Omnissa Cloud Services alignment with the NIS 2 directive
Introduction
The NIS 2 Directive (Directive (EU) 2022/2555) is a legislative act that aims to achieve a high common level of cybersecurity across the European Union.
Member States must ensure that essential and important entities take appropriate and proportionate technical, operational, and organizational measures to manage the risks posed to the security of network and information systems, and to prevent or minimize the impact of incidents on recipients of their services and on other services. The measures must be based on an all-hazards approach.
Purpose
While Omnissa cloud services are yet to undergo formal gap assessment for NIS 2, this whitepaper intends to show the controls and processes our cloud services have in place to address the control requirements in the NIS 2 Directive. For a full listing of our current certifications, see the Omnissa Trust Center.
Audience
This document is intended for Omnissa commercial cloud administrators and our customers’ information security organizations. It assumes at least intermediate knowledge of Omnissa cloud services and focuses on the policies, processes, and controls supporting the cloud-delivered services. Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP), on-premises, and third-party offerings are not in scope for this document.
Note: You can find the definitions for acronyms used in this document in Acronyms used in the Workspace ONE Security Series.
Structure of the NIS 2 Directive (Directive (EU) 2022/2555) Requirements
A general summary of the directive includes the requirements to:
- Implement required security technical and organizational measures to prevent risks and manage the security of the network and information systems, and
- Notify relevant national authorities of serious incidents.
The graphic below shows the 10 key control areas prescribed in the NIS 2 Directive Article 21: Cybersecurity risk management measures.1
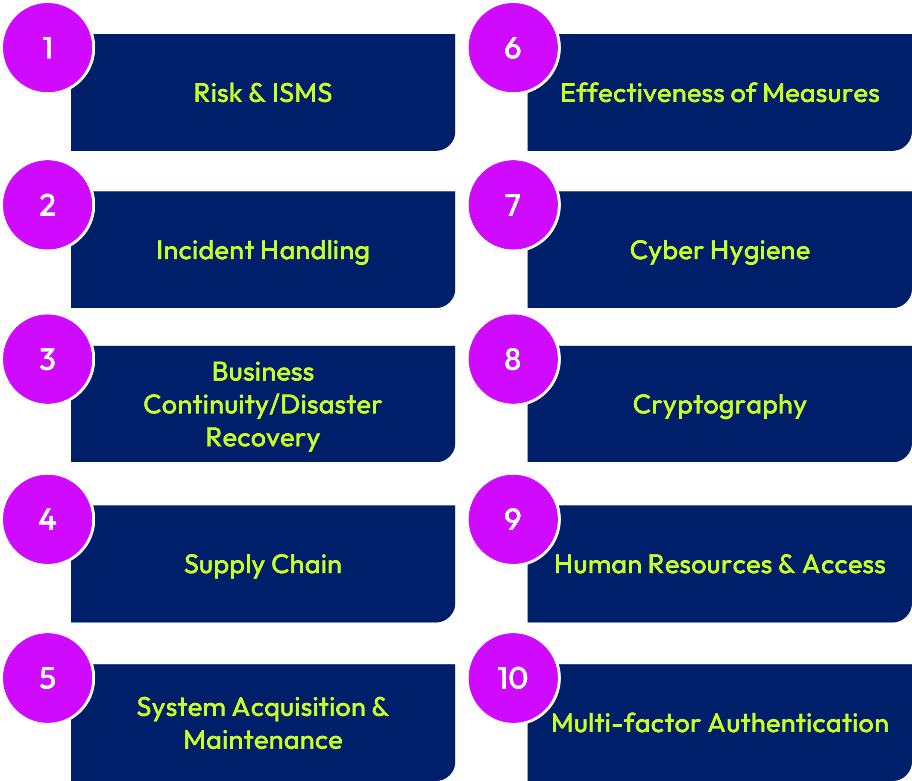
Figure 1: The NIS 2 Directive Cybersecurity Risk Management Measures
Source: NIS 2 Directive, Article 21: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32022L2555#d1e3337-80-1
In this whitepaper, we will discuss how the Omnissa cloud services information security programs support these 10 control areas, as well as Article 20: Governance.
Omnissa Cloud Service Alignment with the NIS 2 Directive Requirements
The following sections provide a general overview of how Omnissa cloud security controls are aligned with the NIS 2 Directive control area objectives and the applicable ISO 27001 reference mapping.
Governance
Table 1: NIS 2 Area - Governance
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 20 | Governance | A.5.1 Policies for information security A.5.2 Information security roles and responsibilities A.5.3 Segregation of duties A.5.4 Management responsibilities A.5.5 Contact with authorities A.5.6 Contact with special interest groups A.5.31 Legal, statutory, regulatory and contractual requirements A.5.34 Privacy and protection of personally identifiable information (PII) A.5.35 Independent review of information security A.5.36 Compliance with policies, rules and standards for information security 7.3 Awareness 7.4 Communication 7.5 Documented information A.6.3 Information security awareness, education and training |
Omnissa Governance of ISMS
Omnissa cloud services have established an Information Security Management System (ISMS) based on ISO 27001 standards to manage risks relating to confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. Internal and external audits are performed annually under the Omnissa information security management system (ISMS) program. Omnissa has established information security policies in line with the ISO 27001 framework. The policies are published on the intranet, and the name of the person responsible for the policy is shown. Policies are reviewed at least annually.
Teams responsible for governance, risk and compliance include Information Security, Data Center Operations, Compliance, Change Management Board, Vulnerability Management, Incident Response Team, senior management, and more. All access privileges are enforced using role-based access control, separation of duties, and the principle of least privileges. Omnissa has a dedicated Security, Governance, Risk and Compliance team that oversees risk management and compliance across the organization. Where needed, the team liaises with relevant regulatory authority to address specific regulatory concerns.
Omnissa has organizational charts in place to communicate the defined key areas of authority, responsibility, and lines of reporting to personnel related to the design, development, implementation, operation, maintenance, and monitoring of the system. These charts are communicated to employees via the company intranet and updated as needed.
Information Security Program Documentation
Omnissa has documented policies, standards, and system and network diagrams supporting Omnissa cloud services. Omnissa documents, updates, and maintains baseline configurations for software and hardware installed in the production environment; changes are governed by a defined change management policy and baseline configurations are securely managed. Security baselines are documented to guide personnel to help ensure appropriate configurations are in place to protect sensitive information.
Omnissa uses various internal tools for communication of our security policies. These policies are published on the intranet, version controlled, reviewed, and updated on an annual basis. Managers are responsible for addressing known compliance issues with information security policies. Compliance issues are corrected, and if a compliance issue cannot be corrected, then managers must seek approval for an Information Security policy exception.
Employee Training and Communication
In alignment with the ISO 27001 standard, all Omnissa personnel are required to complete annual business conduct and security awareness training. Personnel with access to cloud production environments receive additional training as they assume job roles and responsibilities. Omnissa periodically validates that those employees understand and follow the established policies through compliance audits.
Omnissa uses an enterprise Learning Management System (LMS) to deliver required onboarding and annual security awareness training. The LMS records successful completion, and reports are reviewed during ISMS review meetings. This training must be completed before authorizing access to production systems.
Awareness training topics include, but are not limited to:
- Secure system configuration
- User account management policies
- Environmental control implementation and operation procedures
- Incident Response plans and procedures
- Disaster Recovery plans and procedures
- Physical Security controls
Policies on Risk Analysis and Information System Security
Table 2: NIS 2 Directive Area - Policies on risk analysis and information system security
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (a) | Policies on risk analysis and information system security. | 4.4 Information security management system 5.2 Information security policy 6.1.2 Information security risk assessment 6.1.3 Information security risk treatment 8.2 Information security risk assessment 8.3 Information security risk treatment A.5.1 Policies for information security |
The Omnissa Risk Management Framework
Omnissa maintains an ISMS framework to manage information security risks. Omnissa performs annual risk assessments as part of the Omnissa ISMS program to support security and compliance programs.
We have considered significant interactions between our company and relevant external parties and risks that could affect the company’s ability to provide reliable service to its user entities.
Risks identified during the risk assessment process are ranked and formally documented, along with mitigation strategies. A formal process is documented to guide personnel when performing a risk assessment.
The framework security requirements have been designed and implemented to address industry standards around security and privacy. This effort requires the identification of applicable regulatory and contractual requirements, technical compliance with information security policies, protection of records, protection of information systems audit tools, and audit controls and reporting. This policy also requires Omnissa to adhere to the applicable legal, statutory, regulatory, or contractual obligations related to information security and security requirements.
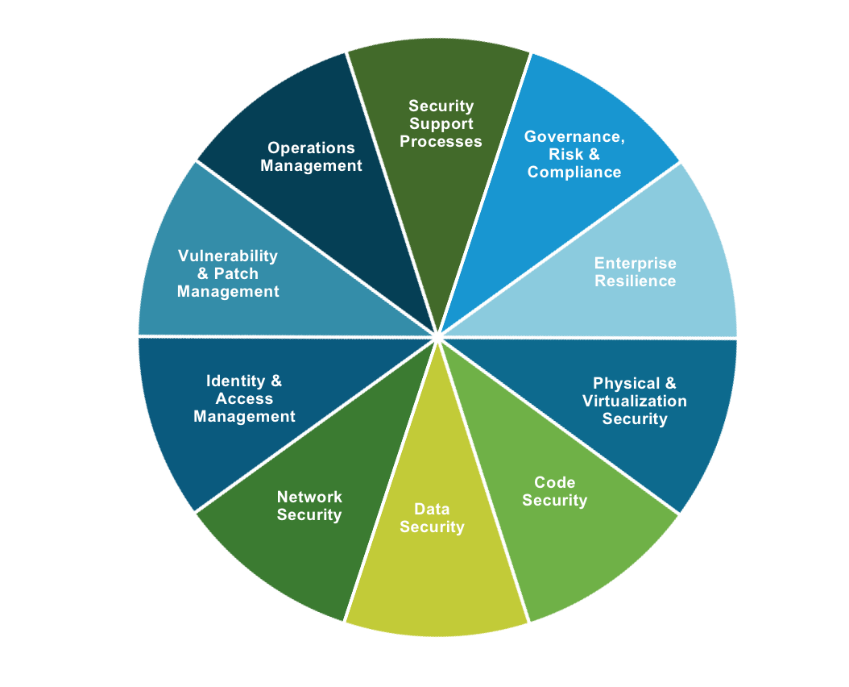
Figure 2: Comprehensive Security Framework
Incident Handling
Table 3: NIS 2 Directive Area - Incident Handling
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (b) | Incident handling | A.5.7 Threat intelligence A.5.24 Information security incident management planning and preparation A.5.25 Assessment and decision on information security events A.5.26 Response to information security incidents A.5.27 Learning from information security incidents A.5.28 Collection of evidence A.6.8 Information security event reporting A.8.16 Monitoring activities |
The Omnissa Incident Response Program
Omnissa has a documented security incident management policy, which is reviewed at least annually. Omnissa has an incident response program, plans, and procedures, which are documented and implemented.
Omnissa maintains an incident response plan, which includes evidence preservation and customer notification processes. Omnissa provides incident and problem management services (for example, detection, severity classification, recording, escalation, and return to service) for the infrastructure over which Omnissa has direct administrative access and control, including servers and services used to provide Omnissa cloud services. Customers are responsible for incident and problem management (for example, detection, severity, classification, recording, escalation, and return to service) for anything not under our direct control and administration, such as on-premises cloud connectors.
The Omnissa Security Operations Center (SOC) uses log capture and SIEM tools, security monitoring technologies, and intrusion detection tools in real-time to identify unauthorized access attempts, and any behaviors that would indicate abnormal activity or by any Omnissa personnel accessing customer data.
The Incident Management team is notified by the Security Operations Center of any potential breach and participates in any investigation. If Omnissa becomes aware of a security incident in Omnissa cloud services that leads to the unauthorized disclosure or access to personal information provided to Omnissa as a processor, we will notify customers without undue delay and will provide information relating to a data breach as reasonably requested by our customers. Omnissa will use reasonable endeavors to assist customers in mitigating, where possible, the adverse effects of any personal data breach.

Figure 3: Omnissa Incident Response Cycle
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Table 4: NIS 2 Directive Area - Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (c) | Business continuity, such as backup management and disaster recovery, and crisis management. | A5.29 Information security during disruption A.5.30 ICT readiness for business continuity A.8.13 Information Backup A.8.14 Redundancy of information processing facilities A.8.15 Logging A.8.16 Monitoring Activities |
An Overview of Our Resiliency Program
Omnissa has a defined Information Security Program that includes Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery strategies for data and hardware redundancy, network configuration redundancy and backups, and regular testing exercises. This program implements appropriate security controls to protect its employees and assets against natural and manmade disasters. Where applicable, Omnissa implements security mechanisms and redundancies to protect equipment from utility service outages.
As a part of the program, an automated runbook system is engaged to help ensure policies and procedures are reviewed and made available to appropriate individuals. Additionally, these policies and procedures include defined roles and responsibilities supported by regular workforce training.
We follow frameworks that specify requirements to plan, establish, implement, operate, monitor, review, maintain, and continually improve a documented management system to protect against, reduce the likelihood of occurrence, prepare for, respond to, and recover from disruptive incidents when they arise. Additionally, Omnissa follows information security standards in the context of a business continuity program.
Omnissa is adequately prepared for a critical business disruption so that its people, processes, systems, facilities, and other assets can respond, recover, and resume operations safely and efficiently and make sure that there is effective communication with stakeholders, thus minimizing financial, customer, brand, and operational impact to the company.
Omnissa has implemented backup and redundancy mechanisms to help ensure compliance with regulatory, statutory, and contractual obligations. The Omnissa business continuity plans and documentation are reviewed annually as part of the enterprise independent attestation in third-party compliance audits.
Redundancy of Information Processing & Disaster Recovery
Omnissa implements security mechanisms and redundancies to protect equipment from utility service outages. Omnissa facilitates the determination of the impact of any disruption to the organization through defined documents that identify dependencies, critical products, and services. The real-time status of the Omnissa cloud services, along with past incidents, is publicly available at https://status.workspaceone.com/
Omnissa maintains the systems it uses to deliver Omnissa services, including the application of patches deemed critical for the target systems. Our policy is to patch or upgrade network, utility, and security equipment after analyzing the severity and impact of potential vulnerabilities. Critical vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner, and changes are made using industry best practices. Testing is conducted by the QE department to help ensure compatibility with the production environment. If required, rollback procedures are conducted by the QE team.
The specific methodology for achieving high availability and disaster recovery varies by Omnissa service; however, in general, we use the principles of:
- Availability Zones
- Daily backups
- Annual disaster recovery exercises
Critical system components are backed up across multiple, isolated locations known as Availability Zones (AZs). Each AZ is engineered to operate independently with high reliability, and Availability Zones are connected easily architect applications that automatically fail-over between availability zones without interruption. Omnissa cloud services employ a highly redundant design with multiple best-in-class redundancy technologies combined with data replication strategies. The hosted infrastructure is designed to help ensure that customers will typically not notice a disruption during a component or system failure inside a primary data center.
Omnissa continuously collects and monitors services operation logs using security information event management (SIEM) technologies. The 24x7x365 Omnissa Security Operations Center uses the SIEM to correlate information with public and private threat feeds to identify suspicious and unusual activities. The Omnissa Security Operations Center (SOC) team takes reported security events and escalates to the Omnissa Security Incident Response Team for security incident management as appropriate based on defined criteria. Logs are stored separately and securely. Access to logs is monitored.
Supply Chain Security
Table 5: NIS 2 Directive Area - Supply Chain Security
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (d) | Supply chain security, including security-related aspects concerning the relationships between each entity and its direct suppliers or service providers. | A.5.19 Information security in supplier relationships A.5.20 Addressing information security within supplier agreements A.5.21 Managing information security in the information and communication technology (ICT) supply chain A.5.22 Monitoring, review and change management of supplier services A.5.23 Information security for use of cloud services |
Our Vendor Risk Management Program
With the global expansion of the software industry, security concerns have increased that a product or service could be compromised by malicious code introduced during product development or maintenance. Technological innovation and changes in sourcing and supply chain strategies have made software supply chain security a global challenge.
Threats ranging from risks associated with using third-party code and open-source components to IP theft have dramatized the vulnerability of this new risk domain. Omnissa actively engages in proactive measures to minimize the occurrence of these risks and has several initiatives to address the security of our supply chain.
Managing Supply Chain Risk
We use a Third-Party Risk Management program that focuses on secure sourcing and software integration relating to building solutions. It includes the use of an approved vendor list and open-source software reviews prior to use. Each vendor Omnissa engages undergoes an extensive onboarding process that includes both security and privacy reviews. Supplier agreements require that providers comply with applicable laws, security, and privacy obligations.
Our R&D team includes specific resources responsible for testing, updating, and reviewing the open-source material used in the product. Management of third-party software in our products adheres to our Secure Development Policy which includes Open-Source/Third-Party Security Scanning also known as Software Composition Analysis (SCA).
Any software deemed “Security Critical” must be appropriately vetted, tested, and maintained. The respective development team incorporating third-party software in their product(s) and services is responsible for the support and fixing of defects and security vulnerabilities, whether they get such support from a vendor contract, or perform this function themselves.
Network and Information System Acquisition & Maintenance
Table 6: NIS 2 Directive Area - System Acquisition & Maintenance
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (e) | Security in network and information systems acquisition, development, and maintenance, including vulnerability handling and disclosure; | A.5.20 Addressing information security within supplier agreements A.5.24 Information security incident management planning and preparation A.5.37 Documented operating procedures A.6.8 Information security event reporting A.8.9 Configuration management A.8.19 Installation of software on operational systems A.8.20 Networks security A.8.21 Security of network services A.5.7 Threat intelligence A.6.8 Information security event reporting A.8.7 Protection against malware A.8.8 Management of technical vulnerabilities |
Third-Party Vendor Agreements
We have an established Third-Party IT Risk Management policy. The policy applies to our management and oversight of third parties (vendors/suppliers) accessing or processing company data facilities, information, and/or information systems. It defines the requirements for assessments to be performed as part of negotiating and reviewing third-party agreements in line with our information security objectives and ongoing monitoring of such third parties for compliance.
Sourcing and business teams collaborate with the information security risk team to assure a risk-based approach is taken with respect to third parties to safeguard the security of information assets. Omnissa also maintains a list of third-party vendors and has a defined procurement process for vendors and contractors that involve multiple levels of due diligence and approvals to affirm that any vendors are selected in line with purpose and desired scope.
We evaluate the service risk based on the type of service and type of data hosted by the supplier and implement appropriate processes to address specific risks. Omnissa also maintains a data processing addendum that covers the requirements for managing and processing personal data in line with applicable data processing regulations.
Cloud Environment Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
Our Cloud Operations is staffed 7x24x365, and the team deploys several commercial and custom purpose-built tools to monitor the performance and availability of all hosted solution components. Components include the underlying infrastructure servers, storage, networks, portals, services, and information systems used in the delivery of Omnissa services.
We deploy several mechanisms to detect intrusions and help protect against distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. These mechanisms range from real-time Intrusion Detection System (IDS) technologies, internal logs and tools, and external intelligence (OSINT) data sources. Omnissa monitors for security events involving the underlying infrastructure servers, storage, networks, information systems, and upstream providers used in service delivery.
Omnissa applications are also assessed against the ‘OWASP Top Ten’ to identify potential application codes and identify/remediate potential errors that could lead to unauthorized access or a DDoS. In alignment with PCI-DSS, Omnissa services use file integrity monitoring to detect malicious behavior or changes in system files or libraries. In addition, all Omnissa cloud services either use a web application firewall (WAF) or use compensating controls which provide application-layer protection against common web exploits.
Configuration Management & System Hardening
We maintain a detailed Configuration Management policy based on industry best practices to harden the cloud environment; revisions and exceptions to the Configuration Management policy are processed through the Change Management policy to help ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of our hosted offering.
Baseline configuration standards include, but are not limited to:
- Deactivating unnecessary ports, services, protocols, and physical connections
- Reviewing server builds for gaps prior to image configuration
- Hardening server configurations
Baseline configurations are documented for all software installed in the production environment. Baseline configurations include the following information about system components:
- Standard software packages installed on servers and network components
- Current version numbers and patch information on operating systems and applications
- Logical placement of all components within the system architecture
We deactivate unnecessary ports, protocols, and services as part of baseline hardening standards, and we follow industry best practices in applying secure configurations to managed servers.
For Omnissa cloud servers that use Windows operating systems, the team hardens server configurations using Group Policy Object (GPO) policies (such as account policies, user rights, security options, event log settings, app restrictions). Omnissa cloud servers using Linux use Amazon Linux 2/Azure Linux images for system hardening. These images include default security configurations, such as limited remote access using SSH key pairs, remote root login deactivation, reduced non-critical package installation, and automatic security-related updates.
Protection Against Malware
We implement industry best practices for both administrative and technical controls to prevent, detect, and respond to viruses and malware, including ransomware. As part of our annual security training programs, Omnissa operates a Phishing Prevention Program to help train our employees to recognize threats. Social engineering topics (such as tailgating, badge access, and vishing) are also covered in our annual security training. As our employees moved to a remote work model during the global pandemic, Omnissa created a Working from Home security guide that covers topics such as mobile device security, securing home Wi-Fi, phone and email scams, and securing homes for natural disasters.
In alignment with PCI-DSS, Omnissa has deployed and centrally manages Anti-Virus and endpoint protection on all employee workstations, which is configured to scan for updates to Anti-Virus definitions and update clients continuously. Additionally, the software performs on-demand virus scans of any attachments or content introduced into the workstation. Systems settings prohibit end users from deactivating endpoint protection software. All corporate-owned and personal devices are also enrolled in an Omnissa-managed instance of Workspace ONE UEM. Note that employees are prohibited from accessing Omnissa production environments using personal devices.
Our cloud services also implement strong technical controls, including encrypted backups, network segmentation, firewalls, and access control lists (ACLs) for mitigation, and containment from potential attacks, as well as to remediate from active attacks. For systems commonly susceptible to malicious attacks, such as Windows OS, we deploy enterprise-grade Anti-Virus software, which is automatically patched, and signature updated with logging enabled; files are scanned on access. Other production systems that are Linux-based and are hardened using Amazon Linux/Azure Linux to secure images.
Our Vulnerability Management Program
We have a Vulnerability Management program backed by approved and tested policies and procedures. Vulnerability scans are performed regularly on our developed products and cloud services.
System and application owners must address critical and high vulnerabilities with a corrective action plan. The vulnerability severity drives the level of responsiveness requirements. Risk analysis and acceptance tests are performed on vulnerabilities to confirm the vulnerability and to determine the appropriate means of addressing the vulnerability.
Effectiveness of Cybersecurity Risk Management Procedures
Table 7: NIS 2 Area - Effectiveness of Cybersecurity Risk Management Procedures
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (f) | Policies and procedures to assess the effectiveness of cybersecurity risk-management measures. | 9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation 9.2 Internal audit 9.3 Management review A.5.35 Independent review of information security A.5.36 Compliance with policies, rules and standards for information security |
Omnissa has a compliance program in place that is designed after several industry standards and frameworks including ISO 27001 and SOC 2. We regularly conduct internal and external audits that include results from security and compliance assessments. The program utilizes internal/external audits to measure the effectiveness of the controls applied to reduce risks associated with safeguarding information and to identify areas of improvement.
Security is of the utmost importance to us. Our programs are continually evolving based on our own experiences, changes in the threat landscape, and our learnings based on industry observation and collaboration. For more information about Omnissa Compliance initiatives and Security programs, visit the Omnissa Trust Center.
Cybersecurity Hygiene & Training
Table 8: NIS 2 Directive Area - Cybersecurity Hygiene & Training
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (g) | Basic cyber hygiene practices and cybersecurity training. | 7.3 Awareness 7.4 Communication A.5.15 Access Control A.5.16 Identity Management A.5.18 Access Rights A.5.24 Information security incident management planning and preparation A.6.3 Information security awareness, education and training A.6.5 Responsibilities after termination or change of employment A.6.8 Information security event reporting A.8.2 Privileged access rights A.8.3 Information access restriction A.8.5 Secure authentication A.8.7 Protection against malware A.8.9 Configuration management A.8.13 Information Backup A.8.15 Logging A.8.19 Installation of software on operational systems A.8.22 Segregation of networks |
Our Overall Cybersecurity Posture
The confidentiality, availability, and integrity of our customers’ data is of the utmost importance to our team, and we achieve integrity in our cloud environments through a combination of the security controls and procedures, including:
- Limited and controlled access to the production environments
- Change management
- Configuration management
- Incident and problem management
- Source Control and management
- Encryption controls
- Employee Training
- Human Resource Policies
We also use NIST 800-53 and ISO 27001 guidelines to benchmark our security program. We designed our security architecture using a defense-in-depth approach to implement multiple layers of security throughout the SaaS environment and to mitigate any potential attacks through multiple safeguards, including:
Access control mechanisms, firewalls, anti-virus/malware software, auditing mechanisms, network controls, deactivation of unnecessary services, and maintaining defined configuration settings.
Cryptography & Key Management
Table 9: Cryptography & Key Management
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (h) | Policies and procedures regarding the use of cryptography and, where appropriate, encryption. | A.8.20 Network security A.8.21 Security of network services A.8.22 Segregation of networks A.8.24 Use of cryptography |
Our Cryptographic Controls
Omnissa has an encryption policy that provides guidelines on the use of cryptographic controls and key management. The policy is reviewed on an annual basis. Cryptographic keys for Workspace ONE UEM and Workspace ONE Assist are stored securely on protected servers (such as access controls and encryption). For Omnissa Access and Omnissa Intelligence, the service uses the AWS Key Management Service (KMS) key generated and stored by KMS. For Horizon, the service uses Microsoft Azure Key Vault. Keys are managed in alignment with PCI-DSS.
Omnissa services do not support the use of customer-managed keys in the hosted environment. As part of the shared responsibility model, customers can manage their own encryption keys for on-premises hosted resources, such as establishing and managing certificates for any on-premises integration connectors.
Network Security
We provide 24/7 monitoring for Omnissa cloud environments, and we closely monitor network performance in addition to network security perimeter controls.
All access is technically enforced, logged, and monitored; access to the production environment requires a secure connection (VPN, SSH, and so on.). Firewalls are configured to deny-all settings to prevent intrusion into our production and corporate environments. Additionally, Omnissa deploys anti-virus/malware suites on servers commonly impacted by malware in our production environment that operate independently of our redundant firewalls. Networks are separated into tiers, and micro-segmentation is used (where applicable) to protect against unauthorized access.
We have full auditing capabilities on all environments to enable the reconstruction of security incidents and events (such as syslog, firewall logs, alerting tools, access control lists) and deploy several mechanisms to detect intrusions and help protect against distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks.
These mechanisms range from real-time firewalls, Intrusion Detection System (IDS) technologies, internal logs and tools, and external intelligence (OSINT) data sources. Omnissa monitors for security events involving the underlying infrastructure servers, storage, networks, information systems, and upstream providers used in service delivery.
Human Resources, Access Controls & Asset Management
Table 10: Human Resources, Access Controls & Asset Management
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (i) | Human resources security, access control policies and asset management. | A.5.9 Inventory of information and other associated assets A.5.10 Acceptable use of information and other associated assets A.5.11 Return of assets A.5.15 Access Control A.5.16 Identity Management A.5.17 Authentication information A.5.18 Access Rights A.5.33 Protection of records A.6.1 Screening A.6.2 Terms and conditions of employment A.6.4 Disciplinary process A.6.5 Responsibilities after termination or change of employment A.6.6 Confidentiality or non-disclosure agreements A.6.7 Remote working A.5.12 Classification of information A.5.13 Labelling of information A.5.14 Information transfer A.5.15 Access control A.5.16 Identity management A.5.17 Authentication information A.5.18 Access rights A.8.01 User end point devices A.8.02 Privileged access rights A.8.03 Information access restriction |
Human Resources Security
In alignment with the ISO 27001 standard, our personnel are required to complete annual security awareness training. Personnel supporting Omnissa managed services receive additional role-based security training to perform their job functions in a secure manner. Compliance audits are periodically performed to validate that employees understand and follow the established policies. Formal procedures are in place for granting and revocation access for employees, and these procedures are validated by external auditors as part of compliance audits.
Omnissa has also documented terms and conditions for maintaining confidentiality as part of the Omnissa Terms of Service and Data Processing Addendum. Abuse of policies may result in disciplinary action, including possible termination, and civil and/or criminal liability. Employees are made aware of their responsibilities for these terms and conditions at the time of employment and through annual training.
Access Controls, Identity Management & Secure Authentication
Omnissa has established an authentication and password policy that outlines the password requirements for our information assets, such as minimum password configurations, password restrictions, secure logon procedures, criteria for strong passwords, and password administration.
Access privileges to Omnissa cloud-hosted systems are controlled based on the principle of least privilege – only the minimum level of access required shall be granted. Access is based on an individual’s “need to know” as determined by job functions and requirements. Managing access to information systems is implemented and controlled through centralized identity stores and directory services.
A quarterly review is performed to help ensure service access is still appropriate. Controls are in place confirming the timely removal of systems access that is no longer required for business purposes. Entitlement actions are recorded via the systems used to grant/revoke access and provide evidence to support compliance programs.
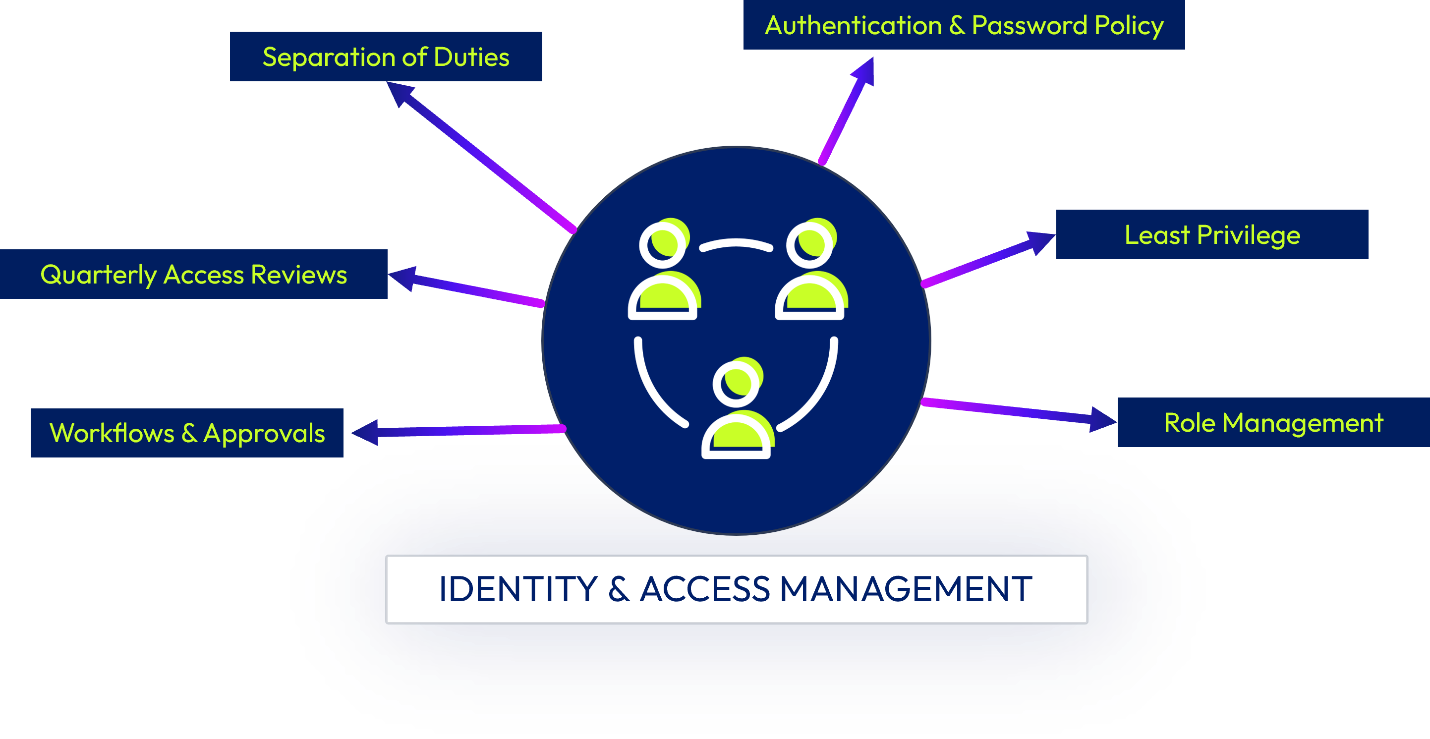
Figure 4: Identity & Access Management
Asset Management & Acceptable Use
Omnissa has an established Asset Management policy that outlines the management of assets, including creation, processing, storage, transmission, deletion, and destruction. Omnissa maintains inventories of critical assets, including asset ownership and location.
We also maintain an acceptable use policy that dictates employee responsibility toward protecting and managing the company’s assets. Our Corporate Human Resources has an established policy for employee termination processes and provides procedures for management to help ensure that company-owned assets are returned within the specified timeframe.
Multifactor Authentication
Table 11: NIS 2 Directive Area - Multifactor Authentication
No. | Area | Applicable ISO Reference |
Article 21 (j) | The use of multi-factor authentication or continuous authentication solutions, secured voice, video and text communications and secured emergency communication systems within the entity, where appropriate. | A.5.14 Information transfer A.5.16 Identity management A.5.17 Authentication information A.8.01 User end point devices A.8.24 Use of cryptography |
Secure Communications Protocols
Omnissa is a multi-tenant cloud service. Service systems are accessed for maintenance and support purposes only. Omnissa does not request prior approvals to access service systems. Access privileges are enforced using role-based access control, separation of duties, and the principle of least privileges. Production environment access is secured through a combination of VPN, IP address allow-listing or jump servers using Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) and directory credentials.
In accordance with ISO 27001 and PCI-DSS, access is restricted to authorized members of applicable teams, and system sessions are set to an idle timeout of 15 minutes. Logs are in place to review support staff access to all systems and environments. Quarterly User Access Reviews are conducted to review privileged access and to remove or deactivate accounts with 90 days of inactivity.
Each service within the Omnissa platform leverages encryption to help protect data both in transit and at rest. Workspace ONE UEM, Omnissa Access, Omnissa Intelligence, and Horizon collect varying data points intended to achieve different outcomes in the delivery of the service. Due to these differences in functionality, the specific encryption approach varies to align with the intended function of each service. See the Workspace ONE Cloud Security Whitepaper and the Horizon Cloud Service Next-Gen Whitepaper for details.
Summary and Additional Resources
Omnissa undergoes independent third-party audits regularly to assure our customers that Omnissa has implemented industry-leading controls. Information contained in this document is solely for the use of evaluating Omnissa security controls against the NIS 2 Directive and does not represent an official endorsement or attestation.
Additional Resources
For more information about Omnissa cloud services, you can explore the following resources:
- Workspace ONE Cloud Services Security whitepaper
- Horizon Cloud Service Next-Gen Security whitepaper
- Unofficial NIS 2 to ISO mapping tool
Changelog
The following updates were made to this guide:
| Date | Description of Changes |
| 12/13/2024 |
|
| 11/21/2024 |
|
| 10/02/2024 |
|
About the Author and Contributors
The following people contributed their knowledge and assistance with this document:
- Andrea Smith, Sr. Program Manager, Customer Security Assurance.
- Andrew Osborn, Omnissa alumni.
Feedback
Your feedback is valuable.
To comment on this paper, contact Omnissa Technical Marketing at tech_content_feedback@omnissa.com.