Omnissa Cloud Services security alignment with DORA requirements
Introduction
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (Regulation (EU) 2022/2554) lays down uniform requirements concerning the security of network and information systems supporting the business processes of financial entities in the EU. These requirements cover five main operational areas for third-party service providers such as Omnissa:
- Risk management
- Incident reporting and response
- Operational resilience testing
- Information sharing of vulnerabilities
- Third-party risk management
This whitepaper outlines how current Omnissa security practices and procedures support the above requirements for Omnissa Workspace ONE® cloud services, Omnissa Platform Services, and Omnissa Horizon® Cloud Service.
Risk management
Omnissa maintains an ISMS framework to manage information security risks. Omnissa performs annual risk assessments as part of the Omnissa ISMS program to support security and compliance programs.
We have considered significant interactions between our company and relevant external parties and risks that could affect the company’s ability to provide reliable service to its user entities.
Risks identified during the risk assessment process are ranked and formally documented along with mitigation strategies. A formal process is documented to guide personnel when performing a risk assessment.
The framework security requirements have been designed and implemented to address industry standards around security and privacy. This effort requires the identification of applicable regulatory and contractual requirements, technical compliance with information security policies, protection of records, protection of information systems audit tools, and audit controls and reporting. Our risk management policy also requires Omnissa to adhere to the applicable legal, statutory, regulatory, or contractual obligations related to information security and security requirements.
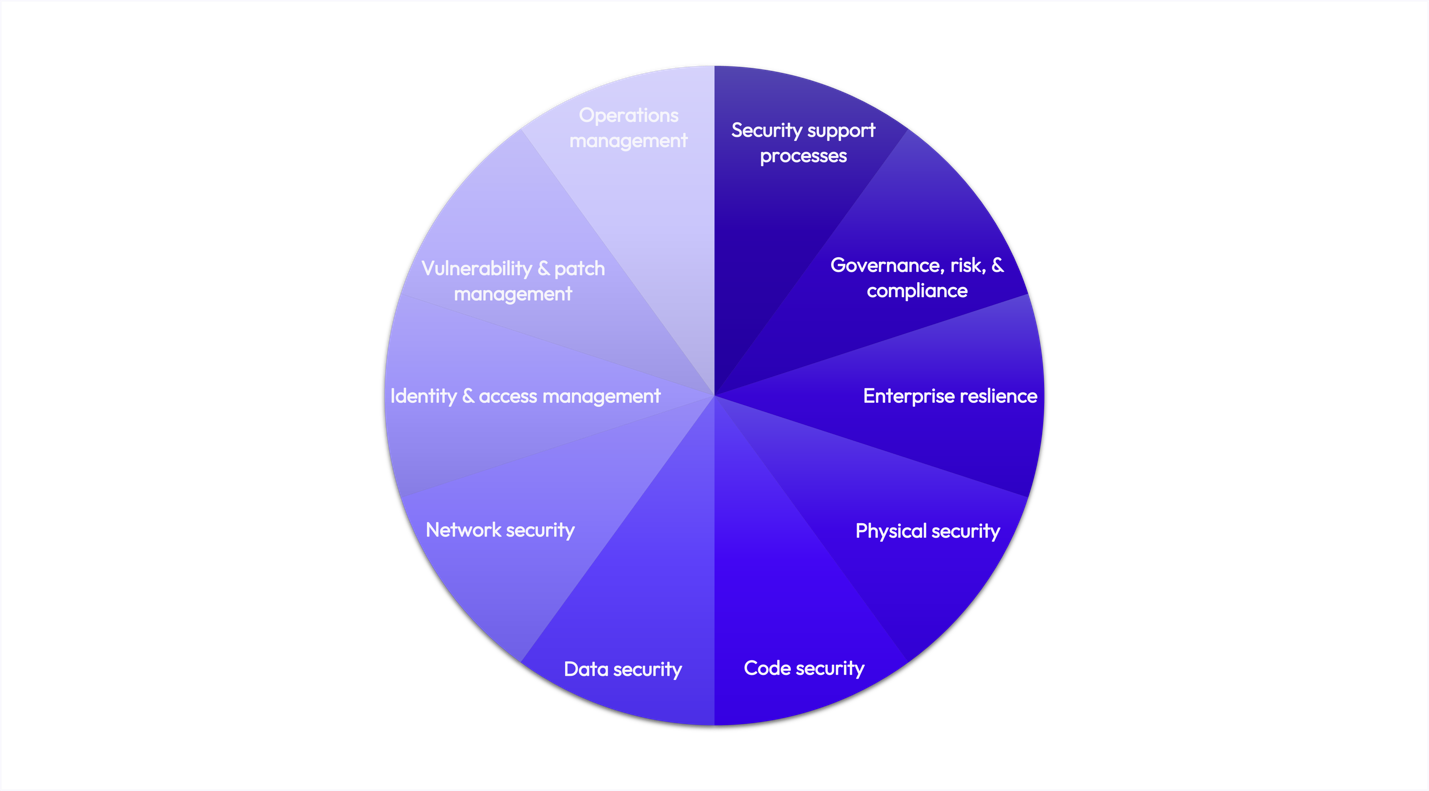
Figure 1: Omnissa comprehensive security framework
Incident reporting and response
Omnissa has a documented security incident management policy which is reviewed at least annually. Omnissa has an incident response program, plans, and procedures which are documented and implemented.
Omnissa maintains an incident response plan, which includes evidence preservation and customer notification processes. Omnissa provides incident and problem management services (for example, detection, severity classification, recording, escalation, and return to service) for the infrastructure over which Omnissa has direct, administrative access and control, including servers and services used to provide Omnissa cloud services. Customers are responsible for incident and problem management (for example, detection, severity, classification, recording, escalation, and return to service) for anything not under our direct control and administration such as on-premises cloud connectors.
The Omnissa Security Operations Center (SOC) uses log capture and SIEM tools, security monitoring technologies and intrusion detection tools in real-time to identify unauthorized access attempts, any behaviors that would indicate abnormal activity or by any Omnissa personal accessing customer data.
The Incident Management team is notified by the Security Operations Center of any potential breach and participates in any investigation. If Omnissa becomes aware of a security incident in Omnissa cloud services that leads to the unauthorized disclosure or access to personal information provided to Omnissa as a processor, we will notify customers without undue delay and will provide information relating to a data breach as reasonably requested by our customers. Omnissa will use reasonable endeavors to assist customers in mitigating, where possible, the adverse effects of any personal data breach.

Figure 2: Omnissa incident response cycle
Operational resilience testing
Omnissa has a defined Information Security Program that includes business continuity and disaster recovery strategies for data and hardware redundancy, network configuration redundancy and backups, and regular testing exercises. This program implements appropriate security controls to protect its employees and assets against natural and manmade disasters. Where applicable, Omnissa implements security mechanisms and redundancies to protect equipment from utility service outages. As a part of the program, an automated runbook system is engaged to help ensure policies and procedures are reviewed and made available to appropriate individuals. Additionally, these policies and procedures include defined roles and responsibilities supported by regular workforce training.
We follow frameworks that specify requirements to plan, establish, implement, operate, monitor, review, maintain and continually improve a documented management system to protect against, reduce the likelihood of occurrence, prepare for, respond to, and recover from disruptive incidents when they arise. Additionally, Omnissa follows information security standards in the context of a business continuity program. Omnissa is adequately prepared for a critical business disruption so that its people, processes, systems, facilities, and other assets can respond, recover, and resume operations safely and efficiently; and make sure that there is effective communication with stakeholders, thus minimizing financial, customer, brand, and operational impact to the company.
Omnissa has implemented backup and redundancy mechanisms to help ensure compliance with regulatory, statutory, and contractual obligations. The Omnissa business continuity plans and documentation are reviewed annually as part of the enterprise independent attestation in third-party compliance audits.
Redundancy of information processing & disaster recovery
Omnissa implements security mechanisms and redundancies to protect equipment from utility service outages. Omnissa facilitates the determination of the impact of any disruption to the organization through defined documents that identify dependencies, critical products, and services. The real-time status of Omnissa cloud services, along with past incidents, is publicly available at https://status.workspaceone.com/
Omnissa maintains the systems it uses to deliver our cloud services, including the application of patches deemed critical for the target systems. Our policy is to patch or upgrade network, utility, and security equipment after analyzing the severity and impact of potential vulnerabilities. Critical vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner, and changes are made using industry best practices. Testing is conducted by the quality engineering (QE) department to help ensure compatibility with the production environment. If required, rollback procedures are conducted by the QE team.
The specific methodology for achieving high availability and disaster recovery varies by Omnissa cloud service; however, in general, we use the principles of:
- Availability Zones
- Daily backups
- Annual disaster recovery exercises
Critical system components are backed up across multiple, isolated locations known as Availability Zones (AZs). Each AZ is engineered to operate independently with high reliability, and Availability Zones are connected easily architect applications that automatically fail-over between availability zones without interruption. Omnissa cloud services employ a highly redundant design with multiple best-in-class redundancy technologies combined with data replication strategies. The infrastructure is designed to help ensure that customers will typically not notice a disruption during a component or system failure inside a primary data center.
Omnissa continuously collects and monitors services operation logs using security information event management (SIEM) technologies. The 24x7x365 Omnissa SOC uses the SIEM to correlate information with public and private threat feeds to identify suspicious and unusual activities. The Omnissa SOC team takes reported security events and escalates to the Omnissa Security Incident Response Team for security incident management as appropriate based on defined criteria. Logs are stored separately and securely. Access to logs is monitored.
Information sharing of vulnerabilities
We understand that unless our products adhere to the utmost standards for security, customers will lack the confidence to use them. To achieve this, Omnissa maintains a program to identify, respond, and manage vulnerabilities.
Omnissa follows responsible vulnerability disclosure protocols, where researchers privately report newly identified vulnerabilities directly to us. This allows Omnissa to address the vulnerability in the impacted product and services before any party publicly discloses the vulnerability/exploit details. Omnissa may credit the researcher in alignment with responsible vulnerability disclosure guidelines for vulnerability discovery and reporting. Omnissa response timelines are dependent on several factors, such as severity, complexity, impact, and product lifecycle. Omnissa will make every effort to publish a fix or a corrective action to customers as follows:
- Critical – Begin work on a fix or a corrective action immediately and provide the fix to customers in the shortest commercially reasonable time.
- High – Deliver a fix in the next planned maintenance or update release of the product where relevant.
- Moderate, Low – Deliver a fix with the next planned release of the product.
Omnissa security advisories
Omnissa discloses vulnerabilities in Omnissa Security Advisories. OMSAs (Omnissa Security Advisories) will include:
- CVSS Scoring & Severity Rating
- Affected Products/Services
- Vulnerability Details
- Remediation Information
- Acknowledgements
- References
See the Omnissa Security Response page for examples of our disclosures.
Third-party risk management
With the global expansion of the software industry, security concerns have increased that a product or service could be compromised by malicious code introduced during product development or maintenance. Technological innovation and changes in sourcing and supply chain strategies have made software supply chain security a global challenge. Threats ranging from risks associated with using third-party code and open-source components to IP theft have dramatized the vulnerability of this new risk domain. Omnissa actively engages in proactive measures to minimize the occurrence of these risks and has several initiatives to address the security of our supply chain.
Managing supply chain risk
We use a Third-Party Risk Management Program that focuses on secure sourcing and software integration relating to building solutions. It includes the use of an approved vendor list and open-source software reviews prior to use. Each vendor Omnissa engages undergoes an extensive onboarding process that includes both security and privacy reviews. Supplier agreements require that providers comply with applicable laws, security, and privacy obligations.
Our R&D team includes specific resources responsible for testing, updating, and reviewing the open-source material used in the product. Management of third-party software in our products adheres to our secure development policy which includes open-source/third-party security scanning also known as software composition analysis (SCA).
Any software deemed “Security Critical” must be appropriately vetted, tested, and maintained. The respective development team incorporating third-party software in their product(s) and services is responsible for the support and fixing of defects and security vulnerabilities, whether they get such support from a vendor contract, or perform this function themselves.
Third-party vendor agreements
We have an established third-party IT risk management policy. The policy applies to our management and oversight of third parties (vendors/suppliers) accessing or processing company data facilities, information, and/or information systems. It defines the requirements for assessments to be performed as part of negotiating and reviewing third-party agreements in line with our information security objectives and ongoing monitoring of such third parties for compliance.
Sourcing and business teams collaborate with the information security risk team to assure a risk-based approach is taken with respect to third parties to safeguard the security of information assets. Omnissa also maintains a list of third-party vendors and has a defined procurement process for vendors and contractors that involve multiple levels of due diligence and approvals to affirm that any vendors are selected in line with purpose and desired scope.
We evaluate the service risk based on the type of service and type of data hosted by the supplier and implement appropriate processes to address specific risks. Omnissa also maintains a data processing addendum that covers the requirements for managing and processing personal data in line with applicable data processing regulations.
Summary and additional resources
Introduction
Workspace ONE has undergone independent third-party audits on a regular basis to provide assurance to our customers that Omnissa has implemented industry leading controls. Information contained in this document is solely for the use of evaluating Omnissa security controls and does not represent an official compliance with DORA.
Additional resources
For more information about our cloud services, you can explore the following resources:
- Workspace ONE Cloud Services Security whitepaper
- Horizon Cloud Service Next-Gen Cloud Security Whitepaper
Changelog
The following updates were made to this guide:
| Date | Description of Changes |
| 11 February 2025 | Document published. |
About the author and contributors
The following people contributed their knowledge and assistance with this document:
- Andrea Smith, Sr. Program Manager, Customer Security Assurance
Feedback
Your feedback is valuable.
To comment on this paper, contact Omnissa Technical Marketing at tech_content_feedback@omnissa.com.