Workspace ONE Cloud Services alignment with NIST SP 800-171
Introduction
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-171 was developed to provide guidance to organizations, such as U.S. government contractors, on how to protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) in non-federal systems. CUI is information that the government considers sensitive but not classified.
There are over 100 security requirements of NIST SP 800-171 organized into 14 requirement families, which are summarized in the image below.
Note: You can find the definitions for acronyms used throughout this document in Acronyms used in the Workspace ONE Security Series.
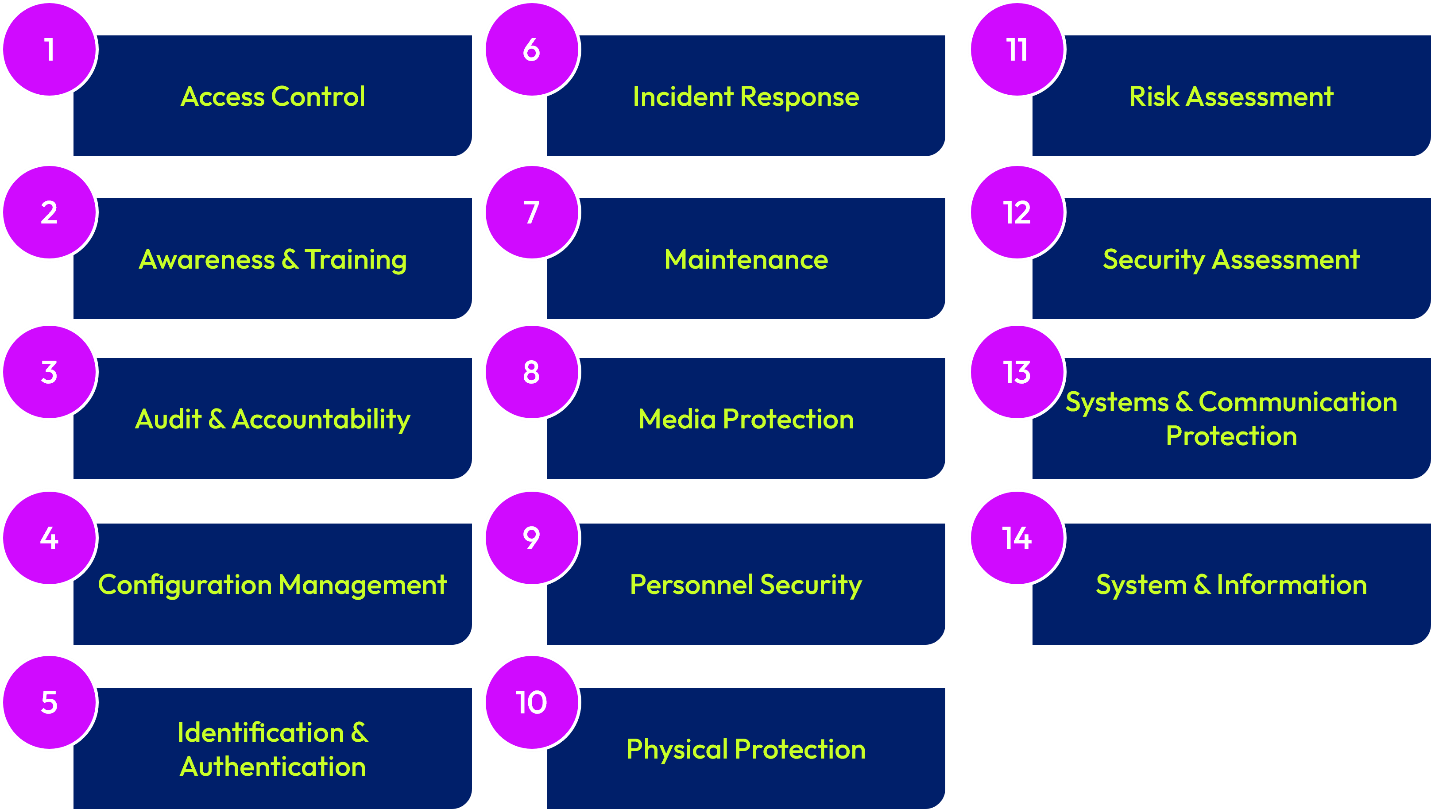
Figure 1: NIST 14 Requirement Families
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to provide a general overview of the security controls implemented within the Omnissa Workspace ONE® commercial cloud services and their alignment with the 14 requirement families of the NIST SP 800-171 standards. This document does not represent full compliance with the NIST SP 800-171 requirements; customers that require full compliance with NIST SP 800-171 or a formal attestation should consider the Workspace ONE Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) environments. Information contained in this document is solely for the use of evaluating Workspace ONE security controls and does not represent an official endorsement by NIST or a NIST SP 800-171 attestation.
This whitepaper applies to the following Workspace ONE commercial cloud service offerings:
- Omnissa Workspace ONE® Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)
- Omnissa Access
- Omnissa Intelligence
- Omnissa Workspace ONE® Assist
FedRAMP, on-premises, and third-party offerings are not in scope for this document.
Audience
This document is intended for Workspace ONE commercial cloud administrators. It assumes at least intermediate knowledge of Workspace ONE cloud services and focuses on the policies, processes, and controls supporting the cloud-delivered services.
Shared Responsibilities
The end-to-end security of the Workspace ONE cloud-delivered service offerings is shared between Omnissa and our customers. Omnissa provides security for the aspects of the Workspace ONE service offerings over which we have sole physical, logical, and administrative-level control. Customers are responsible for ensuring compliance with all applicable laws and regulations, including those aspects of the service offerings over which they have administrative-level access or control. Information provided in this document does not constitute legal advice regarding Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) compliance, and in that regard, customers should consult either relevant legal advisors or compliance auditors for any questions regarding regulatory compliance for their organization on NIST SP 800-171.
How we design our information security program
The Omnissa Information Security Governance Policy starts with the company’s commitment to information security and the protection of our customers’ data. The policy defines the baseline for establishing an information security program, policies, and practices, and defines our key information security principles:
|
|
Omnissa has implemented and maintains a complete set of information security policies based on international standards ISO/IEC 27001 and consistent with industry-accepted practices and security frameworks, many of which are aligned with the guidance provided by the 14 control families of NIST SP 800-171. Appendix D of the NIST SP 800-171 provides mapping tables and derived security requirements to the security controls in NIST SP 800-53 and secondary mappings to the security controls to the relevant controls in ISO 27001. This control mapping information can be useful to organizations that wish to demonstrate compliance with the security requirements in the context of their established information security programs, when such programs have been built around the NIST or ISO/IEC security controls.
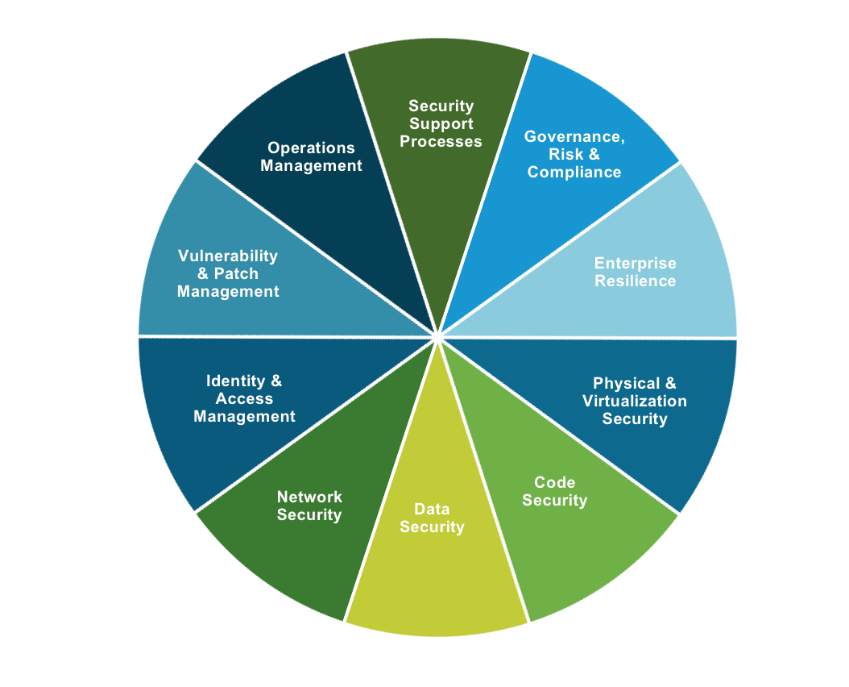
Figure 2: The Omnissa Information Security Framework
Workspace ONE alignment with NIST SP 800-171
This document addresses the Omnissa enterprise Information Security Program, as well as policies and procedures in relation to the 14 control families of NIST SP 800-171 for the following cloud-hosted services: Omnissa Workspace ONE® UEM, Omnissa Access, Omnissa Intelligence, and Omnissa Workspace ONE® Assist. The Omnissa Access cloud environment also hosts data for Omnissa Workspace ONE® Hub Services and Omnissa Identity Services. Similarly, the Omnissa Intelligence cloud environment hosts data for the Omnissa Connect, Digital Employee Experience Management (DEEM), and Omnissa Intelligence for Consumer Apps. Within this whitepaper, these services are collectively referred to as “Workspace ONE.”
1. Access Control
In the Access Control family of controls, NIST SP 800-171 prescribes the recommended security requirements for limiting system access, including restricting access and privileged functions, controlling and logging remote access, controlling the connection to secure mobile devices, preventing the exfiltration of data, and so on.
Omnissa Access to Cloud-Hosted Systems
Omnissa secures highly privileged access to the Workspace ONE services through a layered defense model that requires strong authentication prior to performing service management functions and applies industry best practices for access control, such as implementing role-based least privilege and separation of duties, limiting unsuccessful login attempts, and enforcing session timeouts. Omnissa Cloud Operations personnel use separate user accounts for administration and normal user activities, and production environment access is secured through a combination of VPN, IP address allow listing, or jump servers using Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) and directory credentials. Logs are in place to review support staff access to all systems and environments. Quarterly User Access Reviews are conducted to review privileged access and to remove or deactivate accounts with 90 days of inactivity.
Personnel must use Omnissa-owned equipment when accessing production environment systems, and all Omnissa-owned laptops and mobile devices are enrolled in a corporate-maintained instance of Workspace ONE UEM. Employees are also prohibited from transferring customer data from the production environment and are prohibited from storing customer data on portable storage devices.
Omnissa Access to Customer Consoles
Omnissa Global Customer Support (GCS) may require access to customer consoles to resolve certain support tickets. Access to the customer console is tied to a support request and is granted after GCS obtains permission from the customer. Application logs are available to customers within the Workspace ONE consoles to review the actions taken by Omnissa GCS.
Customer Access to Workspace ONE Console
As Workspace ONE services are SaaS-based offerings, customer administrators do not directly manage access to the production environment but rather, access Workspace ONE services through web-based consoles. Granular role-based access controls restrict the depth of device management information and features available to each Workspace ONE console user, and Workspace ONE services can integrate with the customer’s directory services instance to inherit password policies and access controls. For access to the web-based Workspace ONE consoles, customers can also implement MFA mechanisms through Okta Verify, Duo, PingID, RADIUS, RSA SecurID, and RSA SecurID Access, and through the use of Omnissa Workspace ONE® Intelligent Hub Verify. All Workspace ONE administrator changes are retained for review within the console event log. Customer administrators also manage access and entitlements for end-user devices.
2. Awareness and Training
The Awareness and Training family of NIST SP 800-171 covers the implementation of a corporate-wide information security training program that covers security awareness techniques commensurate with the organization’s needs and employees’ specific access and duties.
The Omnissa Security Awareness Program
All Omnissa personnel are required to complete annual business conduct and security awareness training that covers key best practices for preventing, detecting, and responding to potential security incidents. It also introduces personnel to the Omnissa security policies that are enforced to protect information and information systems, how to report a suspected security incident, as well as help to ensure the security of physical facilities such as offices. Personnel with access to cloud production environments receive additional training as they assume job roles and responsibilities.
Omnissa periodically validates those employees understand and follow the established policies through compliance audits.
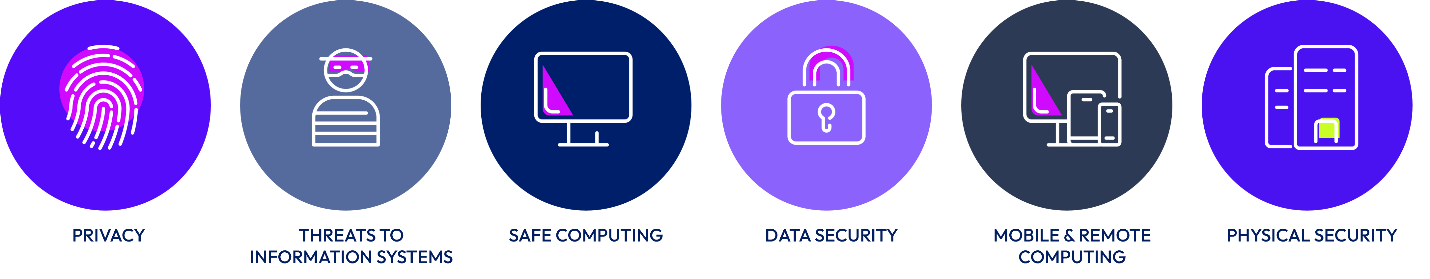
Figure 3: Omnissa Security Awareness Training Topic Areas
3. Audit and Accountability
The Audit and Accountability family of NIST SP 800-171 controls defines system events (for example, failed logins and administrative privilege usage) and the logging requirements to enable the monitoring, analysis, investigation, and reporting of unlawful or unauthorized system access.
Workspace ONE Infrastructure Logs
Workspace ONE cloud-hosted services have full auditing capabilities on all environments to enable the reconstruction of security incidents and leverage a robust centralized SIEM infrastructure for logging and monitoring. Critical systems and privileged access to Workspace ONE infrastructure, firewall and IDS logs, and Domain Name System (DNS) Queries are logged and monitored. Auditable events include user identification, type of event, date and time, success or failure indication, and origination of event. Access to the audit trail is protected, and logs are stored separately and securely. All logs are correlated to a centralized time source.
Note: Omnissa does not provide Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) infrastructure logs to customers; however, console application logs are available to customers to help audit console access and actions.
Workspace ONE Console Application Logs
Customers can access application-level logs within Workspace ONE UEM and Omnissa Access that record administrator and end-user device events. Workspace ONE UEM event logs include:
- Device events show the commands sent from the console to devices, device responses, and device user actions.
- Console events show actions taken from the Workspace ONE UEM console, including login sessions, failed login attempts, admin actions, system settings changes, and user preferences.
The audit events report in the Omnissa Access service that lists the events related to a user, including:
- The type of action within a specific date with criteria such as user, type, action, object, and date range
These logs can be exported as CSV for storage offline to meet regulatory or business requirements. Workspace ONE UEM event logs can also be integrated with a customer’s existing SIEM solution using Syslog.
4. Configuration Management
In the Configuration Management family of controls, NIST SP 800-171 defines baseline configurations and outlines the best practices for establishing and enforcing configuration baselines, including procedures for change management, preventing the use of nonessential programs, functions, ports, protocols, and services, and controlling the installation of software.
Omnissa Configuration Management and Change Management Procedures
Omnissa maintains a detailed Configuration Management policy based on industry best practices to harden the cloud environment; revisions and exceptions to the Configuration Management policy are processed through the Change Management policy to help ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of our hosted offering.
Omnissa establishes security baseline configurations based on industry best practices such as Center for Internet Security (CIS) Benchmarks and Amazon Linux images. Our Change Management policy defines controlled changes to production environments. Changes are processed through a formal program that includes approval, testing, implementation, and rollback plans. Omnissa disables unnecessary ports, protocols, and services as part of baseline hardening standards. Furthermore, Omnissa has restricted the ability to install, modify, and replace operating systems and other system programs to authorized personnel.
5. Identification and Authentication
The Identification and Authentication control family of NIST SP 800-171 covers user identity (that is, verifying the identity of a user, process, or device accessing the system) and authentication (authenticating the identity of a user, process, or device accessing the system). This topic area includes best practices for the use of authenticators (such as passwords and MFA), password policies, and the protection of identifiers (such as the use of unique IDs and disabling inactive IDs).
Omnissa Password and Authentication Policies
The Omnissa Authentication and Password Policy is based on industry best practices and includes strong password guidelines that require a minimum number of characters. Entropy is used to help ensure password strength.
The Omnissa Authentication and Password policy prohibits passwords from being stored in an unprotected manner. Additionally, passwords are prohibited from being shared or transmitted over unencrypted paths. Passwords are stored using state-of-the-art encryption. Employees are assigned unique IDs and are prohibited from sharing passwords. Remote access to the production environment (including the use of MFA) and other access controls are outlined in 1. Access Control.
Workspace ONE Console Authentication
Customers manage authentication types for access to Workspace ONE consoles. See Customer Access to Workspace ONE Console for details.
6. Incident Response
In the Incident Response family of controls, NIST SP 800-171 provides guidance for establishing an incident response program that includes capabilities for preparation, detection, analysis, containment, recovery, and user response activities.
Omnissa Incident Management and Response
Omnissa has an established Incident Response Policy to help ensure the critical elements of the incident lifecycle are managed in a structured manner. The policy and associated procedures address the key elements of incident response, such as the handling, monitoring, and reporting of an information security incident, and forensics and remediation after an incident occurs, as relevant and applicable. Any suspicious or unusual activity must be reported to the incident response team. Incidents are reported to the appropriate Cloud Operations team for categorization and resolution, and issues are escalated to senior management according to a pre-defined protocol.
Omnissa tracks alerts, responses, and resolutions throughout completion: Incident response teams prepare postmortem reports to internal stakeholders and our Information Security Governance Committee for review.

Figure 4: Omnissa Incident Response Cycle
7. Maintenance
The Maintenance control family of NIST SP 800-171 provides guidance for the maintenance of system components, including hardware, software, and firmware.
Application and Software Patching Processes
Omnissa maintains the systems it uses to deliver the Workspace ONE offerings, including the application of patches it deems critical for the target systems. We have the capability to rapidly patch vulnerabilities across all computing devices, applications, and systems. Remediation efforts and timelines are prioritized and applied using industry best practices. Critical vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner. Other vulnerabilities are addressed with a plan of corrective action within a reasonable period.
Hardware Maintenance
Omnissa leverages Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) providers to support the Workspace ONE service offerings, and Omnissa manages these environments from the OS layer up. Under the shared responsibility model, these providers maintain the hardware for each cloud-delivered service. Our cloud hosting providers are minimally ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS certified and undergo annual SOC 2 Type 2 audits to verify their procedures.
Where applicable (U.S.-based co-located data centers only), Omnissa has procedures in place when hardware requires maintenance, including remote access, physical access, and equipment sanitization.
8. Media Protection
The Media Protection control family of NIST 800-171 outlines procedures for protecting system media – both digital and non-digital media. Guidance includes controls for the physical protection of media, access controls for media, sanitization of media, encryption of media during transport, use of removable media, and so on.
Digital Media Protection
Note: Omnissa does not use removable media in our cloud-hosted environments, and our Acceptable Use policy prohibits the transfer of customer data via portable media, which includes laptops, thumb drives, CDs, DVDs, and other related portable media. Customer data is encrypted at-rest within Workspace ONE services. For more information on data encryption at-rest, see 13. System and Communication Protection.
Non-digital Media Protection
Note: In-scope service data (for example, data collected from mobile devices in Workspace ONE UEM) is not removed from the production environment and converted to a non-digital format. Clear desk practices are in place in accordance with the Omnissa Data Classification Policy, and Omnissa implements secure document disposal where appropriate.
9. Personnel Security
In the Personnel Security family of controls, NIST 800-171 provides guidance for personnel security screenings and protecting data during personnel transfers and at termination.
Human Resources and Personnel Security
The Omnissa Human Resources Information Security Policy outlines policies and procedures related to the onboarding and offboarding of Omnissa employees. These include processes for background screening, employment agreements, training, and employee terminations.
The satisfactory completion of a background check is a condition of all offers of employment. Subject to applicable legislation, candidates are informed regarding the scope of the background check and must consent to the background screens before the screens are run. Background checks are performed in accordance with the Omnissa Pre-Employment Background Check protocols applicable to the region and are subject to local laws and regulations. As a general matter, Human Resources Operations initiates and oversees the background check process. Results are treated as confidential personnel records, made available only to those outside Human Resources Operations with a business reason to review or be consulted regarding the results.
Subject to applicable law, Omnissa, or its background check vendor, typically performs the following background checks:
- A verification of the applicant’s recent work history
- Confirmation of highest degree obtained, and professional qualifications required for the position
- Credit review for employees at the level of VP or higher in the Finance organization
- Review of certain criminal records, consistent with availability of records and limitations imposed by applicable law
Omnissa also has a standard termination process that involves coordination between HR and IT teams to help ensure access revocation and to maintain a standard process for corporate asset return. Quarterly access reviews are performed against access to the production environments to verify that any transferred or terminated employees have been removed or disabled.
10. Physical Protection
In the Physical Protection family of controls, NIST SP 800-171 provides guidance for limiting physical access to organizational systems, equipment, and operating environments, as well as guidance for monitoring and managing physical access.
The Omnissa Physical Security Program
The role of the Omnissa Physical Security team is to help ensure perimeter security, establish and maintain physical access controls (card readers, cameras, badges, and so on), provide ongoing security monitoring, and create awareness training and events around the physical security program (for example, training employees on tailgating and social engineering).
Key elements of our Physical Security policy include controls around: physical security perimeters, physical entry controls, physical access, securing offices, rooms, and facilities, visitors to facilities, records, preventing the misuse of facilities, protecting against external and environmental threats, working in secure areas, access to restricted areas, delivery and loading areas, equipment siting and protection, supporting utilities, equipment maintenance, removal of assets, security of equipment and assets off-premises, secure disposal or reuse of equipment, unattended user equipment, and clear desk and clear screen.
Data Center Physical Security
Omnissa leverages co-located data center facilities in the U.S. and IaaS providers (in the U.S. and globally) to support the Workspace ONE service offerings. Under the shared responsibility model, these providers maintain physical and environmental security controls for the cloud-delivered services.
Workspace ONE co-location and cloud-hosting partners are at least Tier III, have undergone SOC 2 Type 2 audits, and have achieved at least ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS certifications. Physical addresses for Workspace ONE hosting locations are confidential, and on-site visits are forbidden.
11. Risk Assessment
The Risk Assessment control family of NIST SP 800-171 outlines guidelines for assessing risk to organizational operations as well as vulnerability scanning and remediation of vulnerabilities.
The Omnissa Risk Management Program
The Omnissa Risk Management team provides risk management oversight that represents our appetite and tolerance for risk. Identify and monitor initiatives to remediate the risk. Activities include:
- Proactively identifying existing and potential areas of information security risk.
- Assessing potential impact to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and reliability of information assets.
- Using a risk assessment framework and methodology to identify, assess, and prioritize those risks.
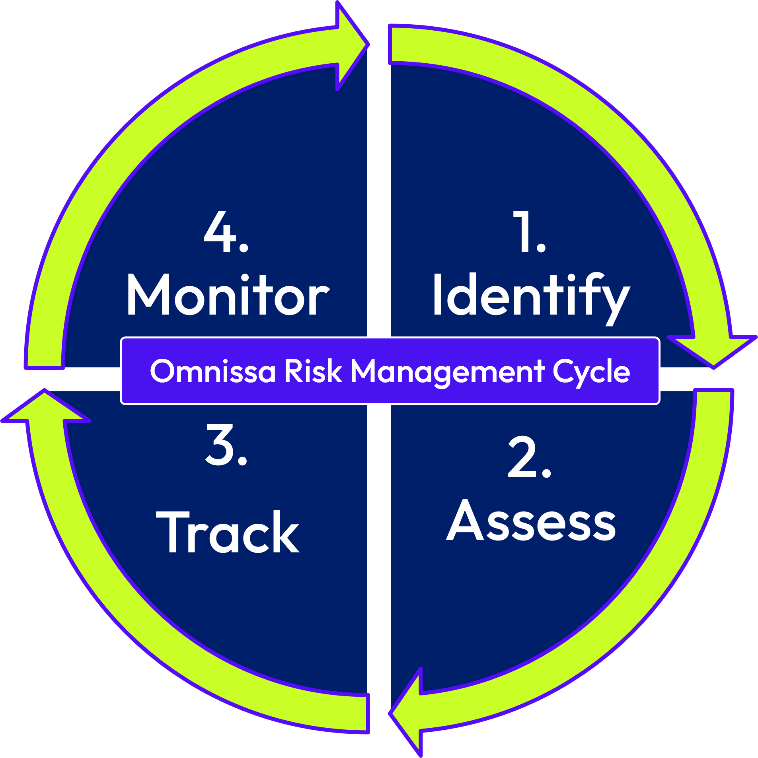
Figure 5: The Omnissa Risk Management Process
Vulnerability Management
The Omnissa Vulnerability Management program is based on industry best practices, including ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS. Vulnerability scans are performed at least monthly on internal and external systems. Risk analysis and acceptance are performed on vulnerabilities to confirm the vulnerability, and to determine the appropriate means of addressing the vulnerability. In alignment with PCI-DSS, system and application owners are required to address critical and high vulnerabilities with a plan of corrective action after vulnerability discovery. Rescans are used to verify the remediation of high-risk vulnerabilities. Other vulnerabilities are addressed with a plan of corrective action within a reasonable period.
12. Security Assessment
The Security Assessment control family of NIST SP 800-171 advises conducting periodic security assessments to determine the effectiveness of security controls and developing and implementing plans of action designed to correct deficiencies. NIST also recommends monitoring security controls on an ongoing basis to ensure the continued effectiveness of the controls.
The Omnissa Cloud Compliance Program
The role of the Omnissa Cloud Compliance team is to continuously monitor existing and emerging security standards and requirements and integrate applicable requirements into the Workspace ONE cloud service compliance programs. The Cloud Compliance team, along with embedded security personnel within each cloud service, performs gap assessments on new and existing compliance initiatives, engages with third-party auditors to perform annual compliance assessments, and tracks any non-conformities resulting from evaluations. Each Workspace ONE cloud service undergoes annual compliance assessments, including SOC audits.
Refer to the Omnissa Trust Center to see the latest list of industry certifications.
The Workspace ONE Continuous Monitoring Program
The Workspace ONE Commercial Cloud Continuous Monitoring Program is implemented in conjunction with the Omnissa Cloud compliance team’s efforts by creating ongoing security assessments around identified security standards and requirements. These activities are completed to help ensure each requirement remains effective and maintained throughout the year by each cloud service. Any risks identified during these activities are either remediated immediately or assessed for risk ranking and remediation planning within the Omnissa Risk Management Program.
13. Systems and Communication Protection
The Systems and Communication Protection family of controls provides recommendations for monitoring, controlling, and protecting communications at boundary components, including gateways, routers, firewalls, guards, network-based malicious code analysis and virtualization systems, or encrypted tunnels. It also discusses the use of subnets/demilitarized zones (DMZs), encryption in transit and at rest, and key management.
Omnissa Defense-in-Depth Approach
Combined with robust administrative controls and a strong Information Security Governance model, Workspace ONE cloud services have been architected with a Defense-in-Depth approach, including a series of defensive mechanisms such as:
- Public and private subnets, perimeter firewalls, network access control lists, and micro-segmentation
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and other security monitoring tools
- Antivirus and hardened Linux security configuration base images
- Identity and Access Management (IdAM) tools that enforce role-based access controls
- Encryption of Data-at-Rest and in-Transit
- Strong key management practices, including generation, storage, access, and destruction
- Secure software design practices such as secure coding techniques, threat modeling, and annual penetration testing
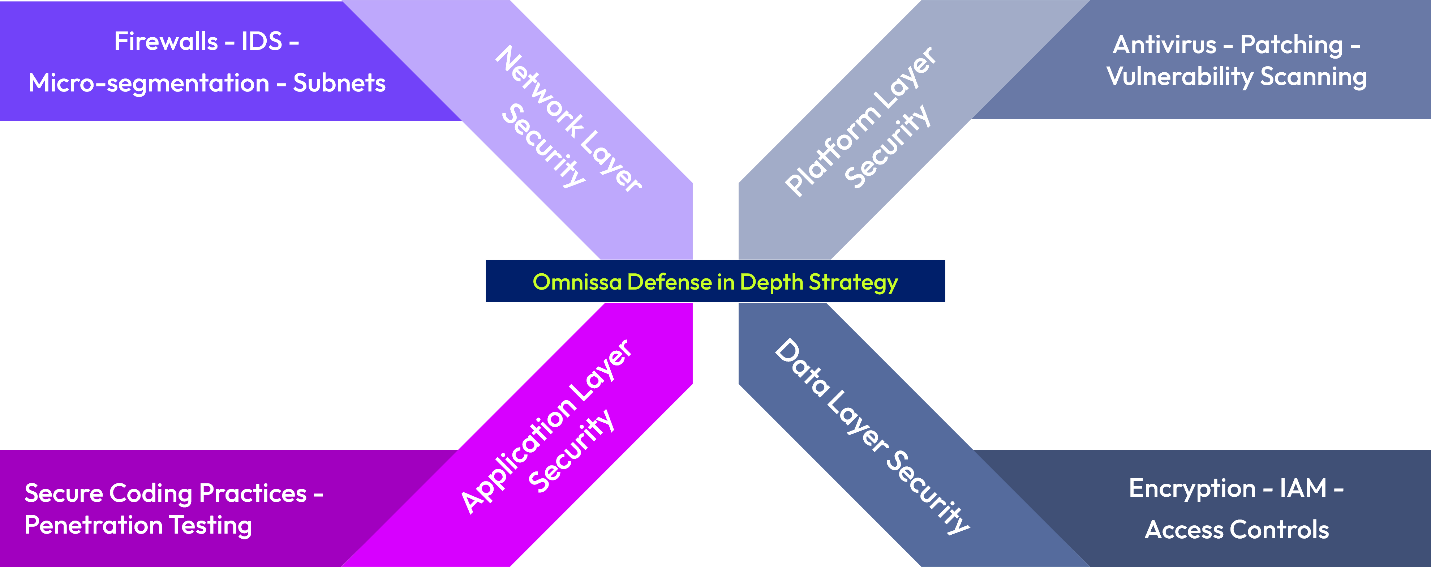
Figure 6: The Omnissa Defense in Depth Strategy
14. System and Information
In the System and Information control family, NIST SP 800-171 provides recommendations for protecting systems from malicious code and identifying unauthorized use of organizational systems.
Malicious Code Protection
Omnissa implements industry best practices for both administrative and technical controls to prevent, detect, and respond to viruses and malware, including ransomware. Social engineering topics (such as tailgating, badge access, and vishing) are also covered in our annual security training.
In alignment with PCI-DSS, Omnissa has deployed and centrally manages antivirus and endpoint protection on all employee workstations, which is configured to scan for updates to antivirus definitions and update clients continuously. Additionally, the software performs on-demand virus scans of any attachments or content introduced into the workstation. Systems settings prohibit end users from disabling endpoint protection software. All corporate-owned and personal devices are also enrolled in an Omnissa-managed instance of Workspace ONE UEM.
Intrusion, Detection, and Prevention
Omnissa deploys several mechanisms to detect intrusions and help protect against distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks in Workspace ONE cloud services. These mechanisms range from real-time IDS technologies, internal logs and tools, and external intelligence (OSINT) data sources. Omnissa monitors for security events involving the underlying infrastructure servers, storage, networks, information systems, and upstream providers used in service delivery. As part of our software development lifecycle (SDLC), Workspace ONE applications are also assessed against the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top Ten to identify potential application code to identify and remediate potential errors that could lead to unauthorized access and DDoS. In addition, Omnissa Access and Omnissa Intelligence use a web application firewall (WAF), which provides application layer protection against common web exploits.
Summary and additional resources
This document addresses the security for Workspace ONE cloud services in relation to the NIST SP 800-171 standards. For more information on NIST SP 800-171, see the NIST Special Publication 800-171 Revision 2.
Additional resources
For more information about Workspace ONE cloud services, you can explore the following resources:
Changelog
The following updates were made to this guide:
|
Date |
Description of Changes |
|
10/04/2024 |
|
About the author and contributors
The following people contributed their knowledge and assistance with this document:
- Andrea Smith, Sr. Program Manager, Customer Security Assurance.
- Andrew Osborn, Omnissa alumni.
Feedback
Your feedback is valuable.
To comment on this paper, contact Omnissa Technical Marketing at tech_content_feedback@omnissa.com.