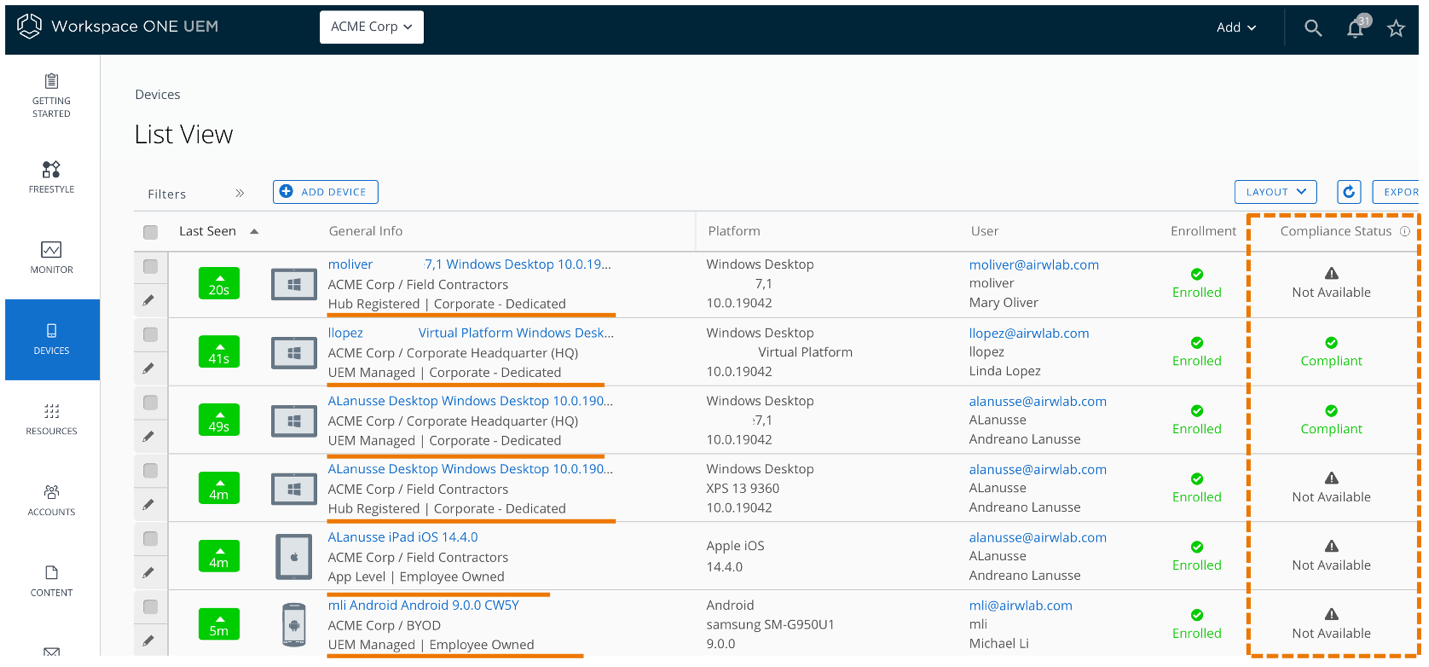
Figure 3: Device List View in Workspace ONE UEM
The management mode will determine what actions the admin can take on the device and what data can be collected. For example, device compliance status is not available for Hub Registered or App Level management modes.
Then if we look at the device details page for an iPad and compare UEM Managed to Hub Registered mode, we can see several differences.
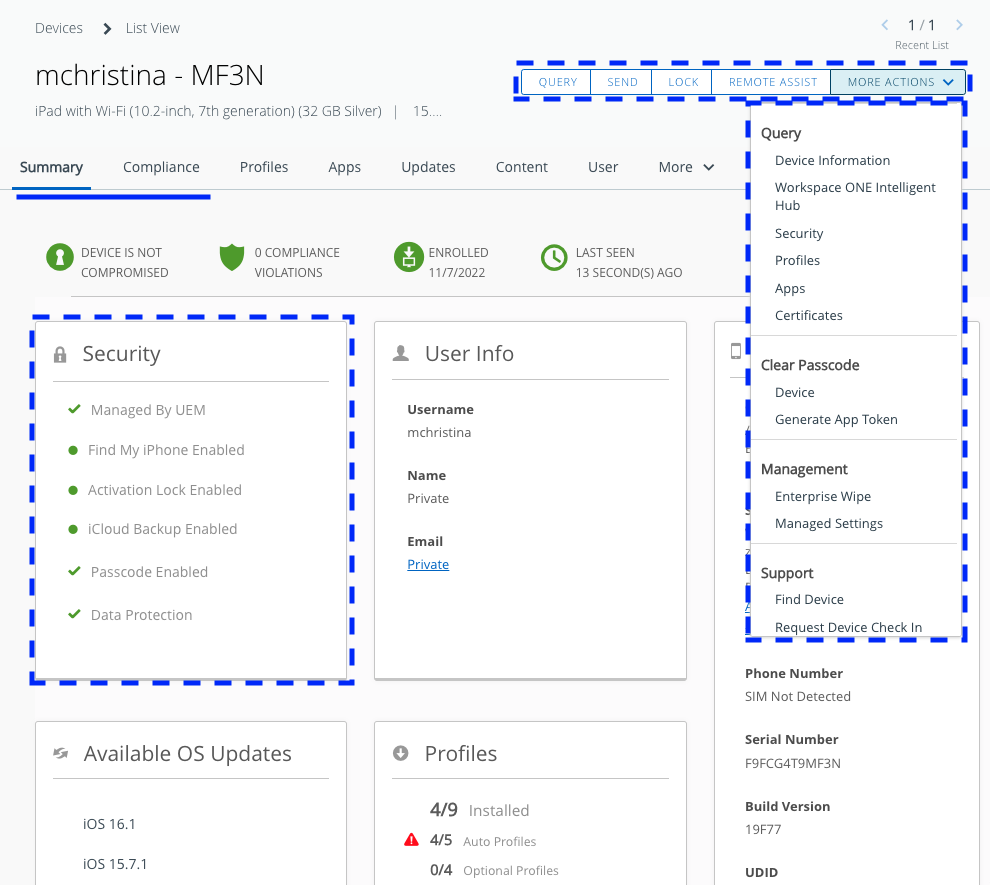
Figure 4: Device Details page in Workspace ONE UEM for UEM Managed iPad
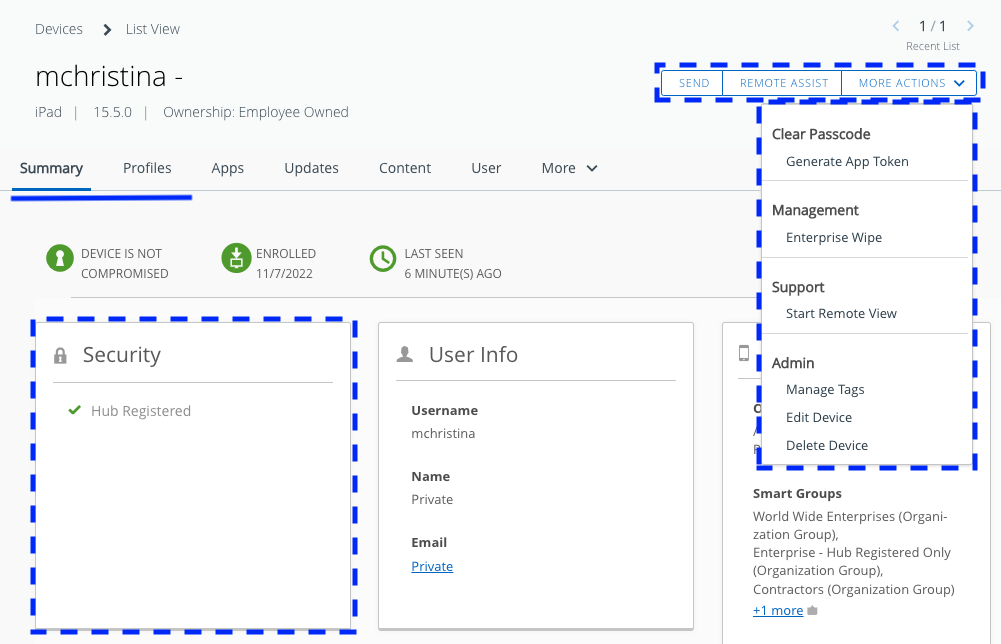
Figure 5: Device Details page in Workspace ONE UEM for iPad in Hub Registered mode
For example, the action bar in the top right has significantly more options for a device that is UEM Managed. In addition, you can query a fully managed device for compliance status, operating system version, and serial number, which is not collected from a Hub Registered device.
When do I use each management mode?
Even though every organization is unique and there are an unlimited number of scenarios, let’s discuss a few examples.
“I just need email access on my phone.”
Enabling email access on a mobile device is the most common use case when a user is trying to access corporate resources. The quickest method to achieve email access when full device management is not required is to utilize the App Level management method. All the user needs on their device is Workspace ONE Boxer, and they can register their device and get access to corporate email without downloading any management profiles. Sometimes this is referred to as “stand-alone Boxer.” The Workspace ONE Productivity apps can be utilized without installing Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub. However, the user would not have access to the app catalog, people search, self-service support resources, and other services found within Intelligent Hub.
“Contractors need access to internal web applications.”
A contractor may only need access to an internal web application to do their job. However, we want to maintain user privacy on a BYO device and ensure secure access to internal resources at the same time. There are two options to achieve this.
Option one is to leverage Workspace ONE Web – Omnissa’s secure mobile web browser for iOS and Android - in App Level management mode, allowing IT to control only the Workspace ONE Web app and related data, and fully configure the app.
DLP, or data loss prevention policies, such as passcode, copy/paste, cache control, and bookmark list can be configured and applied only to the Workspace ONE Web app.
This option only requires a single app for the end-user to download simplifying the experience. Although the user would only have access to bookmarked sites in the Workspace ONE Web app.
A better long-term option might be to utilize Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub in Hub Registered mode to provide additional capabilities to any BYO devices. Users can install native apps and launch web apps directly from the unified app catalog. In addition, when Omnissa Access is utilized, web applications can be forced to open in Workspace ONE Web instead of the device’s native browser for additional security and network tunneling.
“I need access to corporate Wi-Fi in several offices.”
Access to Wi-Fi from within a corporate office is another common use case and is critical to automate for employees because most Wi-Fi still relies on password authentication, which can lead to support tickets and can impact employee experience.
One option is the use of the AirWatch Cloud Connector integrated with an internal PKI to manage the certificate lifecycle and automate certificate deployment to the device. This will enable certificate-based authentication for Wi-Fi, and several other use cases such as single-sign-on to apps and provide immediate access to corporate resources.
However, the device must be fully managed to achieve certificate authentication for Wi-Fi as this requires interaction with the device certificate store, which is not possible when using Hub Registered mode.
“I want to apply Zero Trust principles to determine access to internal applications, SaaS and VDI.”
Enabling external users not physically on the network to access restricted internal applications is a particularly critical use case today with the rise of remote and hybrid work and the shift toward Anywhere Organizations. Management of user identity is mandatory for this use case since admins must deal with different personas (e.g., full-time employees versus contractors, etc.)
The Workspace ONE platform provides a comprehensive solution for secure application access based on device and user posture that aligns with Zero Trust principles. Using Omnissa Access we can authenticate and authorize the user leveraging an advanced mechanism based on user behavior called Risk Score, in addition to device posture information, to only allow devices in compliance to access internal applications. This solution combines device posture information from UEM with machine learning models in Omnissa Intelligence that calculate user risk. The most accurate user risk score and device posture can only be obtained when the device is fully UEM Managed.
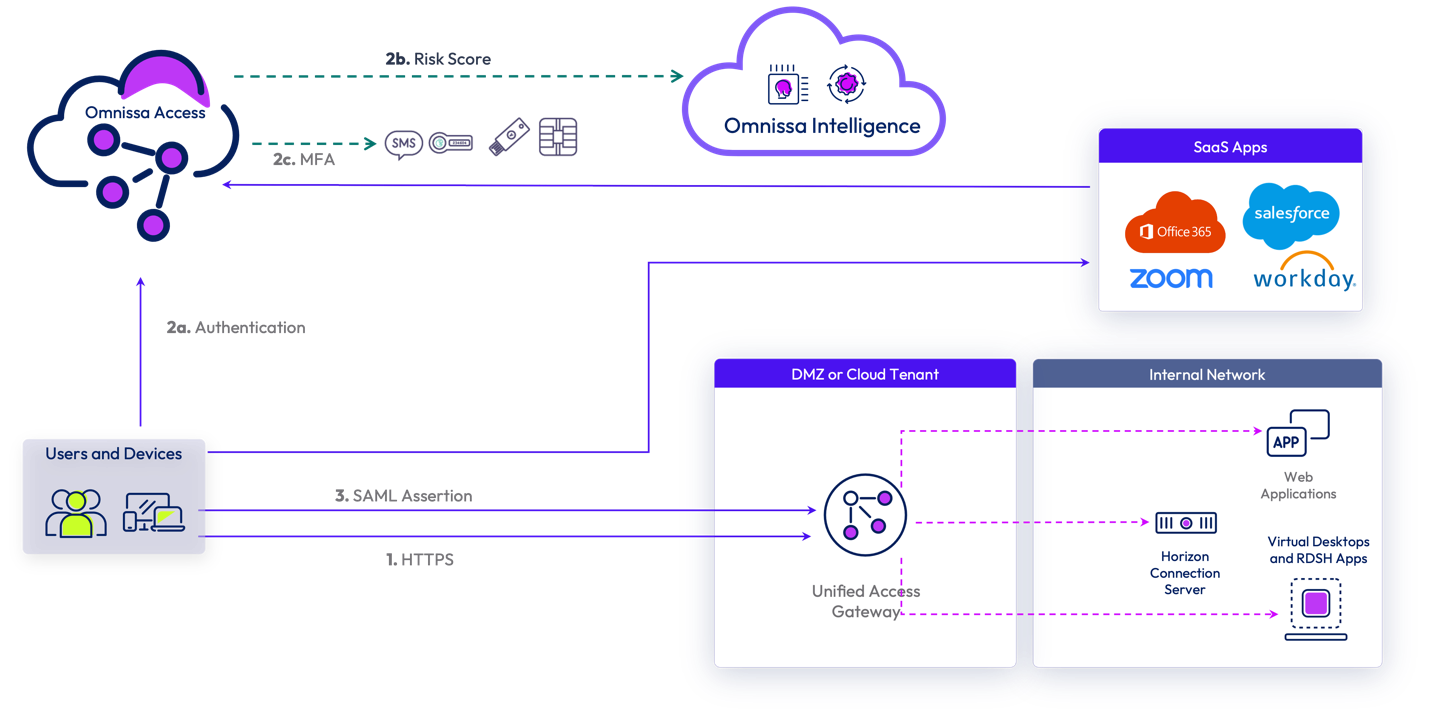
Figure 6: Workspace ONE secure access to applications example
Summary and Additional Resources
Workspace ONE provides a flexible platform to deliver an engaging digital workspace to any device supporting any type of user while ensuring a positive digital employee experience (DEX) and maintaining enterprise-grade security.
Additional Resources
Check out these resources to learn more about Workspace ONE UEM.
- What is Workspace ONE UEM?
- Why so many Workspace ONEs and how are they different?
- Workspace ONE UEM Product Page
- Workspace ONE UEM Architecture
Changelog
The following updates were made to this guide:
| Date | Description of Changes |
| 2024/23/10 |
|
| 2024/01/11 |
|
| 2022/10/24 |
|
Author and Contributors
- Christina Minihan, Staff Architect, Technical Marketing, Omnissa
- Andreano Lanusse, Staff Architect, Technical Marketing, Omnissa
Feedback
Your feedback is valuable.
To comment on this paper, either use the feedback button or contact us at tech_content_feedback@omnissa.com.