Workspace ONE Cloud Services Security
Introduction
This document provides a general overview of the security controls implemented in Omnissa Workspace ONE® commercial cloud offerings and includes information on the following services:
- Omnissa Workspace ONE® Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)™
- Omnissa® Access™ and Omnissa® Workspace ONE Hub Services
- Omnissa Intelligence™
- Omnissa Workspace ONE® Assist™
- Omnissa Connect
Purpose
The intent of this document is to provide readers with an understanding of how Workspace ONE cloud services approach security, the key mechanisms, and processes that Omnissa uses to manage information security, as well as describing the shared responsibilities for providing security in a modern cloud computing environment.
Audience
This document is intended for Workspace ONE commercial cloud administrators. It assumes at least intermediate knowledge of Workspace ONE cloud services and focuses on the policies, processes, and controls supporting the cloud-delivered services. Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP), on-premises, and third-party offerings are not in scope for this document.
Note: You can find the definitions for acronyms used in this document in Acronyms used in the Workspace ONE and Horizon Cloud Security Series.
Shared responsibilities
The end-to-end security of the Workspace ONE cloud-delivered service offerings is shared between Omnissa and our customers. Omnissa provides security for the aspects of the Workspace ONE service offerings over which we have sole physical, logical, and administrative-level control. Customers are responsible for the aspects of the service offerings over which they have administrative-level access or control. The primary areas of responsibility between Omnissa and customers are outlined in the Omnissa Cloud Services Guide.
Omnissa leverages co-located data center facilities and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) providers to support the Workspace ONE service offerings. These providers maintain physical and environmental security controls for the cloud-delivered service. For more information, see Data Center Locations.
Compliance reports
Refer to the Omnissa trust center list to see the latest list of industry certifications.
Data center locations
Workspace ONE service offerings are available in the US, Canada, the European Economic Area (EEA), and Asia-Pacific (APAC) regions. Data center partner hosting facilities’ physical addresses are confidential and on-site visits are prohibited. U.S.-based Workspace ONE UEM deployments are in either co-located data centers or Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Information Security program
Maintaining hosted services and securing data confidentiality, integrity, and availability requires a wide array of tools and processes that must all be expertly designed to comply with laws and regulations while balancing customer satisfaction, business needs, product development, and shareholder expectations. Omnissa balances these needs with a set of controls and management processes designed to both mitigate risk and enhance our product and service offerings. Overarching principles include:
- Risk – Managing risk by understanding the threat landscape, building a solid platform, and leveraging all decision makers when calculating risk.
- Controls – Establishing a balance of effectiveness and efficiency by implementing the appropriate controls for the associated risk.
- Security – Providing preventative and protective capabilities to ensure a secure service.
- Privacy – Integrating privacy-by-design into our business and as a service provider in the delivery of our products and services
The Information Security Program leverages guidance from industry best practices and regulatory standards, including National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) SP 800-53, Payment Card Industry-Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), and International Standards Organization (ISO) 27001. We maintain a written Information Security Program and Policies to protect customer data hosted in our systems, and we perform annual reviews and audits of our program to help ensure the integrity of our hosted offerings.
Omnissa has also signed the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency's (CISA) Secure by Design Pledge. By participating in the Secure by Design Pledge, Omnissa gains a third-party framework and criteria to measure against, in addition to our internal standards that incorporate industry best practices. Adoption of the CISA Secure by Design Pledge includes the acceptance of specific goals, some of which have already been attained here at Omnissa. The list of goals includes heightened use of MFA; the reduction of default passwords; reduction of entire classes of vulnerability; the acceleration of security patch adoption; the adoption of vulnerability disclosure policies; and the increased ability to gather evidence of cybersecurity intrusions. To read more about this topic, see this blog.
Omnissa has an Information Security Governance Committee (ISGC) chaired by members of senior management and representatives from our Information Security, IT Operations, HR, Marketing, Facilities, Privacy and Legal teams.
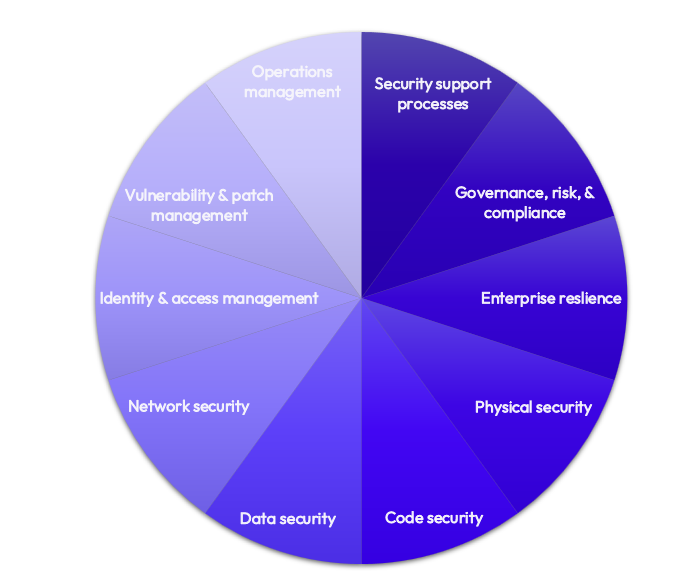
Figure 1: Comprehensive Security Framework
The Omnissa Information Security Management system
Omnissa has implemented various information security policies and procedures that are in line with its overall corporate objectives, which demonstrate a commitment to the management of a formal Information Security Management System (ISMS) that fulfills our obligations to its customers regarding information confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Our ISMS includes, but is not limited to, the following considerations and objectives:
- The threats, vulnerabilities, and the likelihood of occurrences identified by risk assessments relative to the overall business strategy and objectives.
- The legal, statutory, regulatory, and contractual requirements with which Omnissa and relevant applicable partners, contractors, and service providers must comply.
- The principles, objectives, and business requirements for information handling, processing, storing, and archiving data developed by Omnissa to support its business operations.
Omnissa personnel are obligated to comply with Omnissa ISMS data protection requirements in their respective roles, processes, projects, and programs. Failure to adhere to these policies and procedures may result in disciplinary action, including possible termination, and civil or criminal liability.
Asset management
Omnissa maintains an asset management program as part of our ISMS to categorize both physical and logical assets. The Asset Management policy is reviewed at least annually, and all changes are approved by our Information Security Governance Committee.
Data Center Operations teams maintain an inventory of all production assets, including but not limited to software license information, software version numbers, component owners, machine names, and network addresses. Inventory specifications may include device type, model, serial number, and physical location where applicable (such as corporate assets and in co-located data centers). The asset inventory is regularly reviewed in accordance with PCI-DSS requirements.
Data classification and handling
Data classification is one of the foundational elements of the Omnissa ISMS. As such, Omnissa has a comprehensive data classification policy and data handling and protection standards for all electronic and paper media. Data controls and protections are implemented according to their classification.
Our data classification policy provides a matrix of controls arranged by the data lifecycle, from creation of the data to its destruction, and covers all forms of media while in use, in transit, or archived. The policy focuses on data classification sources, status, risks, and categories associated with the normal data lifecycle. Assets are classified in terms of their value, legal requirements, sensitivity, and criticality to Omnissa and to our customers. Customer-owned information is classified as “Restricted,” which is the most stringent data classification at Omnissa. Data classification and handling policies are audited at least annually by independent third-party auditors.
Physical security
The Omnissa physical security policy governs security for our offices, data centers, support centers, and other global business locations to safeguard information systems and staff.
Key elements of this policy include controls around physical security perimeters, physical entry controls, physical access, securing offices, rooms and facilities, visitors to facilities, records, preventing the misuse of facilities, protecting against external and environmental threats, working in secure areas, access to restricted areas, delivery and loading areas, equipment siting and protection, supporting utilities, equipment maintenance, removal of assets, security of equipment and assets off-premises, secure disposal or reuse of equipment, unattended user equipment and clear desk and clear screen.
Omnissa leverages co-located data center facilities in the U.S. and IaaS providers (in the U.S. and globally) to support the Workspace ONE service offerings. These providers maintain physical and environmental security controls for our cloud-delivered services.
Data center security
Our data center partners are at least Tier III, have undergone SOC 2 Type 2 audits, and have achieved at least ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS certifications. Physical addresses for hosting locations are confidential and on-site visits are forbidden.
Although each facility is unique, our data center providers are required to follow the same minimum requirements for redundancy and physical access control, including:
- Ingress and egress points are secured with devices that require individuals to provide multi-factor authentication before granting entry or exit through a minimum combination of badge access, biometrics, and mantraps.
- Physical access is controlled at building ingress points by 24x7 on-site professional security staff using surveillance, detection systems, and other electronic means.
- Door alarm devices are configured to detect instances where an individual exits or enters a data layer without providing multi-factor authentication.
- Physical access points to data centers are recorded by Closed Circuit Television Camera (CCTV). Recordings are retained according to legal and compliance requirements.
- Environmental control systems are equipped minimally with N+1 power, cooling, and fire suppression measures to ensure continuous operations.
- Data center partners must maintain certifications minimally aligned with ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS standards.
Omnissa offices
All Omnissa offices deploy physical and environmental security measures to safeguard Omnissa facilities, staff, and assets. Omnissa uses a combination of building design, environmental controls, security systems, and designated security personnel, in conjunction with corresponding procedures, physical, and environmental controls to restrict access to information services and information assets. Controls include, but are not limited to:
- Implementing entry controls to secure Omnissa facilities.
- Maintaining and monitoring an audit trail of all access to the site through badge and visitor logs.
- Requiring visitors to sign in with date and time of entry and departure, and supervising visitation.
- Performing regular access rights reviews to secure areas and updating or revoking these rights as necessary.
- Revoking all access rights to Omnissa facilities and restricted areas immediately and deactivating access codes known by the staff upon staff termination.
Human Resources and personnel security
Human Resource considerations include processes for background screening, employment agreements, training, and employee termination.
Employee background screening
Pursuant to local laws, regulations, ethics, and contractual constraints, all employment candidates, contractors, and involved third parties are subject to background verification. Omnissa conducts criminal background checks, commensurate with the employee position and level of access to the service.
Confidentiality agreements
Omnissa employees and alternative workforce (AWF) are required to sign confidentiality agreements. Also, upon hire, personnel must read and accept the Acceptable Use Policy and the Omnissa Business Conduct Guidelines. Personnel who violate Omnissa standards or protocols are subject to appropriate disciplinary action.
Employee training
In alignment with the ISO 27001 standard, all Omnissa personnel are required to complete annual business conduct and security awareness training. Personnel with access to cloud production environments receive additional training as they assume job roles and responsibilities. Omnissa periodically validates that those employees understand and follow the established policies through compliance audits.
Omnissa uses an enterprise Learning Management System (LMS) to deliver required onboarding and annual security awareness training. The LMS records successful completion, and reports are reviewed during ISMS review meetings. This training must be completed before authorizing access to production systems.
Awareness training topics include, but are not limited to:
- Secure system configuration
- User account management policies
- Environmental control implementation and operation procedures
- Incident Response plans and procedures
- Disaster Recovery plans and procedures
- Physical Security controls
Employee termination
Omnissa terminates access privileges to systems when an employee leaves the company. An employee who changes roles within the organization will have access privileges modified according to their new position. Terminated employees are required to return assets.
Business continuity
Our business continuity program implements appropriate security controls to protect its employees and assets against natural or man-made disasters. Policies and procedures include defined roles and responsibilities supported by regular workforce training. Omnissa determines the impact of any disruption to the organization through identifying dependencies, critical products, and services.
Our global teams are located around the world, giving us strong geographic resilience in terms of our ability to provide continuity of service for our customers. Omnissa Global Customer Service operates 24x7, and all Omnissa employees are fully equipped to work from home efficiently and effectively if needed.
Our business continuity plans are reviewed annually to determine which business processes are most critical and what resources – people, equipment, records, computer systems, and office facilities – are required for operation. All documented plans follow an annual standard maintenance, assessment, and testing schedule. Workspace ONE operations teams also maintain service-specific business continuity plans to address the unique needs of each cloud service.
Business impact assessments (BIAs) are performed on at least an annual basis to identify critical functions and requirements for business continuity. The results of BIAs are documented and used to inform the business continuity plans (BCP) which are reviewed on an annual basis.
Omnissa also has a crisis management team (CMT), comprised of an Executive Sponsor (Incident Commander), Program Manager and representatives from all lines of business at Omnissa, that activates in the event of a global critical business disruption that significantly disrupts normal operations of Omnissa, our customers and/or partners.
Disaster recovery
Disaster recovery plans are defined for various scopes of potential disaster or failure scenarios. These plans are reviewed by Engineering, Operations and Product leadership on an annual basis. Disaster recovery strategies are tested on at least an annual basis through simulated, real-world functional and tabletop tests to help ensure disaster recovery plans are appropriately designed and in place. For more information on system availability by service, see the cloud security architecture sections below.
Risk management
In alignment with the ISO 27001 standard, Omnissa maintains a risk management program to mitigate and manage risk companywide. We perform risk assessments at least annually to ensure appropriate controls implementation to reduce the risk related to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information.
Omnissa cloud management has a strategic business plan to mitigate and manage risks. This plan requires management to identify risks within their areas of responsibility and to implement appropriate measures designed to address those risks.
Our risk management program includes:
- Identifying and characterizing threats
- Assessing the vulnerability of critical assets to specific threats
- Determining the risk (such as the expected likelihood and consequences of specific types of attacks on specific assets)
- Identifying ways to reduce those risks
- Prioritizing risk reduction measures based on a strategy
A key activity of our risk management program is risk identification and assessment which includes:
- Proactively identify existing and potential areas of information security risk.
- Assessing potential impact to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information assets.
- Using a risk assessment framework and methodology, identify, assess, and prioritize those risks.
Our risk management team then consolidates risks into our risk register and prioritizes risks based on rating/severity.
Vendor risk management
Omnissa uses a third-party risk management program that focuses on secure sourcing and software integration relating to building solutions. It includes the use of an approved vendor list and open-source software reviews prior to use. Each vendor that Omnissa engages undergoes an extensive onboarding process which includes both security and privacy reviews. Supplier agreements require that providers comply with applicable laws, security, and privacy obligations.
Our development team includes specific resources responsible for testing, updating, and reviewing the open-source material used in the product. Management of third-party software in Omnissa products adheres to our Secure Development Policy which includes Open-Source/Third-Party Security Scanning also known as Software Composition Analysis (SCA).
Any software deemed “Security Critical” must be appropriately vetted, tested, and maintained. The respective development team incorporating third-party software in their product(s) and services is responsible for the support and fixing of defects and security vulnerabilities, whether they get such support from a vendor contract, or perform this function internally.
For a list of the open-source material used in our services, see our Open-source notices.
Sub-processors
Omnissa leverages sub-processors to provide certain services on our behalf. Omnissa enters into an agreement with each sub-processor that obligates the sub-processor to process the Personal Data in a manner substantially similar to the standards set forth in the Data Processing Addendum and at a minimum, at the level of data protection required by applicable Data Protection Laws.
Change management
Omnissa maintains a detailed change management policy that defines controlled changes to production environments. This process has been established to plan, schedule, approve, apply, distribute, and track changes to the production environment through designated responsibilities, with the objective of minimizing risk and customer impact. Changes are processed through a formal program that includes approval, testing, implementation, and rollback plans.
Omnissa application development and change control processes are designed to enforce key development controls each time a change to the software is made, including development, hot fix, and emergency changes for Omnissa cloud services. Application and infrastructure are managed through code and processed through the same procedures. The code pipeline includes automated testing procedures. Backout procedures are in place in the production environment to allow for rollback of changes if a new change disrupts system activity.
Test environments are logically separated from production environments. No production data is replicated to development or staging environments.
Omnissa uses source code control management or version control to protect the security and integrity of written, developed, tested, and evaluated code. Source control covers code creation, modifications, deletion, and incorporation of the code into more significant parts. Audit controls within the source control system automatically track what changes have been made, who made them, when a change was made, and other consequences of those changes. The product source code is stored on centrally managed servers in a secure area and protected behind a network firewall. Promotion to production requires a minimum number of approvers prior to the manual push of application or infrastructure as code changes.
Third-party and internal audits of these processes are performed at least annually under the Omnissa ISMS program and are essential to the Omnissa continuous improvement programs.
Configuration management
Omnissa maintains a detailed configuration management policy based on industry best practices to harden the cloud environment; revisions and exceptions to the configuration management policy are processed through the change management policy to help ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of our hosted offering.
Baseline configuration standards include, but are not limited to:
- Deactivating unnecessary ports, services, protocols, and physical connections
- Reviewing server builds for gaps prior to image configuration
- Hardening server configurations
Baseline configurations are documented for all software and hardware (where applicable – such as U.S.-based co-located data centers) installed in the production environment. Baseline configurations include the following information about system components:
- Standard software packages installed on servers and network components
- Current version numbers and patch information on operating systems and applications
- Logical placement of all components within the system architecture
System hardening
Omnissa deactivates unnecessary ports, protocols, and services as part of baseline hardening standards. We follow best practices in applying secure configurations to managed servers: our cloud service hardening is based on secure configuration recommendations such as Security Technical Implementation Guides (STIGs), Security Requirements Guides (SRGs), or publicly available secure configuration guidelines such as Center for Internet Security (CIS) benchmarks.
For servers that use Windows operating systems, the team hardens server configurations through code using Group Policy Object (GPO) policies (such as account policies, user rights, security options, event log settings, app restrictions). Linux-based servers use Amazon Linux 2 images for system hardening. The Amazon Linux 2 images include default security configurations, such as limited remote access using SSH key pairs, remote root login deactivation, reduced non-critical package installation, and automatic security-related updates.
Time synchronization
All cloud service components are synchronized with a common centralized time source per ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS requirements.
Vulnerability and patch management
Omnissa employs a rigorous Vulnerability Management program as part of the Omnissa ISMS. Risk analysis and acceptance activities are performed on vulnerabilities to confirm the vulnerability and to determine the appropriate means of addressing the vulnerability.
System monitoring
Omnissa Cloud Operations is staffed 7x24x365, and the team deploys several commercial and custom purpose-built tools to monitor the performance and availability of all hosted solution components. Components include the underlying infrastructure servers, storage, networks, portals, services, and information systems used in the delivery of Omnissa cloud services.
Patch management
Omnissa maintains the systems it uses to deliver our cloud services, including the application of patches deemed critical for the target systems. Our policy is to patch or upgrade network, utility, and security equipment after analyzing the severity and impact of potential vulnerabilities. System administrators and information security personnel monitor a variety of industry patch and vulnerability notification websites, vendor newsletters, and mailing lists. Critical vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner, and changes are made using industry best practices. Testing is conducted to ensure compatibility with the production environment. If required, rollback procedures are conducted by our deployment teams.
For Workspace ONE UEM, technical standards and baselines have been established and communicated for Windows and Linux operating system deployments. A process is in place for services to re-image production servers with the latest baseline configurations every month.
Automated mechanisms and periodic scanning have been deployed to detect and troubleshoot exceptions or deviations from the baseline in the Omnissa Access and Hub Services production environment. Mechanisms are in place for services to re-image production servers with the latest baseline configuration monthly through Amazon Linux 2 and Docker images using infrastructure as code.
Omnissa Intelligence base images receive patches and reboots as part of the bootstrap process. Containers are generated on a weekly basis, with all patches included. As instances are terminated, new instances are deployed: No instances live more than seven days.
For Workspace ONE Assist, patches are released in accordance with change and release management procedures and are implemented using AWS Systems Manager.
Vulnerability scanning
Vulnerability scans are performed at least monthly on internal and external systems. In alignment with PCI-DSS, system and application owners are required to address critical and high vulnerabilities with a plan of corrective action after vulnerability discovery. Rescans are used to verify the remediation of high-risk vulnerabilities. Other vulnerabilities are addressed with a plan of corrective action within a reasonable period.
Note that Omnissa does not provide the results of vulnerability scans to customers. We do not feel these isolated pieces of information are of use to our customers in protecting their security objectives. Results are not in context, often generate a large volume of false-positives, and do not accurately represent the current security posture of a product or service.
Security Development Lifecycle
The Omnissa Security Development Lifecycle (SDL) program is designed to identify and mitigate security risks during the development phase of Omnissa software products. The development of our SDL has been heavily influenced by industry best practices and organizations such as the Software Assurance Forum for Excellence in Code (SAFECode) and the Building Security in Maturity Model (BSIMM).
The Omnissa Security Evangelism team works to actively cultivate relationships in the security community. Omnissa has been an active participant in the broader software industry security community and became an early BSIMM member in 2009. We have completed several reviews by BSIMM of our SDL. Findings are incorporated into our SDL to drive continuous improvements. Omnissa is a member of the Software Assurance Forum for Excellence in Code (SAFECode), an organization driving security and integrity in software products and solutions. Omnissa also works closely with Industry Organizations, Security Analysts and Researchers, and more to stay current on the industry threat landscape and security best practices. Omnissa Product Security Omnissa SDL is continuously assessed for its effectiveness at identifying risk, and new techniques are added to SDL activities as they are developed and mature.
SDLC best practices
We follow a defined Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC), which incorporates security into each phase (such as requirements, design, implementation, and verification) of development. Our programs and practices focus on:
- Building secure software
- Protecting the intellectual property related to software products
- Managing software security supply chain risks
- Managing technology and partner ecosystem risks
- Delivering secure product support
Our SDLC is based on industry-recognized best practices and standards, including PCI-DSS common coding vulnerabilities, OWASP, Open-Source Security Testing Methodology Manual (OSSTMM), SANS/CWE, and SCRUM methodologies. Code undergoes rigorous review by our Engineering and Development Security teams. We consider attacker-centric categorizations (Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information Disclosure, Denial of Service, and Elevation of Privilege (STRIDE)) and defensive-centric perspective (ASF) for threat modeling. Additionally, Omnissa cloud services undergo multiple tests prior to release, including static and dynamic code reviews, penetration tests, fuzz and unit testing, attack surface reviews, and so on.
In alignment with PCI-DSS requirements, Omnissa encourages continuous employee training through annual training in up-to-date secure coding techniques, including how to avoid common coding vulnerabilities. Omnissa also subsidizes certification attempts (such as ISC2’s Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) and Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP), including relevant conference passes, training classes, and subscriptions to leading online training platforms for enhancing technical and business acumen. Additionally, employees can participate in job rotation programs designed to reignite and broaden employee work experience.
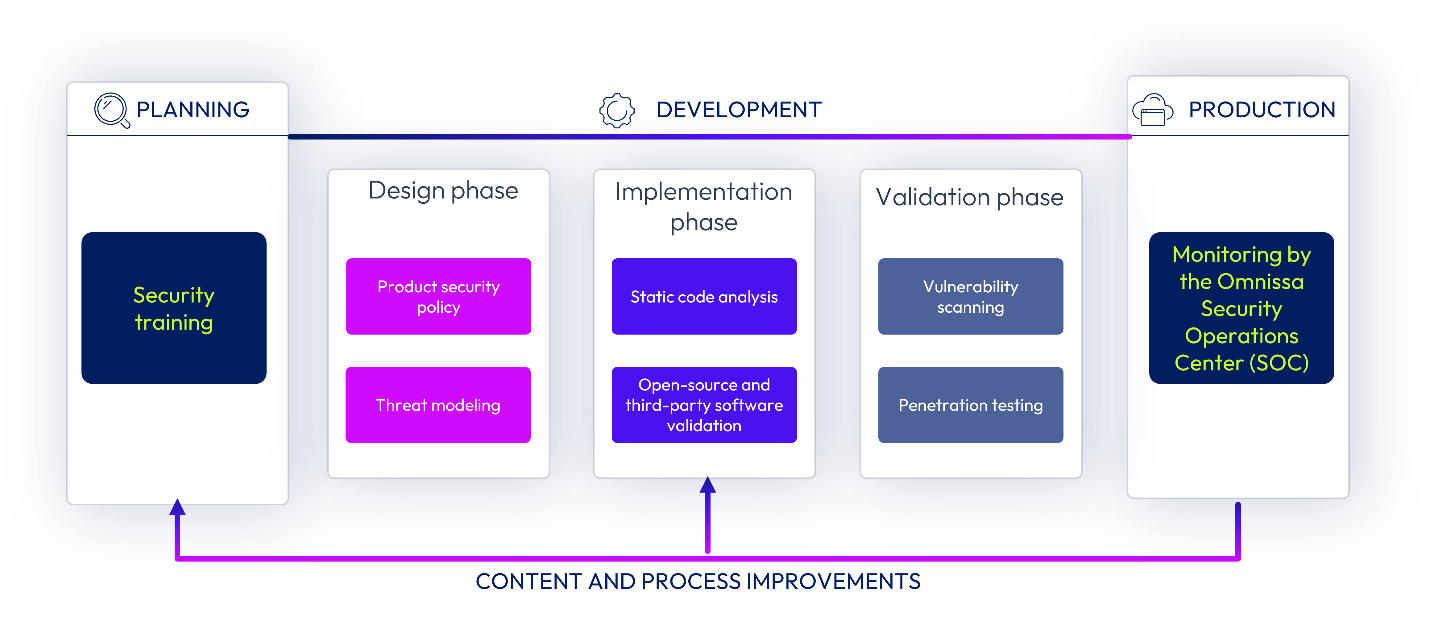
Figure 2: Omnissa SDLC
Open-source software
Omnissa uses some third-party and open-source code in our solution offerings, and we perform open-source and third-party (OSS/TP) software validation to safeguard against known vulnerabilities prior to being included in an Omnissa product release. For a list of the open-source material used in our services, see our Open-source notices.
Penetration testing
Penetration testing includes testing of Omnissa and third parties and customer penetration testing.
Omnissa Red Team and third-party testing
The Omnissa penetration testing program is a rigorous set of processes that include automated tooling built into the Omnissa Security Development Lifecycle (SDL), Omnissa Red Team penetration testing, and third-party internal and external testing initiatives, all in alignment with industry best practices, standards, and frameworks such as NIST and PCI-DSS. Red Team and third-party tests are performed at least once per calendar year and include testing at the web application, network, logging, and infrastructure layers.
The penetration tests focus on identifying high-impact vulnerabilities that could lead to exploitation, theft of data, or overall privilege escalation. Tests follow a method intended to simulate real-world attack scenarios and threats that could critically impact data privacy, integrity, and overall business reputation. Experienced internal security engineering staff and penetration testing vendors use their industry expertise to develop a risk-informed threat model based on the criticality of resources and data and any specific areas of concern.
To increase the efficiency of testing and to achieve more meaningful results, tests are performed using a white box testing approach – during which the tester has access to source code.
Remediation approach
To protect our customers and the integrity of our cloud services, Omnissa does not disclose detailed information or comment on the nature of findings or remediation status. All identified findings are remediated in alignment with applicable compliance and regulatory requirements, including FedRAMP and PCI-DSS. Each finding undergoes a rigorous evaluation based on severity, complexity, potential impact, product lifecycle, and whether it is internally or externally exploitable. Remediation efforts are subject to independent verification by third-party auditors to help ensure that all findings are documented and addressed in alignment with compliance, regulatory, policy, and security requirements. Third-party audit reports and compliance attestations can be provided upon request.
Customer penetration testing
Customer-initiated penetration testing, port and vulnerability scanning, spoofing, web application scanning, protocol flooding, denial-of-service attacks, installation of malware, attempts to decompile source code, or any other actions that may disrupt the cloud-hosted production environment are explicitly forbidden in the environment (see Acceptable Use in the Omnissa Cloud Services Exhibit).
For Workspace ONE UEM and Omnissa Access only: With prior approval and under certain circumstances, customers can perform penetration tests in a simulated environment. All results must be made available to Omnissa for analysis and remediation (if necessary). Reach out to your Omnissa representative for more information and to set up one of these simulated environments.
Cloud environment monitoring
Omnissa Cloud Operations is staffed (7x24x365) and deploys several commercial and custom purpose-built tools to monitor the performance and availability of all hosted solution components. Components include the underlying infrastructure servers, storage, networks, portals, services, and information systems used in the delivery of Omnissa cloud services.
Intrusion detection and prevention
Omnissa deploys several mechanisms to detect intrusions and help protect against distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. These mechanisms range from real-time intrusion detection system (IDS) technologies, internal logs and tools, and external intelligence (OSINT) data sources. Omnissa monitors security events involving the underlying infrastructure servers, storage, networks, information systems, and upstream providers used in service delivery.
Omnissa applications are also assessed against the ‘OWASP Top Ten’ to identify potential application code and identify/remediate potential errors that could lead to unauthorized access or a DDoS. In alignment with PCI-DSS, our cloud services use file integrity monitoring to detect malicious behavior or changes in system files or libraries. In addition, our cloud services use a web application firewall (WAF), which provides application-layer protection against common web exploits.
Anti-virus, anti-malware and endpoint protection
Omnissa implements industry best practices for both administrative and technical controls to prevent, detect, and respond to viruses and malware, including ransomware. As part of our annual security training programs, Omnissa operates a quarterly Phishing Prevention Program to help train our employees to recognize threats. Social engineering topics (such as tailgating, badge access, and vishing) are also covered in our annual security training.
End user devices
In alignment with PCI-DSS, Omnissa has deployed and centrally manages anti-virus and endpoint protection on all employee workstations, which is configured to scan for updates to anti-virus definitions and update clients continuously. Additionally, the software performs on-demand virus scans of any attachments or content introduced into the workstation. Systems settings prohibit end users from deactivating endpoint protection software.
Production environments
Our cloud services also implement strong technical controls, including encrypted backups, network segmentation, firewalls, and access control lists (ACLs) for mitigation, and containment from potential attacks, as well as to remediate from active attacks. For systems commonly susceptible to malicious attacks, such as Windows OS, Omnissa deploys enterprise-grade anti-virus software and is automatically patched, and signature updated with logging enabled; files are scanned on access. Linux-based systems are hardened using Amazon Linux to secure images.
End user device security
Omnissa is committed to implementing appropriate security precautions to minimize the risk of vulnerabilities presented when corporate and personal devices are used to access Omnissa information systems. In alignment with our End User Device Security and Access Control policies, corporate-owned and personal devices accessing Omnissa corporate resources must be enrolled in an Omnissa-managed instance of Workspace ONE UEM. Any personal devices not enrolled in device management have restricted access to resources and must use a secured virtual desktop to access Omnissa information systems. End user devices are required to implement full disk level encryption, screen lock (with 15-minute timeout) and proper password protections.
If a device is lost or stolen, to help ensure confidentiality, privacy, and security, Omnissa conducts a device wipe. This includes conducting an enterprise wipe to remove corporate information from a personal device or a full device wipe to remove all data and applications from a corporate-owned device.
Log management
Log management includes both infrastructure and application event logs.
System security logs
Workspace ONE services leverage a robust centralized Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) infrastructure. Critical systems and privileged access to Workspace ONE infrastructure, firewall and IDS logs, and Domain Name System (DNS) Queries are logged and monitored. Auditable events are in alignment with PCI-DSS requirements and include user identification, type of event, date and time, success or failure indication, and origination of event. Access to the audit trail is protected, and logs are stored separately and securely.
Note: Omnissa does not provide SaaS infrastructure logs to customers. See Application Event Logs for customer-accessible logging options.
Omnissa System Security logs and events are centrally aggregated and monitored in real-time 7x24x365 by the Omnissa Security Operations Center (Omnissa SOC). Logs forwarded to the Omnissa SOC are retained for at least one year, in alignment with PCI-DSS requirements, with up to five years of archive storage.
Application Event Logs
Customers can access application-level logs within Workspace ONE UEM and Omnissa Access that record administrator and end-user device events. Workspace ONE UEM event logs include:
- Device events show the commands sent from the console to devices, device responses, and device user actions.
- Console events show actions taken from the Workspace ONE UEM console, including login sessions, failed login attempts, admin actions, system settings changes, and user preferences.
The audit events report in the Omnissa Access service lists the events related to a user, including:
- The type of action within a specific date with criteria such as user, type, action, object, and date range.
Logs are available within the Workspace ONE UEM console for (30) days and the Omnissa Access console for (90) days. These logs can also be exported as *.csv files for storage offline to meet regulatory or business requirements. Workspace ONE UEM event logs can also be integrated with a customer’s existing Security Information & Event Mgt. (SIEM) solution using syslog.
Omnissa Security Operations Center (SOC)
The Omnissa SOC is staffed and monitors alerts on security anomalies 7x24x365. The Omnissa SOC leverages multiple log capture, security monitoring technologies, and intrusion detection tools to look for unauthorized access attempts, monitor for incoming threats, and detect activity from malicious insiders.
Incident management and response
The Omnissa Incident Response (IR) program, plans, and procedures are developed in alignment with the ISO 27001 standard. Omnissa maintains contacts with industry bodies, risk and compliance organizations, local authorities, and regulatory bodies. Points of contact are regularly updated to ensure direct compliance liaisons have been established and prepared for a forensic investigation requiring rapid engagement with law enforcement. Under the Omnissa ISMS program, the incident response plan is tested at least once annually, regardless of whether a security incident has occurred.
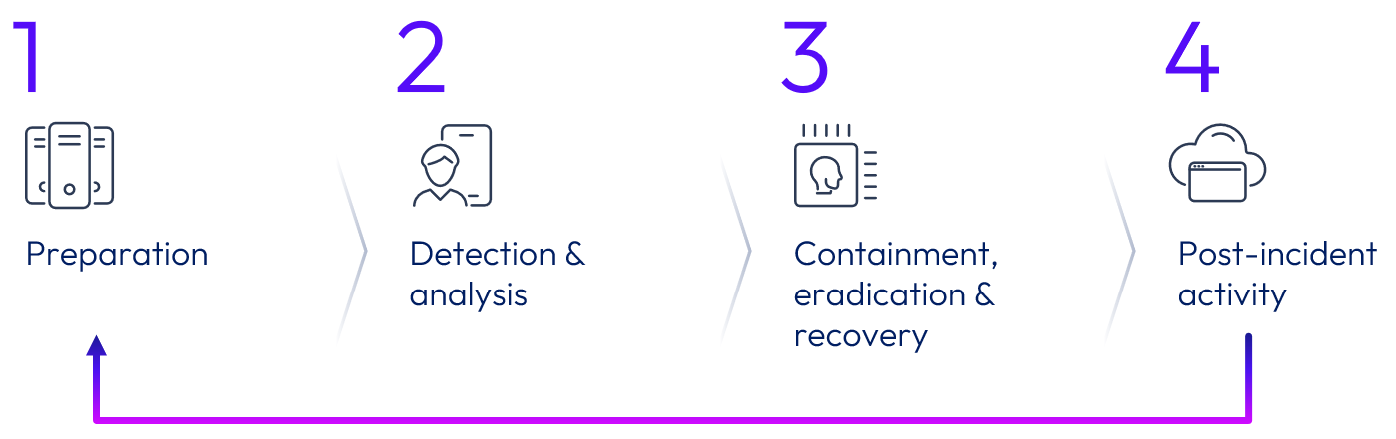
Figure 3: Omnissa incident and response cycle
Incident reporting
All staff are responsible for reporting information security events as quickly as possible. At a minimum, these scenarios include:
- Ineffective security controls or access violations
- Breach of information integrity, confidentiality, or availability expectations
- Human errors
- Non-compliance with policies or guidelines
- Breach of physical security arrangements
- Uncontrolled system changes
- Malfunction of software or hardware
Breach notification
In the case of a confirmed data breach, Omnissa shall, without undue delay, notify affected customers of the breach in accordance with applicable laws, regulations, or governmental requests.
Identity and access management
Managing identity and access includes access of both customers and Omnissa to production environments, as well as Omnissa access to customer networks.
Customer access to production environment
As Workspace ONE services are cloud-based offerings, customer administrators do not directly manage access to the production environment but rather access Workspace ONE services through web-based consoles. Granular role-based access controls (RBAC) restrict the depth of device management information and features available to each Workspace ONE console user. All Workspace ONE administrator changes are retained for review within the console event log. Customer administrators also manage access and entitlements for end-user devices.
Omnissa access to production environments
Workspace ONE is a multi-tenant cloud service. Service systems are accessed for maintenance and support purposes only. Omnissa does not request prior approvals to access service systems to perform maintenance tasks such as patching and upgrades. Access privileges are enforced using role-based access control, separation of duties, and the principle of least privileges. Production environment access is secured through a combination of VPN, IP address allow-listing or jump servers using Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) and directory credentials.
In accordance with ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS, access is restricted to authorized members of applicable teams, and system sessions are set to an idle timeout of 15 minutes. Logs are in place to review support staff access to all systems and environments. Quarterly User Access Reviews are conducted to review privileged access and to remove or deactivate accounts with 90 days of inactivity.
Omnissa access to customer consoles
Omnissa Global Customer Service may require access to customer consoles to resolve certain support tickets. Access to the customer console is tied to a support request and is granted after Customer Service obtains permission from the customer. Application logs (called Event Logs) are available to customers within the Workspace ONE consoles to review the actions taken by Omnissa Customer Service. Event logs are available in the Workspace ONE UEM console for 30 days and the Omnissa Access console for 90 days. For more information, see our Support Privacy Datasheet.
Omnissa access to customer networks
Workspace ONE services integrate with customer resources using optional customer-managed on-premises connectors. Workspace ONE services, therefore, do not require direct access to internal customer networks, and Omnissa support personnel do not have access to internal customer networks. For more information on the optional on-premises components, see the Common Components section of the Workspace ONE Reference Architecture.
Session controls
Session controls include production environment sessions, the use of Workspace ONE UEM and Omnissa Access management consoles, and Hub Services, as well as the Omnissa Access administrative panel, Workspace ONE Assist customer and administrator sessions, and Omnissa Connect sessions.
Omnissa production environment sessions
Workspace ONE production environment: In line with PCI-DSS, Omnissa administrator sessions are set to time out after fifteen (15) minutes of inactivity.
Workspace ONE UEM Management Console
The cloud-hosted Workspace ONE UEM console has a session timeout maximum of 60 minutes for customer administrators based on the load balancer persistence settings. Workspace ONE administrators can also configure an authentication timeout for end-user applications using the Workspace ONE Software Development Kit (SDK). Workspace ONE UEM console sessions include the following security controls:
- HTTP sessions are secured using state and session tokens created and validated by the server.
- Session control tokens are present on every HTTP transaction.
- Authenticated sessions do not tie identity and authentication to anti-CSRF (cross-site request forgery) tokens.
Omnissa Access Management Console
Customer administrators set Workspace ONE single sign-on (SSO) session and per-app re-authentication policies to force users to authenticate again after a configurable length of time.
The Omnissa Access Administrative Console and Workspace ONE app catalog include the following security controls:
- HTTP sessions are secured using state and session tokens created and validated by the server.
- The solution uses HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) headers.
- Session control tokens are present on every HTTP transaction.
- XSRF-TOKEN cookie is used to help prevent CSRF (or XSRF) attacks.
The Omnissa Workspace ONE® Intelligent Hub mobile app for end users leverages OAuth tokens which are stored encrypted within the app tokens using standard device-level encryption supported by each mobile operating system. All mobile Workspace ONE apps require a device-level or app-level passcode input by the end user to access the app. Expiry of these tokens is controlled by the server. The admin gets to choose how long the session is valid and how frequently it needs to be renewed. These tokens cannot be removed from the device and used elsewhere.
Workspace ONE Hub Services
Workspace ONE Hub Services is configured with the Omnissa Access and Workspace ONE UEM administrator consoles. Omnissa Access management console security is outlined above.
Omnissa Intelligence administrative panel
Generally, customers enable the Omnissa Intelligence administrative panel through the Workspace ONE UEM console.
Omnissa Intelligence administrative panel sessions include the following controls:
- JSON Web Tokens use certificates for authentication.
- Access tokens expire.
- Certificate downgrade is not possible.
- CSRF tokens and security headers are configured to mitigate XSS.
Workspace ONE Assist – Customer and administrator sessions
A separate agent is required to be installed on a covered device, by Workspace ONE UEM on the Android, Windows 10, MacOS, and Windows CE operating systems. The capabilities are embedded in the Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub application on iOS. Workspace ONE Assist includes the following session protections:
- HTTP sessions are secured using state and session tokens created and validated by the server.
- HSTS headers are used.
- Session control tokens are present on every HTTP transaction.
- XSRF-TOKEN cookie is used to prevent CSRF attacks.
Omnissa Connect console
Customer administrators can set an ideal session timeout to force users to authenticate again after a configurable length of time of inactivity. The default is 15 minutes.
The Omnissa Connect includes the following security controls:
- HTTP sessions are secured using state and session tokens created and validated by the server.
- The solution uses HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) headers.
- Session control tokens are present on every HTTP transaction.
Cloud security architecture
Workspace ONE cloud services leverage robust perimeter defenses, including access control mechanisms, perimeter firewalls, malware controls, auditing mechanisms, network controls, deactivation of unnecessary services, and maintaining defined configuration settings.
On-premises components are required to support certain solution features. Omnissa does not have, nor do we require access to customer internal networks. Customers manage on-premises connectors for the solution. Documentation on connectors is available on Tech Zone.
Workspace ONE UEM
The security of the Workspace ONE UEM architecture, including its microservices, Control Plane, and infrastructure, is assured through multiple layers of security measures as detailed below.
Resiliency
Workspace ONE UEM is supported by defined enterprise resiliency programs which include business continuity and disaster recovery mechanisms. The Workspace ONE UEM cloud infrastructure is designed with high availability and resiliency by design. Redundancy helps ensure that customers will typically not notice a disruption during a component or system failure.
Disaster recovery (DR) plans are rigorously tested against various disaster scenarios and include tabletop and service restoration exercises. Additional DR strategies include:
- Daily backups are stored for (30) days.
- Monthly backups are retained for (60) days.
- Backups are encrypted in-transit and backups are encrypted at-rest via Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-256).
- Backups are stored separately and securely, cannot be altered and ransomware protections are enabled.
Workspace ONE UEM uses an automated backup system for performing scheduled daily backups of production systems and data. The system helps ensure that backup data is readily available should a failure occur. The backup system is configured to send email notifications to operations personnel for successful and failed backups, and backups are reviewed to ensure their success. Backup failures are addressed to help ensure the completeness of backups according to backup policy.
Workspace ONE UEM Modern Stack architecture
A new modernized architecture, called the UEM Modern Stack (Next-Gen SaaS) is composed of multiple microservices, each deploying its own group of service nodes and maintaining its own persistent data storage. The existing UEM components, such as the Console, Device Service, and API, will continue to serve as the application gateway to the modern SaaS architecture.
Workspace ONE UEM also contains an orchestration layer called the Control Plane that uses containerized services for performance and high availability. The UEM Control Plane ecosystem contains an application workloads cluster, a core services cluster, and a management cluster that spans across the web and app, state, and management services tiers. The core services cluster includes Kafka (for messaging), Postgres database, logging, and telemetry.
The boundaries of the Control Plane are completely internal, and it communicates only to the Workspace ONE UEM instance. The Photon-based Linux Control Plane is scanned as a part of the deployment pipeline. The Workspace ONE UEM Control Plane also uses HashiCorp Vault for secrets lifecycle management. Secrets are used for encrypted communication between the Control Plane services. The existing UEM components, such as the Console, Device Service, and API, will continue to serve as the application gateway to the modern SaaS architecture.
For more details on the security features of the UEM Modern Stack, see this whitepaper.
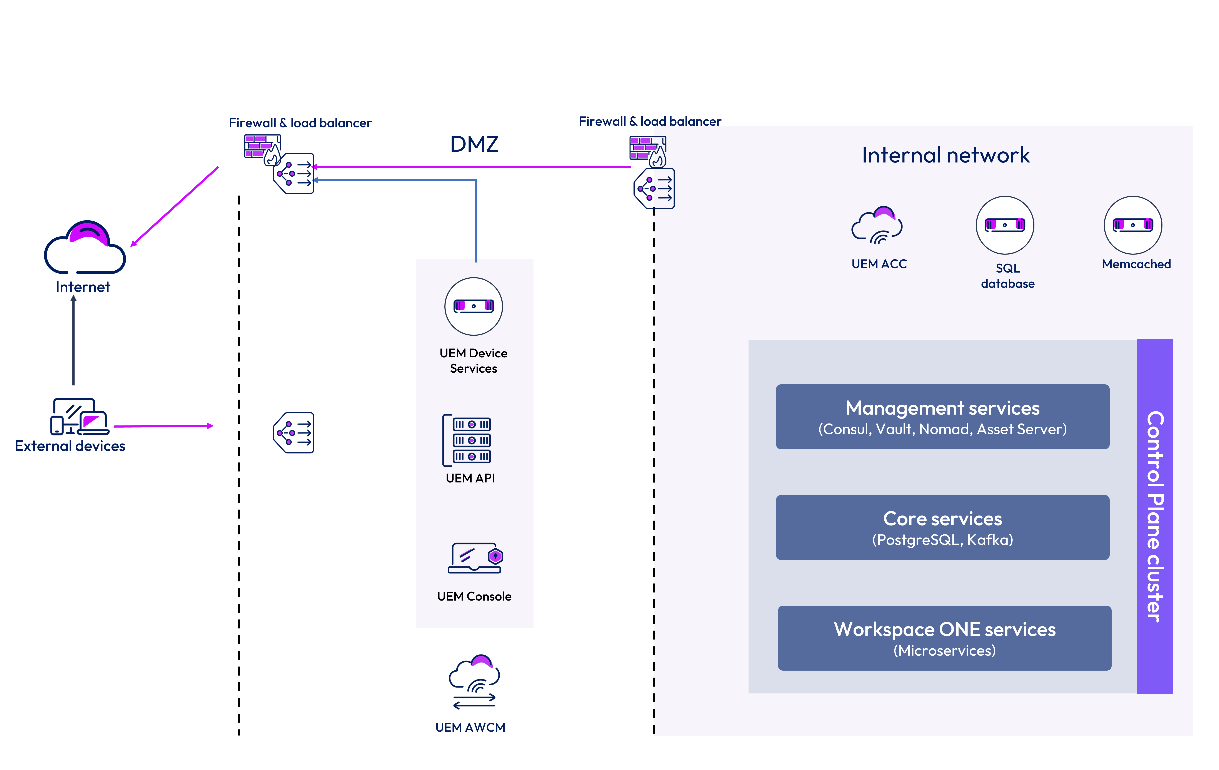
Figure 4: Workspace ONE UEM Modern Stack architecture
Omnissa Access
Omnissa Access architecture includes high availability and disaster recovery (DR) mechanisms based on a three-tiered architecture application replicated through multiple Amazon Availability Zones.
Resiliency
Omnissa Access is supported by defined enterprise resiliency programs which include business continuity and disaster recovery mechanisms. The Omnissa Access service employs a highly redundant design with multiple best-in-class redundancy technologies combined with data replication strategies. The infrastructure is designed to ensure that customers will typically not notice a disruption during a component or system failure inside a primary data center.
DR plans are rigorously tested against various disaster scenarios and include tabletop and service restoration exercises. DR strategies include, but are not limited to:
- Omnissa maintains the production environment in a fully replicated cluster across multiple fault domains in the AWS service region for high availability.
- Daily database snapshots and datastore backups to support service RPO and RTO.
- Database snapshots are stored for 14 days.
- Backups are encrypted in-transit, backups are encrypted at-rest (AES-256) and backups are stored in an immutable format.
Disaster recovery plans are tested and reviewed annually for Recovery Time Objective(s) and Recovery Point Objective(s):
- RTO = (4) hours
- RPO = (4) hours
Omnissa Access uses a managed service database that includes automated backups, and AWS is responsible for monitoring backups as part of the managed service. The managed database performs failover without manual intervention.
Omnissa Access architecture
Omnissa Access is a three-tiered architecture application hosted in a blue-green deployment in multiple AZs in AWS Regions globally. The front-facing web and app servers are isolated in a restricted Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) behind L7 traffic management/TLS acceleration appliances that proxy all connections to the web and app layer. Omnissa Access uses a micro-segmentation approach for the cloud network, and each instance or server belongs to a function-specific security group. A host-based intrusion detection system and file integrity monitoring are also in place. Omnissa Access uses network access control lists (NACLs), pre-defined security groups, and a Web Application Firewall (WAF) to restrict inbound access to the production environment.
Customers can integrate with existing enterprise systems, which are determined by the customer’s service needs and ultimately result in a wide range of external IP address destinations to deliver features. Customers can also configure custom ports for integration. To accommodate customer needs, Omnissa Access does not restrict outbound traffic; however, network address translation (NAT) is in place to track outbound traffic.
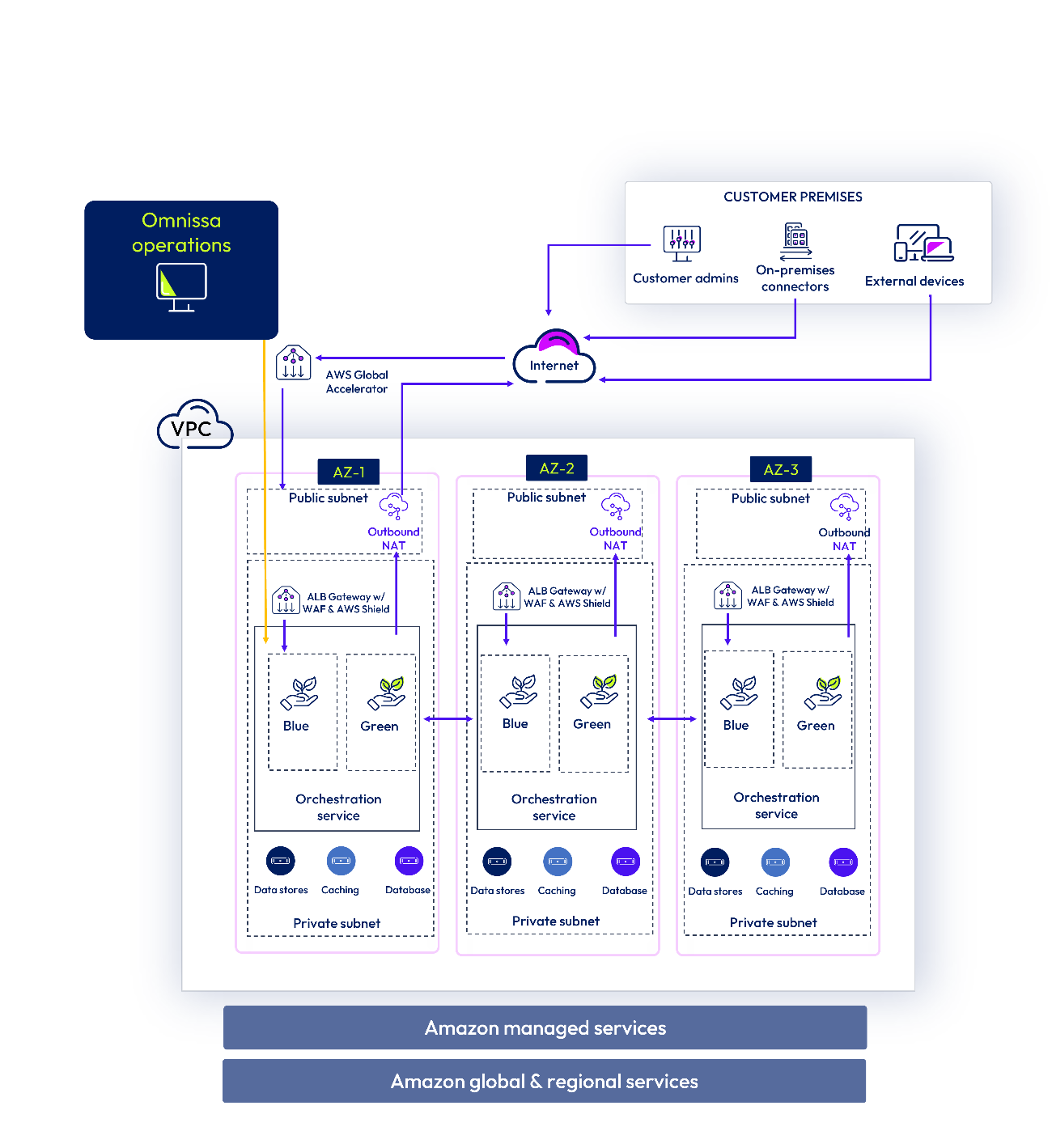
Figure 5 : Omnissa Access production environment architecture
AWS CloudFront Content Delivery Network (CDN) is used for the delivery of some of the Omnissa Access service content (static JavaScript, CSS, and images) for the admin console and end-user experience (login screen, Catalog, and so on) on HTTPS 443. On-premises connectors and third-party Identity Providers (IdPs) do not require any access to AWS CloudFront CDN. The CDN does not store customer Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
Omnissa Intelligence
Omnissa Intelligence architecture includes high availability and DR mechanisms based on a multi-tiered application replicated through multiple Amazon Availability Zones.
Resiliency
Omnissa Intelligence is supported by defined enterprise resiliency programs, which include business continuity and disaster recovery mechanisms. The Omnissa Intelligence service leverages multiple availability zones in each deployment region. Additionally, Omnissa Intelligence infrastructure deployment is automated and can be quickly orchestrated as required. The infrastructure is designed to help ensure that customers will typically not notice a disruption during a component or system failure inside a primary site due to the resilience and redundancy built in. Load balancers are implemented to distribute traffic requests across Availability Zones and provide improved performance and availability for front-end applications.
DR plans are rigorously tested against various disaster scenarios and include tabletop exercises. DR strategies include but are not limited to:
- The use of multiple AWS Availability Zones.
- Databases are configured with daily point-in-time backups going back (30) days for resiliency
- Backups are encrypted in-transit and at-rest, support staff review backup processes to help ensure data integrity and are stored in an immutable format.
Disaster recovery plans are tested and reviewed annually for Recovery Time Objective(s) and Recovery Point Objective(s):
- RTO = (4) hours
- RPO = (4) hours
Omnissa Intelligence architecture
Omnissa Intelligence is a multi-tiered application comprised of microservices applications, which is built on the Spring framework. All containerized services in the Omnissa Intelligence application are running in multiple Availability Zones to help minimize downtime and automate scaling. Omnissa Intelligence further limits downtime risk through a blue-green deployment architecture and a continuous integration, continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline. Services in the state tier are deployed with failover in multiple Availability Zones.
External traffic is routed through web application firewalls (WAF) and external load balancers; all internal microservices are deployed behind internal load balancers in private subnets. Daily snapshots are taken and replicated in-region.
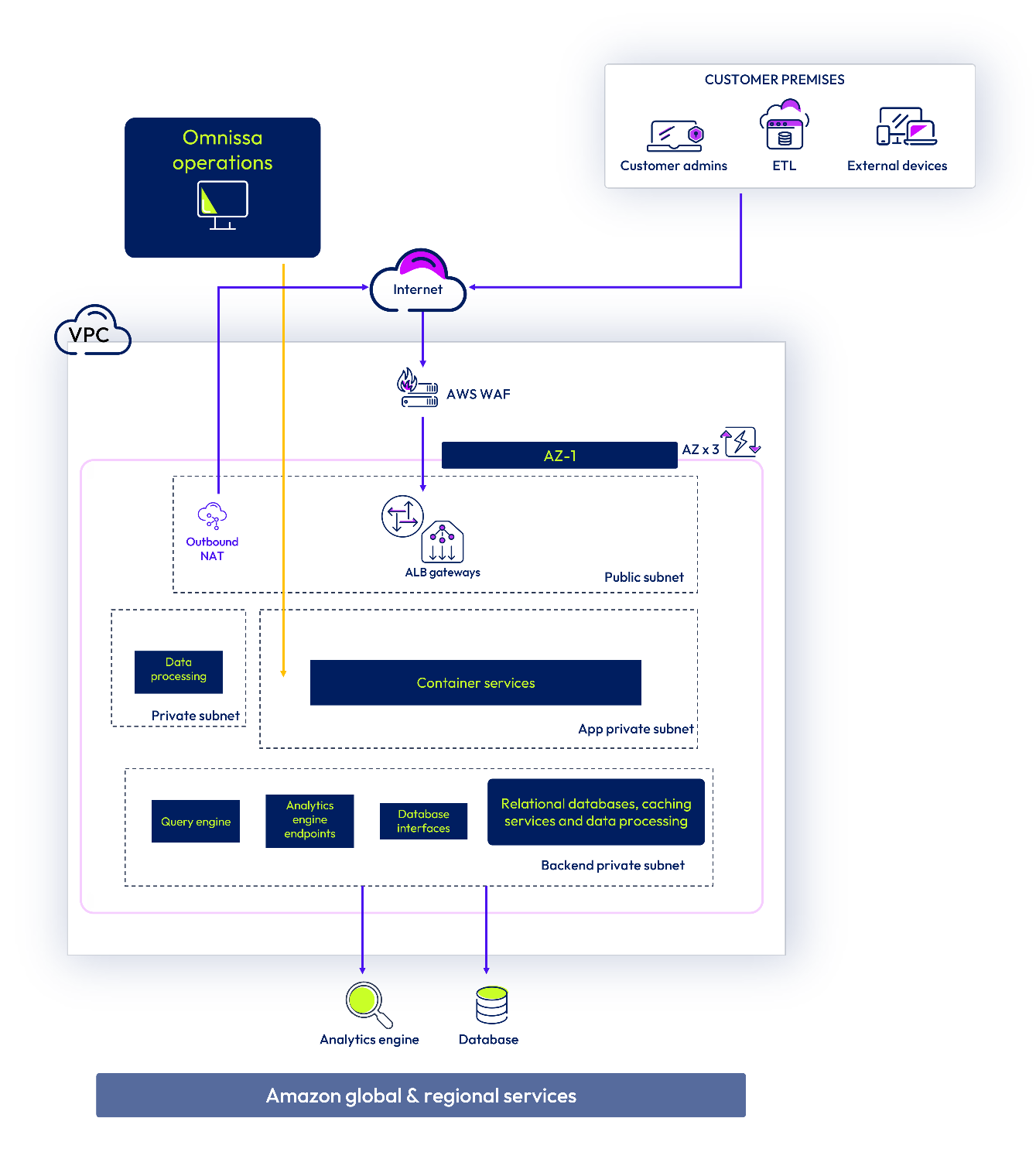
Figure 6 : Omnissa Intelligence production environment architecture
For Workspace ONE UEM SaaS customers, Omnissa hosts the Extract, Transform & Load (ETL) server (in the Workspace ONE UEM cloud environment). The hosted ETL server transmits data from your Workspace ONE UEM cloud deployment to the Omnissa Intelligence cloud environment. On-premises Workspace ONE UEM customers must install an ETL server to connect their on-premises Workspace ONE UEM deployment to the Omnissa Intelligence cloud environment.
Workspace ONE Assist
Workspace ONE Assist architecture includes high availability and DR mechanisms and is replicated through multiple Amazon Availability Zones.
Resiliency
Workspace ONE Assist is supported by defined enterprise resiliency programs, which include business continuity (BC) and disaster recovery (DR) mechanisms.
Omnissa cloud services employ a highly redundant design with multiple best-in-class redundancy technologies combined with data replication strategies. The infrastructure is designed to help ensure that customers will typically not notice a disruption during a component or system failure inside a primary data center. Load balancers are implemented to distribute traffic request across AZs and provide improved performance and availability for front-end applications.
DR plans are rigorously tested against various disaster scenarios and include tabletop and service restoration exercises. DR strategies include, but are not limited to:
- The use of multiple AWS Availability Zones and auto-scaling for capacity adjustments.
- Database backups are transmitted to storage every 30 minutes.
Daily point-in-time snapshots and datastore backups to support service Recovery Point Objective and Recovery Time Objective(s).
- RTO = (4) hours
- RPO = (30) minutes
Workspace ONE Assist architecture
Workspace ONE Assist is a multi-tiered architecture application hosted in multiple Availability Zones (AZs) in AWS Regions globally. The front-facing connection and proctor servers are isolated in public subnets behind a load balancer that proxies all connections to these subnets. Workspace ONE Assist uses a micro-segmentation approach for the cloud network, and each instance or server belongs to a function-specific security group. These predefined security groups are configured to restrict inbound traffic into the production environment. External traffic is routed through AWS security groups, and internal services are deployed behind load balancers in private subnets. VPC peering is used for the optional Workspace ONE Assist satellite servers.
Workspace ONE Assist leverages robust perimeter defenses, including access control mechanisms, perimeter firewalls, auditing mechanisms, network controls, deactivation of unnecessary services, and maintaining defined configuration settings. Security scanner agents are deployed on all internal servers; scanner reports are actively monitored.
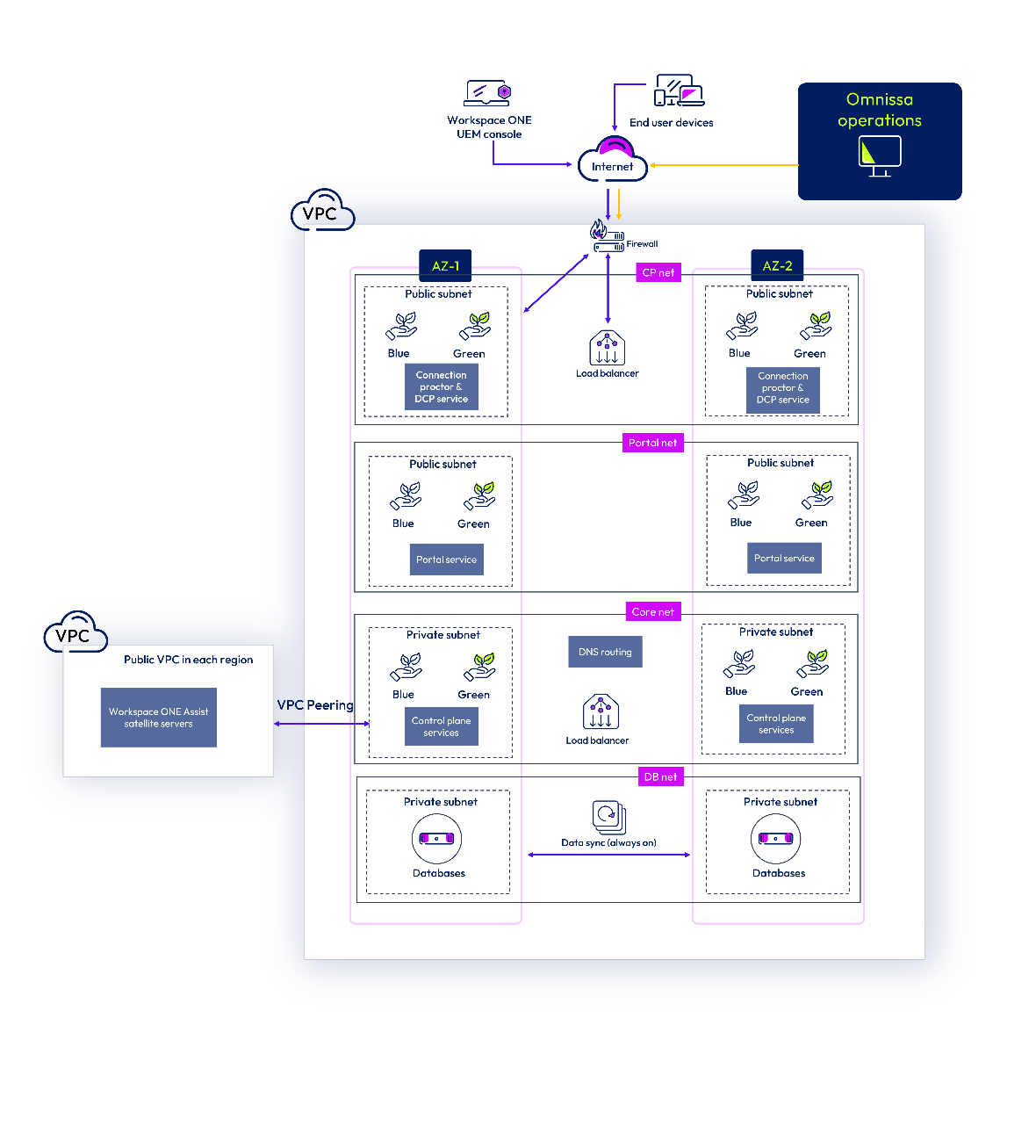
Figure 7: Workspace ONE Assist production environment architecture
Omnissa Connect
Omnissa Connect is an application used by administrators to access their portfolio of Omnissa products and platforms. It is also used by customers to access resources such as Customer Connect, Tech Zone and Test Drive.
Resiliency
Omnissa Connect is supported by defined enterprise resiliency programs, which include business continuity (BC) and disaster recovery (DR) mechanisms.
Omnissa cloud services employ a highly redundant design with multiple best-in-class redundancy technologies combined with data replication strategies. The infrastructure is designed to help ensure that customers will typically not notice a disruption during a component or system failure inside a primary data center. Resiliency is important for Omnissa Connect as it is used to access Omnissa products and platforms. An outage of Omnissa Connect would affect our customers’ ability to access products and platforms.
DR plans are rigorously tested against various disaster scenarios and include tabletop and service restoration exercises. DR strategies include, but are not limited to:
- The use of multiple Amazon Web Services (AWS) Availability Zones and auto-scaling for capacity adjustments.
- Daily point-in-time snapshots and datastore backups to support service Recovery Point Objective and Recovery Time Objective(s).
Omnissa Connect architecture
Omnissa Connect is hosted in AWS running in multiple Availability Zones to help minimize downtime and automate scaling. Omnissa Connect further limits downtime risk through a continuous integration, continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline.
External traffic is routed through a content delivery network (CDN), web application firewall (WAF) and DDoS protections; all internal microservices are deployed behind internal load balancers in private subnets. Outbound traffic flows through a network firewall and outbound NAT. Data is encrypted in transit and at rest.
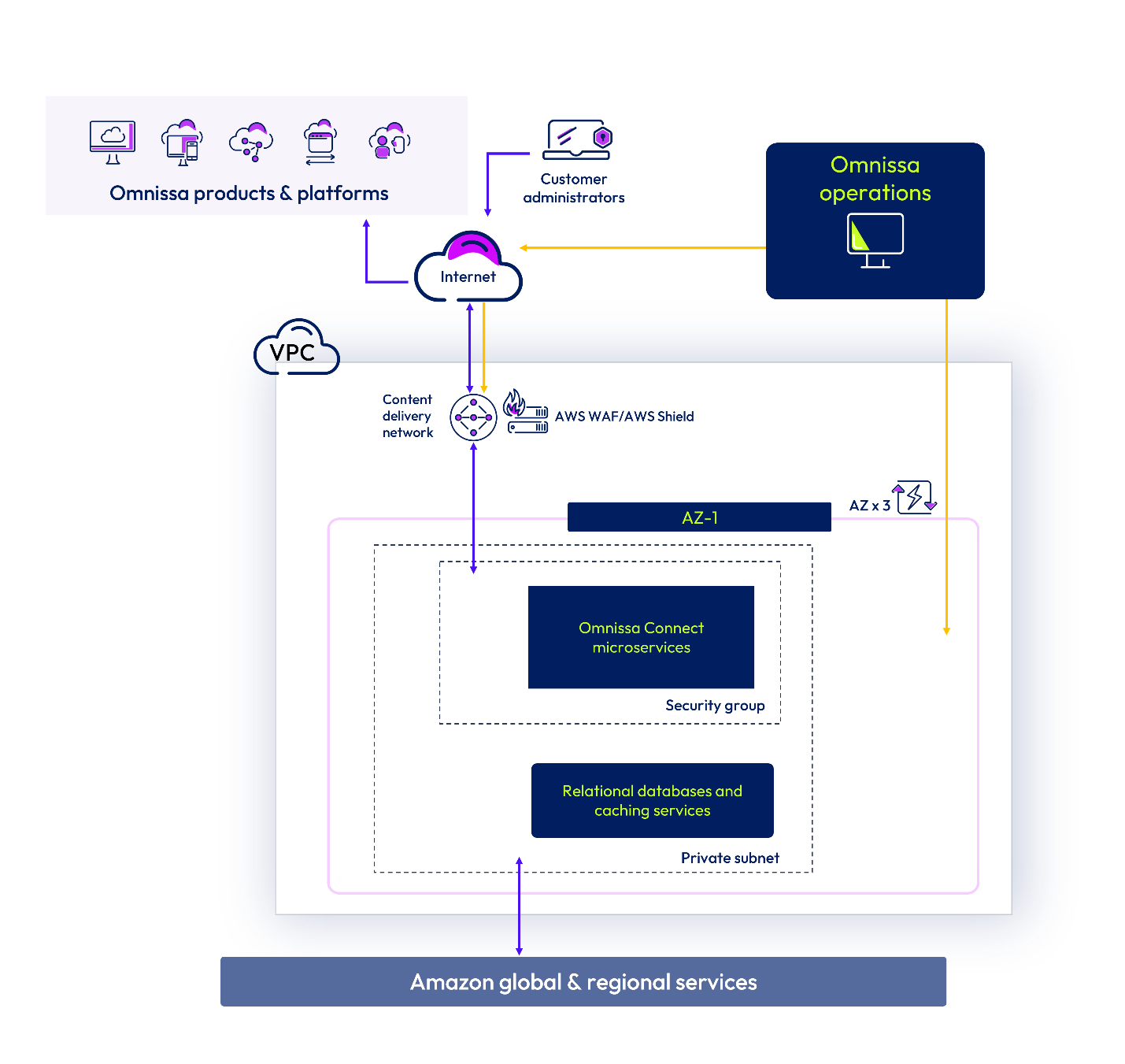
Figure 8: Omnissa Connect architecture diagram
Workspace ONE data processing
Data processing includes data collection, segmentation, and encryption, as well as key and certificate management.
Data collection
By default, Workspace ONE solutions collect information necessary to manage users and devices. Omnissa publishes a Workspace ONE Privacy Disclosure to inform customers who purchase the software to perform unified endpoint management and those individuals whose devices are being managed by the software regarding the types of information collected by the software about users and their devices.
Workspace ONE UEM
Workspace ONE UEM collects limited personal data used for user activation and management. Customers can enable AES-256 encryption at rest for these fields via the Workspace ONE UEM Administrative Console: User first, last name, username, email address, and phone number.
Note: Workspace ONE UEM does not store user credentials derived from customer Active Directory (AD) integration.
Limiting data collection
Customers can also configure privacy settings to activate or deactivate the collection and display of user and device information in the Workspace ONE UEM console according to device ownership type.
Privacy control types include: | ||
|
|
|
| ||
For the following fields: | ||
|
|
|
Omnissa Access and Hub Services
Omnissa Access combines the User’s identity with factors such as device and network information to make intelligence-driven, conditional access decisions for applications delivered by Workspace ONE. Omnissa Access acts as a broker to other identity stores and providers (such as Active Directory (AD), Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS), Azure AD, Okta, and Ping Identity) that customers may already be using to enable authentication across on-premises, SaaS, web and native applications without the need to rearchitect the identity environment. Omnissa Access and Hub Services collect data such as authentication, user data, and logging data. For a complete list, see the Workspace ONE Privacy Disclosure.
Omnissa Intelligence
Omnissa Intelligence consumes data from various sources as configured by customer administrators from Workspace ONE UEM, Omnissa Access, Omnissa Workspace® ONE Software Development Kit (SDK), and the Omnissa Workspace ONE ® Trust Network. Data is aggregated from multiple sources to provide actionable security insights across devices and users. For a complete list, see Supported data categories for Omnissa Intelligence.
Workspace ONE Assist
The Workspace ONE Assist application provides Customer’s IT and support personnel with the ability to remotely view and control the device screen and applications, managed files and run commands with the User’s permission. Assist also provides the ability to capture screenshots and record the device screen for troubleshooting and training purposes. Workspace ONE Assist also collects a limited amount of device data (non-PII data) required for remote device management, such as OEM data, storage, RAM, battery health, Wi-Fi data, and Bluetooth data. Depending on how the Customer has configured Workspace ONE UEM Workspace ONE Assist may have read and write access to the device file system based on the platform type and the permissions granted by the User. The level of access is configurable by the customer.
Omnissa Connect
Omnissa Connect stores a limited amount of personal data used to authenticate administrators to appropriate resources. This includes first name, last name, email address, IP address, and username.
The General Authorization Service (GAZ) service in Omnissa Connect (used for assigning roles for users, groups, and OAuth clients) stores a generated Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) for users and caches in memory, for up to one hour, some personal information (first name, last name, email address).
Data segmentation
Customer data is strictly segmented in all Workspace ONE services, safeguarding their privacy and maintaining data integrity. Workspace ONE UEM is available as a Shared SaaS or a Preferred SaaS solution. Omnissa Access, Omnissa Intelligence, Workspace ONE Assist, and Omnissa Connect are only available as Shared SaaS solutions.
Shared SaaS
The Workspace ONE Shared SaaS offerings are standard multi-tenant implementations in which customers do not have enhanced change management and version control capabilities.
Workspace ONE UEM Preferred SaaS Hosting
The Preferred SaaS offering is also a multi-tenant solution but is designed to provide the customer with more control over change management for Workspace ONE UEM. Customers can opt into one of two release rings: latest release or deferred release. Customers can also create a vanity URL (for example, including a company name). Preferred SaaS also supports BYOK (see the Key management section of this whitepaper for more information.)
Data encryption
Each service within the Workspace ONE platform leverages encryption to help protect data both in transit and at rest. Workspace ONE UEM, Omnissa Access, Omnissa Intelligence, and Workspace ONE Assist collect varying data points intended to achieve different outcomes in the delivery of the service. Due to these differences in functionality, the specific encryption approach varies to align with the intended function of each service.
Encryption in transit
Encryption in transit refers to the practice of encrypting data as it moves between components and systems. This ensures that data remains secure and protected from interception or tampering during transmission. Encryption in transit is used for all Workspace ONE services for data transmitted over the public Internet.
Workspace ONE UEM Modern Stack (Next-Gen SaaS)
As the number of microservices grows and the complexity of service dependencies increases in a distributed microservice-based system, traditional approaches to service networking with load balancers and firewall rules are insufficient to handle the dynamic nature of service communications. By using approaches like service mesh and protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security), the modern UEM architecture helps ensure that customer data is securely encrypted and remains confidential while travelling from one point to another. This is a crucial layer of security as it maintains the integrity and privacy of data exchanges.
A service mesh is a software-driven approach to routing and segmentation. The service mesh, deployed within the Modern SaaS Architecture, is designed to simplify microservice networking by shifting routing, authorization, and other networking functionalities from centralized middleware to the endpoints distributed across the network using software proxies, such as Envoy.
All traffic between services is encrypted and authenticated with mutual TLS. Using TLS provides a strong guarantee of the identity of communicating services and ensures all data in transit is encrypted. TLS certificates are used to identify services and secure communications. These certificates use the Secure Production Identity Framework for Everyone (SPIFFE) format for interoperability with other platforms. Communications over the public internet are also encrypted using TLS 1.2+.
Omnissa Access
Communications for Omnissa Access are encrypted in transit via HTTPS (TLS) over public networks. In alignment with PCI-DSS, Omnissa Access SaaS environments only support TLS 1.2+.
Each customer tenant is assigned a unique private/public key pair. The keys are randomly generated at the time of tenant creation. Private keys are encrypted at rest with AES-256.
Omnissa Intelligence
Communications for Omnissa Intelligence are encrypted in transit via TLS over public networks. In alignment with PCI-DSS, Omnissa Intelligence SaaS environments only support TLS 1.2+.
Workspace ONE Assist
In compliance with PCI-DSS standards, communications for both Workspace ONE Assist are encrypted in transit via TLS 1.2+ over public networks.
Omnissa Connect
Communications for Omnissa Connect are encrypted in transit via TLS over public networks. In alignment with PCI-DSS, Omnissa Connect environments only support TLS 1.2+.
Encryption at rest
Encryption at rest varies by service and is detailed below.
Workspace ONE UEM Modern Stack SaaS (Next-Gen SaaS)
All user data stored within Workspace ONE UEM is encrypted at rest via a combination of both hardware-based array-level encryption and volume-level encryption with a minimum level of AES-256 symmetric encryption.
Additional data-level encryption is implemented for customer content and sensitive fields, as described in the Data Collection section of this document. All locally defined passwords, certificate private keys, client cookie data, tokens, and AD Bind Accounts are stored within the database and are protected with a 256-bit AES symmetric encryption algorithm. Stored credentials use Password Based Key Derivation Function 2 (PBKDF2) with a salt of at least 256 bits and a sufficiently large number of iterations.
Note: Workspace ONE UEM does not store user credentials derived from customer Active Directory (AD) integration.
The UEM modern architecture implements data encryption at rest at the storage block level using Linux Unified Key Setup (LUKS). LUKS is a specification for block device encryption that establishes the on-disk data format and encryption key management policy. Data is encrypted and decrypted transparently when reading from or writing to the disk. LUKS accesses the kernel device mapper using the dm-crypt module, enabling low-level mapping that handles encryption and decryption of data as it is written to or read from the disk. The cryptsetup utility is used for creating and accessing LUKS encrypted mounts on virtual machines (VMs).
In addition to primary data storage, data backups (taken for recovery purposes in case of unexpected events and disasters) are also secured and encrypted using LUKS.
See the Key management section of this document for information around BYOK for Workspace ONE Preferred SaaS.
Omnissa Access and Hub Services
Locally defined Omnissa Access passwords are secured with AES-256 and PBKDF2 and a randomly generated salt. The service does not store user credentials derived from customer Active Directory (AD) integration. The AD BIND account is stored in the Omnissa Access database and is encrypted (AES-256). Data considered sensitive by the application is encrypted (AES-256) with a per-tenant key that is generated by Omnissa Access. Amazon Simple-cloud Storage Service (S3) instances used for Omnissa Access and Workspace ONE Hub Services are encrypted. Encryption is applied at the database level for Workspace ONE Hub Services.
Omnissa Intelligence
Omnissa Intelligence is a cloud service that provides deep insights, analytics, and automation for the entire digital workspace. As such, Omnissa Intelligence was built as a cloud-native service and uses a combination of AWS-managed and Omnissa-managed Key Management Service (KMS) keys for all encryption-at-rest across the solution data stores. Data is encrypted at rest using AES-256 using per-region keys.
Workspace ONE Assist
The playable video file generated during the remote management session is stored as a binary file and is encrypted at the file level following the session. The encrypted binary files are stored in an encrypted Amazon S3 bucket using native AWS encryption (AES-256). No other sensitive customer data is stored in the Workspace ONE Assist database.
Omnissa Connect
All data stored in Omnissa Connect is encrypted at rest using a combination of AWS-managed and Omnissa-managed Key Management Service (KMS) keys. Data at rest is encrypted at the database level using AES-256.
Key management
To help ensure the security and integrity of the cryptography used in the cloud-hosted environments, only authorized Omnissa support personnel have access to encryption keys, and keys are managed in line with PCI-DSS compliance standards.
Workspace ONE UEM
Data in Workspace ONE UEM is encrypted at rest with an Omnissa data encryption key (DEK) that is stored in the database. The Workspace ONE UEM database is encrypted at rest with array- or volume-level encryption. Access to the DEK requires direct Root privileges to the Workspace ONE UEM database where the DEK is stored. Those permissions are only granted to a small subset of senior Omnissa Database Administrators with documented business needs. All interactive root access to the Workspace ONE UEM database and DEK is logged and audited. Workspace ONE UEM server keys are stored in an enterprise-grade key management tool.
BYOK support for Workspace ONE Preferred SaaS
Workspace ONE UEM Preferred SaaS now supports Bring Your Own Key (BYOK), allowing organizations to manage their own RSA-4096 wrapped Key Encryption Keys (KEKs) for data-at-rest encryption. BYOK not only provides encryption but also empowers organizations to define their own security rules and maintain control over their keys. The key capabilities include:
- Customer-Controlled KEK: Organizations using Customer-controlled KEK can manage their own Key Encryption Keys (KEK), set renewal schedules, and control encryption lifecycle operations.
- Secure Storage: Omnissa securely stores the KEK in a Hardware Security Module (HSM), ensuring limited system access to the root of trust.
- Auditability: All key access and encryption operations are fully auditable, supporting governance and compliance requirements.
- Zero Trust Alignment: The BYOK lays the foundation for Zero Trust architecture, enabling agile adaptation to evolving security models and technologies.
- For more information, see Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) Support for Workspace ONE UEM Preferred SaaS.
Omnissa Access
Omnissa Access uses AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to manage encryption keys. Sensitive customer data is encrypted with a per-tenant key and stored encrypted using a separate master key. The master key encrypts all per-tenant keys and is stored encrypted. The key used to encrypt the master key and database snapshots is an AWS KMS key generated and stored by KMS. The private key does not leave KMS; we do not use a customer-supplied key that allows us to hold a copy of the private key outside of KMS. Omnissa double encrypts the master key using the KMS in an alternate AWS region in case the primary region is down, and we need to restore the service in the alternate region.
Omnissa Intelligence
Omnissa Intelligence uses AWS KMS to manage encryption keys. Sensitive customer data is encrypted with per-region keys and stored encrypted in the database. The keys used to encrypt database snapshots are also AWS KMS keys generated and stored by KMS. The private keys do not leave KMS, and we do not use customer-supplied keys that allow us to hold a copy of the private key outside of KMS.
Workspace ONE Assist
Key management practices are in line with PCI-DSS. Keys are stored separately on secure servers located on the internal Omnissa network and are accessible by a small subset of Operations personnel only. Access is monitored and logged.
Omnissa Connect
Omnissa Connect uses AWS Secrets Manager and AWS Parameter Store to manage credentials and are accessible by a small subset of Operations personnel only. Access is monitored and logged.
Certificate management
Certificate management is handled in Workspace ONE UEM and Omnissa Access.
Workspace ONE UEM
Customer certificates uploaded via the Workspace ONE UEM console are encrypted before upload and are password-protected in the PKCS12 format. The passwords are additionally encrypted at-rest using AES-256 encryption utilizing the application encryption key. These certificates can include:
- Registration Authority (RA) Certificates
- TLS Mutual Authentication Certificates (for connecting to a customer's on-premises enterprise CA)
- Gateway TLS Certificates
For certificates issued via integration with a customer’s on-premises Enterprise CA (including S/MIME), Omnissa will collect the certificate from the Enterprise CA and securely forward it to the device. The certificate may be stored in volatile cache memory for up to 4 hours but is never stored or written to non-volatile storage.
For S/MIME certificates uploaded via the Self-Service Portal (SSP), the certificates are automatically purged after 48 hours, and the customer can configure that retention period down to as low as 60 Minutes via the SSP.
Omnissa Access
Omnissa Access uses SAML signing certificates to help ensure that messages are coming from the expected identity and service providers. The SAML certificate is used to sign SAML requests, responses, and assertions from the service to dependent applications, such as WebEx or Google Apps. A self-signed certificate is automatically created in the Omnissa Access service for SAML signing. These SAML certificates are encrypted using tenant-specific keys that are encrypted using Amazon KMS.
Backup retention and data destruction
Retention of data backups varies by service and is outlined in this section. Data destruction practices vary based on hosting type (co-located data center vs. cloud-hosted data center).
Retention
Data retention timeframes vary in Workspace ONE UEM, Omnissa Access, Omnissa Intelligence, and Workspace ONE Assist.
Workspace ONE UEM
Workspace ONE UEM customer application logs (Event Logs) and device data are available within the customer console for 30 days. Daily backups are stored for 30 days, and monthly backups are stored for (60) days.
Exception: By default, Workspace ONE UEM web console administrator login history is purged every (730) days—unless the customer configures an admin Terms of Use (TOU) prompt for users—to support customers’ security and auditing purposes. If the TOU prompt is configured, the admin login history is not automatically purged to store a timestamp and admin record corresponding to the TOU acceptance.
Omnissa Access
Omnissa Access customer application logs (Event Logs) are stored for (90) days. Daily backups are stored for (14) days, and monthly backups are stored for (60) days.
Omnissa Intelligence
Omnissa Intelligence stores data to offer historical analysis. The system stores raw data for three months and stores trend data for (12) months. Examples of raw data can include battery information and operating system versions. Some trend data examples include application installs and application adoption, device category data, enrollment, and OS versions over time. Daily point-in-time backups are stored for (30) days. System audit log data is retained for (90) days.
Workspace ONE Assist
Backups include daily full-backup (24) hours, differential (15) minutes, and transaction log backups, ranging from (5) > (60) minutes. Backups are stored for (180) days.
Omnissa Connect
Relational databases are backed up daily; these daily backups are stored for seven (7) days. Non-relational databases have point-in-time recovery (PITR) enabled; these incremental backups are stored for 35 days.
Destruction
Data retention processes include the destruction of data, both logical and physical.
Logical destruction at contract termination
Refer to the Cloud Services Guide available on the Omnissa Legal Center for our obligations regarding data retention and deletion at termination.
Physical destruction of hardware
Omnissa adheres to U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) Mandate 5220-22M, where applicable (U.S.-based co-located data centers only). Note that Omnissa partners with cloud service providers to support Workspace ONE cloud-delivered environments globally; these providers manage physical media destruction processes according to ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS requirements.
Privacy and compliance
Privacy and compliance include data sovereignty and service sub-processors, the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), binding corporate rules, UK data protection regulations, and data transfer strategies, as well as requests for data protection and for content access.
Data sovereignty and service sub-processors
All Workspace ONE customer production data is replicated to disaster recovery locations in the region. For data processing locations, refer to the sub-processor listings available on the Omnissa Legal Center.
As set forth in the Omnissa Data Processing Addendum, Omnissa has adequate data transfer mechanisms in place with each sub-processor. Refer to our Data Processing Addendum available on the Omnissa Legal Center for additional information.
Omnissa creates microservices in discrete cloud environments to extend the core platform functionality. Processing locations for product functionality delivered via microservices are also outlined in the service sub-processor lists.
Privacy and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Workspace ONE customers are responsible for using and configuring the service in a manner that enables the customer to comply with applicable Data Protection Laws, including the GDPR, as a data controller or as a data processor with respect to Personal Data. Omnissa complies with applicable data processor obligations. For additional information regarding customer and Omnissa responsibilities, refer to our Data Processing Addendum available on the Omnissa Legal Center.
Workspace ONE customer administrators can configure some of the data to be managed, collected, and stored across managed devices. For example, device phone numbers can be collected for corporate-owned iOS devices but not for employee-owned Android devices. Privacy controls can be set up with role-based access, restricting customer IT staff that do not have the appropriate privileges from modifying policies that do not adhere to company policy.
Omnissa has no direct relationship with the Users whose data it processes in connection with providing the Software and any related services. A User who seeks access or who seeks to correct, amend, or delete inaccurate data should direct their query to the Customer. If the Customer requests Omnissa to modify or remove the data, we will respond to the Customer’s request in accordance with our agreement with the applicable Customer or as may otherwise be required by applicable law.
At any time, an appropriately provisioned Workspace ONE administrator can take the following actions to help comply with applicable data protection laws:
- Access, upload, update, or remove data directly from the console at any time.
- Require TOU acceptance prior to end users accessing the service during enrollment. Users must accept the TOU before proceeding with enrollment, installing apps, or accessing the console. The console allows administrators to customize fully and assign a unique TOU to each organization group and child organization group. TOU acceptance can be reviewed in the administrative console or within the end-user Omnissa Intelligent Hub at any time.
- Export solution data, including user reports, via CSV, PDF, and XLS formats.
Data protection requests
If Omnissa receives any requests from individuals or applicable data protection authorities relating to the processing of Personal Data within Workspace ONE services, including requests from individuals seeking to exercise their rights under Data Protection Law, Omnissa will promptly redirect the request to the customer. Omnissa will not respond to such communication directly without the customer's prior authorization unless legally compelled to do so. If Omnissa is required to respond to such a request, Omnissa will promptly notify the customer and provide a copy of the request unless legally prohibited from doing so.
Omnissa will reasonably cooperate with customers to respond to any requests from individuals or applicable data protection authorities relating to the processing of personal data to the extent that a customer is unable to access the relevant personal data in their use of the service. Refer to our Data Processing Addendum available on the Omnissa Legal Center for definitions and standard hosting terms.
Government requests to access customer content
Omnissa may, on occasion, receive a request from a government agency or law enforcement authority seeking access to content belonging to a customer. Regardless of where a request comes from or who the customer is, Omnissa is vigilant about protecting Customer Content. Omnissa will not disclose Customer Content unless required to do so to comply with a legally valid and binding obligation or order. Omnissa reviews each request to determine that it complies with applicable laws.
The following sets forth the steps Omnissa takes when responding to a request for Customer Content, as further set forth in the General Terms (“Required Disclosures” section): Where Customer Notification is Not Legally Prohibited, Omnissa will:
- Provide Customer with notice and a copy of the Demand. If the Demand relates to Cloud Services, Omnissa will
- inform the relevant authority that Omnissa is a service provider acting on Customer’s behalf and that all requests for access to Customer Content must be directed in writing to the contact that Customer identifies (or, if no contact is timely provided, to Customer’s legal department) and
- only provide access to Customer Content if the competent authority rejects the redirect request. If Customer requests, and at Customer’s expense, Omnissa will take reasonable steps to contest the Demand. If Omnissa is legally prohibited from notifying Customer of the Demand, Omnissa will evaluate the validity of the Demand, and, if Omnissa does not believe the Demand is legal, Omnissa will challenge the Demand. Omnissa will limit the scope of any disclosure to the minimum information required to comply with the Demand.
Audit reports and trust assurance
We perform annual third-party audits against our cloud services. Refer to the Omnissa trust center for the latest list of industry certifications.
Release management and maintenance
Workspace ONE services have a 99.9% availablity Service Level Agreement (SLA), as defined in the Workspace ONE SLA documentation available on the Omnissa Legal Center. As part of the cloud offering, Omnissa manages and updates the Workspace ONE SaaS applications and scoped hosting systems on behalf of our customers.
Release schedules
Omnissa communicates feature releases and service announcements through many avenues, including documents, blogs, and whitepapers on Tech Zone, as well as Omnissa Customer Connect, Product Docs, Knowledge Base(s), or through E-Mail distros. Our frequent release schedule demonstrates our commitment to continuous innovation. New software features and operating systems are released daily, and we aim to provide same-day support for new major operating system updates and APIs:
- Workspace ONE shared cloud environments receive updates automatically.
- Workspace ONE UEM Preferred SaaS chooses a deployment ring model.
Scheduled maintenance
Omnissa schedules pre-defined maintenance windows to limit the potential to impact the environment availability. These standing windows are scheduled annually and available on the My Workspace ONE support portal and in this publicly available KB article: 2025 Omnissa Workspace ONE UEM Maintenance (81448).
Routine maintenance
Occasionally, Omnissa must perform maintenance that has the potential to impact the availability of customer environments outside of scheduled maintenance windows, and Omnissa reserves the right to do so. A minimum of five days’ advance notice is given for routine maintenance.
Emergency maintenance
Emergency maintenance is defined as a potentially impactful maintenance activity that must be executed quickly due to an immediate, material threat to the security, performance, or availability of the Service Offerings. Every attempt will be made to provide as much advance notice as possible, but notice depends on the severity and critical nature of the emergency maintenance.
Summary and additional resources
This document provides a general overview of the security controls implemented in Omnissa Workspace ONE commercial cloud offerings. The intent is to provide readers with an understanding of how Workspace ONE cloud services approach security, the key mechanisms, and processes that Omnissa uses to manage information security, as well as describe shared responsibilities for providing security in a modern cloud computing environment.
Additional resources
For more information about Workspace ONE cloud services, you can explore the following resources:
- Workspace ONE UEM Architecture
- Omnissa Access Architecture
- Omnissa Intelligence Architecture
- Workspace ONE Assist Architecture
Changelog
The following updates were made to this guide:
| Date | Description of Changes |
| January 16, 2026 | 2026 version published |
About the author and contributors
The following people contributed their knowledge and assistance with this document:
- Andrea Smith, Sr. Program Manager, Customer Security Assurance