Horizon Cloud Service next-gen alignment with the ACSC ISM
Introduction
This document addresses the security for Omnissa Horizon® Cloud Next-Gen in relation to the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) Information Security Manual (ISM). The purpose of the ISM is to outline a cyber security framework that organizations can apply, using their risk management framework, to protect their information and systems from cyber threats.
Purpose
This whitepaper summarizes the Omnissa information security program alignment with the Cyber Security Principles and Cyber Security Guidelines within the ISM.
Note: You can find the definitions for acronyms used throughout this document in: Acronyms used in the Workspace ONE Security Series.
Audience
This document is intended for Australian government commercial cloud customers to evaluate Horizon Cloud Next-Gen security and any potential risks against the ACSC ISM. It assumes at least intermediate knowledge of Horizon Cloud Next-Gen, and focuses on the policies, processes, and controls supporting the cloud-delivered services. Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP), on-premises, and third-party offerings are not in-scope for this document.
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen Security Compliance
For the most up-to-date list of product audits and certifications, navigate to the Omnissa Trust Center.
Omnissa also publishes extensive documentation to familiarize organizations with our products and services through Omnissa Docs and Tech Zone. See the Cloud Services Guide from the Omnissa Legal Center for detailed descriptions of service components, as well as shared service administration responsibilities between Omnissa and our customers.
Alignment with the ACSC Cyber Security Principles
- Governance – Establishing a balance of effectiveness and efficiency by implementing the appropriate controls and managing risks by understanding the threat landscape and leveraging all decision makers during risk analysis.
- Protection – Providing preventative and protective capabilities to ensure a secure service.
- Detection – Implementing 24x7 proactive monitoring to detect and identify security incidents.
- Response – Developing agile response procedures that address both individual security incidents and disaster recovery.
Alignment with the ISM Cyber Security Guidelines
Guidelines for Cyber Security Roles
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for two main cyber security roles: chief information security officer and systems owners.
Chief Information Security Officer
Omnissa has a Chief Information Security Officer who leads, oversees, and is ultimately responsible for Omnissa’s Information Security program.
Omnissa coordinates cyber security through the Information Security Governance Committee (ISGC) which includes members of senior management and representatives from our Information Security, IT Operations, HR, Marketing, Facilities, and Legal teams.
System Owners
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen uses numerous components and platform services. Horizon Cloud Next-Gen product management has overall system ownership responsibility for the cloud service, although some underlying components have their own product managers. Operational security responsibilities are assigned to applicable operations teams.
Guidelines for Cyber Security Incidents
To help maintain the confidentiality, availability, and security of our customer data, Omnissa has developed controls and processes for detecting, managing, and reporting cyber security incidents.
Detecting Cyber Security Incidents
The Omnissa Security Operations Center (SOC) enables rapid assessment and response to cyber security threats targeting Omnissa services through continuous collection, evaluation, and dissemination of cyber threat intelligence. The Omnissa SOC works with the Horizon Cloud Next-Gen teams to provide proactive monitoring of hosted services and to support incident response activities.
The Omnissa SOC is staffed 24x7 and monitors alerts on security anomalies. The SOC leverages multiple tools for log capture, security monitoring, and intrusion detection to look for unauthorized access attempts, monitor for incoming threats, and detect activity from malicious insiders.

Figure 1: Omnissa Incident Response Cycle
Managing Cyber Security Incidents
The Omnissa Incident Response plans and procedures have been developed in alignment with the ISO 27001 standard. Omnissa follows a formal Incident Management Plan that is maintained as part of our overall Information Security Program. Incidents are reported to the appropriate Cloud Operations team for categorization and resolution, and issues are escalated to senior management according to a pre-defined protocol. Omnissa tracks alerts, responses, and resolutions through to completion: incident response teams prepare post-mortem reports to internal stakeholders and to the Information Security Governance Committee for review.
Reporting Cyber Security Incidents
In the case of a confirmed data breach, Omnissa shall notify affected customers of the breach without undue delay in accordance with applicable laws, regulations, or governmental requests.
Guidelines for Outsourcing
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for cyber security outsourcing, including supply chain risk management, managed services, and cloud services.
Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management
Omnissa has a comprehensive vendor procurement and risk management program to choose providers that meet identified security baseline requirements. Supplier agreements help ensure that providers comply with applicable laws, security, and privacy obligations.
Omnissa has a formal process to document and to track non-conformance as a part of our information security management system (ISMS). To help assure reasonable information security across our information supply chain, Omnissa also conducts risk assessments for service sub-processors at least annually to ensure appropriate controls are in place to reduce risks to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information.
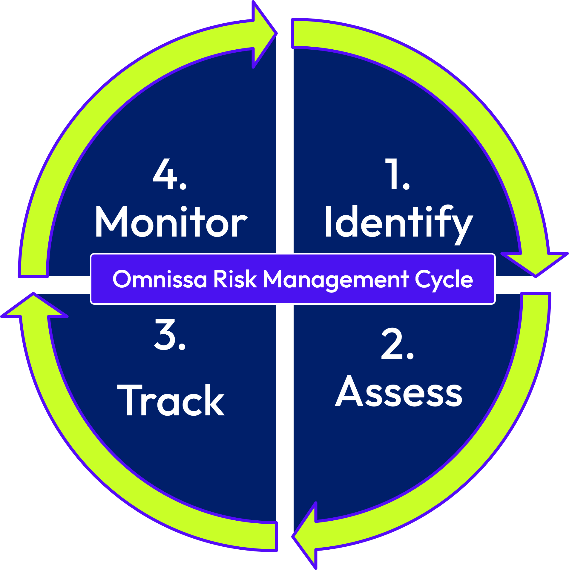
Figure 2: Omnissa Risk Management Cycle
Managed Services and Cloud Services
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen incorporates managed services and cloud services from various service providers. Our standard supplier management processes are used to track and manage the use of these third-party services.
Guidelines for Security Documentation
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for cyber security documentation, including development and maintenance of both general and system-specific security documentation.
Development and Maintenance of Security Documentation
Omnissa maintains an organization-wide Information Security Program and policies, and we perform annual reviews and audits of our program to keep the documentation up to date. Formal documentation, such as business continuity and disaster recovery plans, are reviewed at least annually or upon significant system change.
Security documentation for Horizon Cloud Next-Gen is the responsibility of applicable product managers and is maintained by the relevant operations and engineering teams. Changes to security for Omnissa cloud services have an approval process involving Information Security.
System-specific Security Documentation
Service-specific documentation such as data flow and network diagrams, risk registers, deployment procedures, and so on, are reviewed and updated regularly.
Omnissa applies consistent incident response plans across its cloud services, which are led by the Omnissa SOC.
Cloud services for Omnissa also apply a consistent continuous monitoring plan for proactively identifying, prioritizing and responding to security vulnerabilities. The Omnissa Security Response Center is responsible for managing and resolving security vulnerabilities in Omnissa products and services that are available to customers.
Guidelines for Physical Security
Omnissa and its cloud hosting partners have developed controls and processes for physical security, including facilities and systems, as well as ICT equipment and media.
Facilities and Systems
Omnissa leverages Microsoft Azure data centers within Australia to support the Horizon Cloud Next-Gen offering. Microsoft Azure maintains physical and environmental security controls for the cloud-delivered service and other related ICT equipment. Microsoft Azure environments have undergone IRAP certification (PROTECTED), SOC 2 Type 2 audits and have achieved at least ISO 27001 certification.
Key elements of this policy include controls around: physical security perimeters, physical entry controls, physical access, securing offices, rooms and facilities, visitors to facilities, records, preventing the misuse of facilities, protecting against external and environmental threats, working in secure areas, access to restricted areas, delivery and loading areas, equipment siting and protection, supporting utilities, equipment maintenance, removal of assets, security of equipment and assets off-premises, secure disposal or reuse of equipment, unattended user equipment and clear desk and clear screen.
ICT Equipment and Media
Omnissa leverages Microsoft Azure data centers within Australia to support the Horizon Cloud Next-Gen offering. Microsoft Azure maintains suitable controls to restrict access to the underlying ICT equipment for the services. Microsoft Azure has completed an IRAP assessment (PROTECTED) which includes the ICT equipment for Microsoft Azure services within the assessment scope.
All user data stored within Horizon Cloud Next-Gen is encrypted at rest with a minimum level of AES-256 symmetric encryption. Customers manage encryption of their workload capacities, which include Virtual Desktop Image Virtual Machines (VDI VMs), Multi-session VMs, images, and user data. Customers can also optionally configure Horizon Cloud Next-Gen to communicate to an on-premises, corporate network through a VPN or ExpressRoute connection.
Guidelines for Personnel Security
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for personnel security, including awareness training, and access to systems and respective resources.
Cyber Security Awareness Training
In alignment with the ISO 27001 standard, all Omnissa personnel and alternative workforce are required to complete annual business conduct and security awareness training. Employees undergo annual data handling and privacy training that includes the secure handling of customer data.
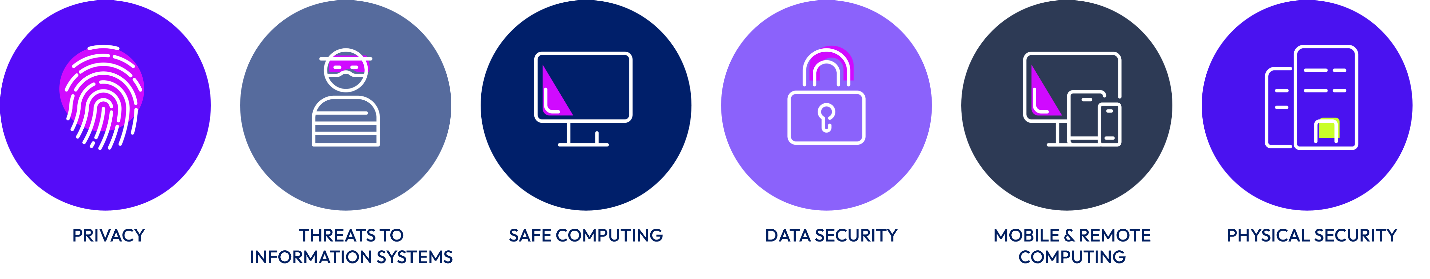
Figure 3: Security Awareness Training Topics
Access to Systems and Their Resources
Omnissa HR applies policies and processes for background screening, employment, and confidentiality agreements, and employee termination procedures.
Access privileges to the Horizon Cloud Next-Gen hosted infrastructure are enforced using role-based access control, separation of duties, and the principle of least privileges. Production environment access requires secure VPN and jump server using MFA and directory credentials and is restricted to authorized members of applicable teams. Logs are in place to review support staff access to all systems and environments.
Australian customer data is stored in regional data shards located in Australia with backups of those data shards also located in Australia. However, Omnissa uses a 24x7 “Follow-the-Sun” support program. This means that outside business hours in Australia, support services may be staffed by employees in our global office locations (for example, United Kingdom, United States) and data may be accessed (or processed) outside of Australia. Remote access to the production environment, for the purposes of maintenance and support, may also be used by our global data center operations team.
Guidelines for Communications Infrastructure
Our cloud hosting partners have developed controls and processes for communications infrastructure, including cabling infrastructure.
Cabling Infrastructure
Omnissa partners with Microsoft Azure to support Horizon Cloud Next-Gen in Australia, and Microsoft Azure manages cabling infrastructure used to host the services. Microsoft Azure services are assessed under the PROTECTED classification of IRAP.
Emanation Security
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen will not be used for SECRET or TOP SECRET systems or information and so emanation security controls are not applicable.
Guidelines for Communications Systems
No controls and processes have been developed for communications systems, including telephone systems, video conferencing, Internet protocol telephony, fax machines, and multifunction devices as these systems are not applicable to Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Telephone Systems
Telephone services are not applicable for Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Video Conferencing and Internet Protocol Telephony
Video and voice over Internet Protocol (IP) services are not applicable for Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Fax Machines and Multifunction Devices
Fax and multi-function device services are not applicable for Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Guidelines for Enterprise Mobility
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for enterprise mobility and mobile device management.
Mobile Device Management
Omnissa secures all company workstations and mobile devices using a centrally managed corporate Workspace ONE UEM instance. Any device connecting to Omnissa corporate resources is required to be enrolled and managed. Systems settings prohibit end users from disabling endpoint protection software.
Staff are permitted to use personal devices to access a limited set of Omnissa corporate services and information. However, personal devices are prohibited from accessing production environments for Omnissa products and services. Omnissa managed laptops must be used to access production environments.
Guidelines for Evaluated Products
No controls and processes have been developed for evaluated products, as this activity is not applicable to Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Evaluated Product Acquisition and Usage
Evaluated products are not procured for the Horizon Cloud Next-Gen. Horizon Cloud Next-Gen is not an evaluated product.
Guidelines for ICT Equipment
Our cloud hosting partners have developed controls and processes for ICT equipment, including usage, maintenance, and repairs, as well as sanitation, destruction, and disposal.
ICT Equipment Usage, Maintenance and Repairs, Sanitation and Destruction, Disposal
Omnissa partners with Microsoft Azure to support Horizon Cloud Next-Gen in Australia, and Microsoft Azure manages the underlying ICT equipment used to host the services. Microsoft Azure services are assessed under the PROTECTED classification of IRAP.
Guidelines for Media
Our cloud-hosting partners have developed controls and processes for cyber security media, including usage, sanitation, destruction, and disposal.
Media Usage, Sanitation, Destruction, Disposal
Omnissa partners with Microsoft Azure to support Horizon Cloud Next-Gen in Australia, and Microsoft Azure manages the physical media that is used for the services. Microsoft Azure services are assessed under the PROTECTED classification of IRAP.
Guidelines for System Hardening
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for system hardening, including processes for operating systems, applications, authentication, and virtualization.
Operating System Hardening
Omnissa disables unnecessary ports, protocols, and services as part of baseline hardening standards. We follow industry best practices in applying secure configurations to managed servers.
Application Hardening
Omnissa uses secure-by-design principles in developing its Horizon Cloud Next-Gen software and applies strong security management practices for the ongoing management of the cloud services.
Authentication Hardening
Omnissa applies authentication standards for all Omnissa products as part of the Omnissa Product Security Requirements (PSR) which are examined during the Security Development Lifecycle.
Omnissa applies industry best practice authentication for Omnissa personnel with access to all Omnissa code, software pipelines or cloud service environments. Industry best practice authentication is also applied for service accounts in cloud service environments. Authentication requirements are verified by our third-party auditors during our annual compliance activities.
Virtualization Hardening
Omnissa leverages host virtualization capabilities from Microsoft Azure. We follow industry best practices in applying secure configurations to virtualization and container platforms.
Guidelines for System Management
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for system management, including system administration, patching, data backup, and restoration.
System Administration
Omnissa applies robust processes for administration of all systems that are involved in providing Horizon Cloud Next-Gen. These systems and associated administrative infrastructure are strictly isolated from the Omnissa corporate network.
System Patching
Omnissa maintains the systems it uses to deliver Horizon Cloud Next-Gen, including the application of patches deemed critical for the target systems. Our policy is to patch or upgrade network, utility, and security equipment after analyzing the severity and impact of potential vulnerabilities. Critical vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner, and changes are made using industry best practices.
Vulnerability scanning and remediation is in line with PCI-DSS. Scans are performed at least monthly, and system and application owners are required to address critical and high vulnerabilities with a plan of corrective action after vulnerability discovery. Other vulnerabilities are addressed with a plan of corrective action within a reasonable period.
Data Backup and Restoration
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen is supported by defined enterprise resiliency programs which include business continuity and disaster recovery mechanisms for Omnissa-managed components per PCI-DSS requirements. We have a defined applicable recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO). Omnissa does not provide disaster recovery and backup processes for customer-hosted infrastructure and customer-managed data.
Guidelines for System Monitoring
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for system monitoring, including event logging and monitoring.
Event Logging and Monitoring
Horizon Cloud Operations is staffed 7x24x365 and the team deploys several commercial and custom purpose-built tools to monitor the performance and availability of all hosted solution components. Components include the Omnissa-managed Horizon Cloud Next-Gen underlying infrastructure servers, storage, networks, portals, services, and information systems.
Omnissa-managed Horizon Cloud Next-Gen infrastructure leverages a robust, centralized SIEM infrastructure per PCI-DSS requirements. All critical systems and privileged access, firewall, and IDS logs are logged and monitored. Omnissa System Security logs and events are centrally aggregated and monitored in real-time 7x24x365 by the Omnissa SOC. Logs forwarded to the Omnissa SOC are retained for one year and up to five years in archive.
Guidelines for Software Development
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for software development, including both application and web application development.
Application Development
Omnissa follows a defined Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) which incorporates security into each phase (that is, requirements, design, implementation, verification) of development. Omnissa’s SDLC is based on industry-recognized best practices and standards, including PCI-DSS common coding vulnerabilities, OWASP, OSSTMM, SANS/CWE, and SCRUM methodologies. For more information on our SDLC, see our whitepaper on Omnissa Tech Zone.
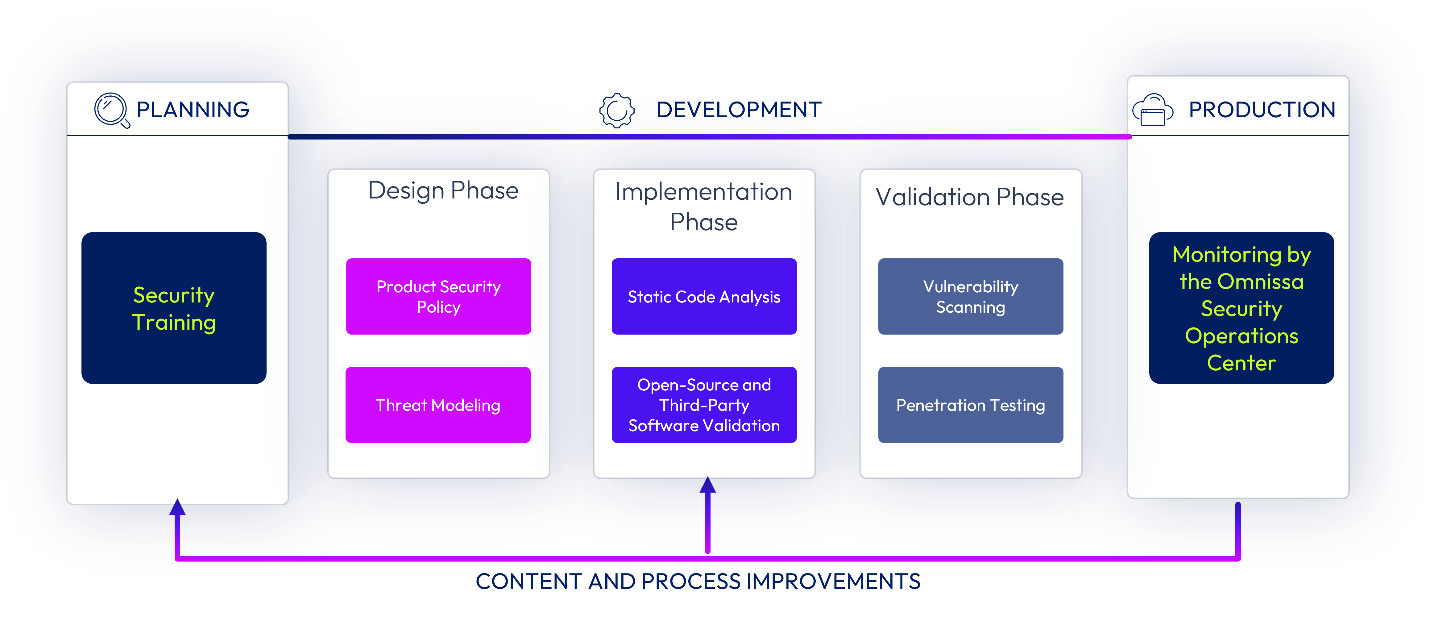
Figure 4: Omnissa Software Development Lifecycle
Web Application Development
Our Security Development Lifecycle applies industry best practices for secure application development, including secure web application development practices.
Guidelines for Database Systems
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for database systems, including database servers, DBMS, and databases.
Database Servers, DBMS, Databases
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen databases are implemented using industry best practices, including hardening by disabling unnecessary services and accounts, applying the principles of least privilege and separation of duty, enforcing network segmentation, executing parameterized queries, and full logging and monitoring capabilities. Horizon Cloud Next-Gen also makes use of MongoDB Atlas, a managed service database solution. MongoDB implements the same stringent industry best practices for hardening of databases.
Guidelines for Email
No controls and processes have been developed for cyber security emails, including usage, gateways, and servers as these systems are not applicable to Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Email Usage, Gateways, and Servers
Email management and email gateways and servers are not applicable for Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Guidelines for Networking
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for networking, including network design and configuration, and service continuity for online services. No controls have been developed for wireless networks, as these are not applicable to Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Network Design and Configuration
To reduce the management footprint and deliver a true desktop virtualization service, Horizon Cloud Next-Gen leverages a “thin edge” architecture. Horizon Cloud Next-Gen service infrastructure components, such as the connection servers, applications volumes manager, pod managers, and databases that are typically deployed in customer environments have been moved into the Omnissa-managed Horizon Control Plane. This new environment, called the Horizon Edge, reduces the footprint within customer environments, translating to increased scalability, reduced management, simplified updates, and more stability. It also separates the management infrastructure and functionality, which is delivered as cloud services from the Horizon Control Plane, from the resource capacity, which is delivered by supported capacity providers.
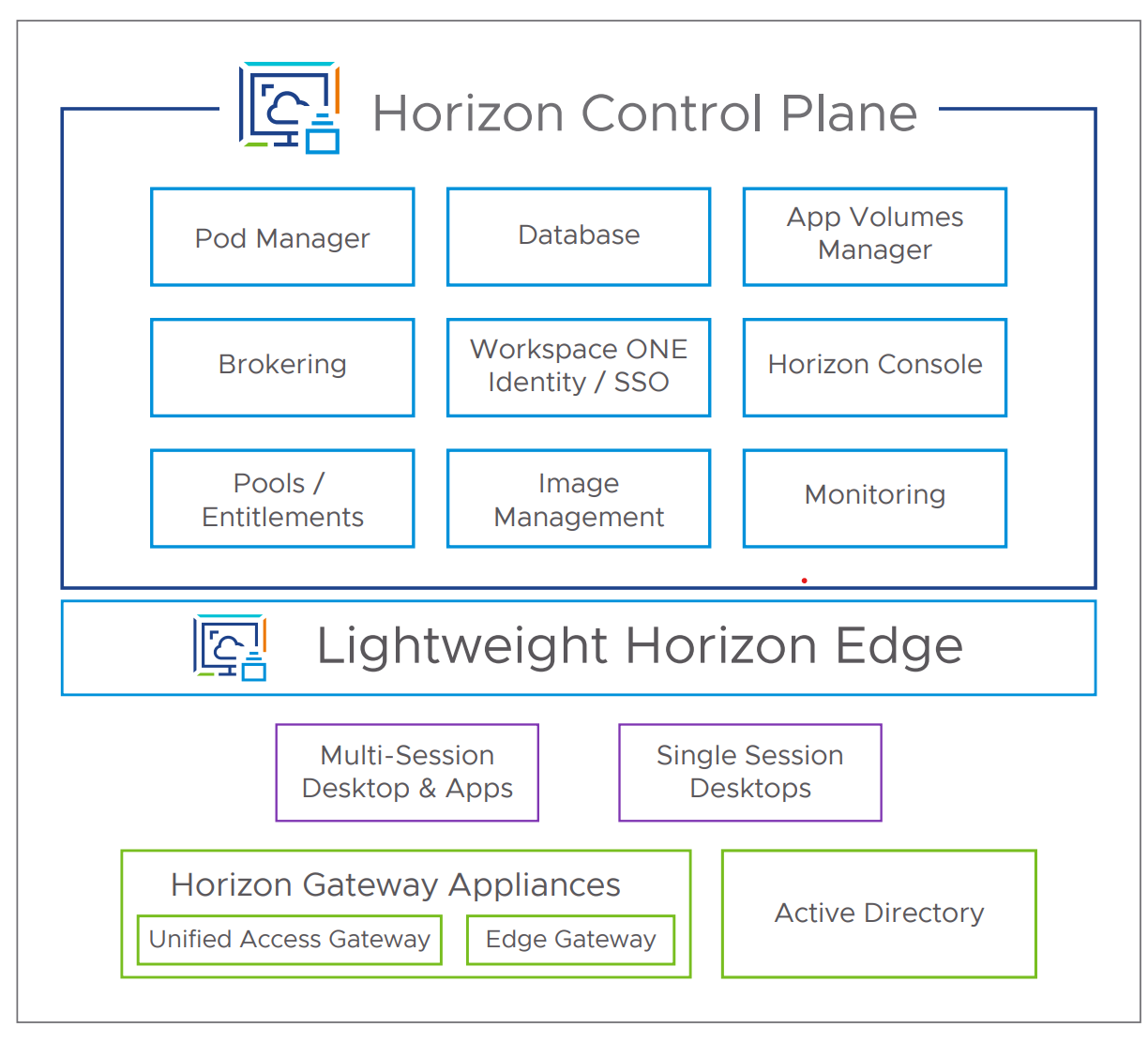
The Omnissa-managed Horizon Control Plane is hosted in Microsoft Azure data centers and is a multi-tenant Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offering. Customers data is separated at the application level and each tenant is encrypted with a per-tenant key. Firewalls are configured to restrict inbound traffic to the Microsoft Azure infrastructure environment, as well as MongoDB. Customers determine where Horizon Edge components reside, including the Horizon Edge Gateway, Unified Access Gateway, and virtual desktops and specify the primary provider in a selected site. Customers may choose to leverage Microsoft Azure as a primary provider for their selected site or use an alternate software-defined data center (SDDC).
Figure 5: Horizon Cloud Next-Gen expanded Horizon Control Plane functionality
Edge Networking Components
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen deployed Edges require three subnets for the delivery of the service:
- DMZ – Enables inbound traffic from the Internet to the external UAGs. Network Security Groups (NSGs) that are a feature of Microsoft Azure are used to control inbound access and allow only the required ports and protocols to the external Unified Access Gateways.
- Management – An internal management network, allowing the Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) clusters on the Horizon Edge to update the UAGs and providing an outbound Internet channel for connection to the Horizon Control Plane and the Azure API.
- Desktop – Customer-controlled network for the VDI desktops and Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH) Farms (supporting both multi-session desktops and applications), and internal UAGs.
Visit the networking section of Horizon Cloud Next-Gen Architecture for additional insight into how the subnets can be used in the implementation of the service.
Wireless Networks
Wireless networks are not applicable for Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Service Continuity for Online Services
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen employs a highly redundant design with multiple best-in-class redundancy technologies combined with data replication strategies deployed at the data layer. The infrastructure is designed to ensure that customers will typically not notice a disruption during a component or system failure inside a primary data center.
Disaster recovery strategies include:
- The use of Microsoft Azure Availability Zones in active-active configurations for applicable locations
- Multi-region (in country) failover in the event of a regional outage
- Database replication
- Encryption of backups in-Transit and at-Rest (AES-256)
Disaster Recovery is a shared responsibility between Omnissa and customers for the Horizon Cloud Next-Gen service. Customers fully manage the data, such as routine backups and content, stored or accessed through the Horizon Cloud Next-Gen service on Microsoft Azure solution. Omnissa provides disaster avoidance and recovery for top-layer and user-management interfaces which are owned and operated by Omnissa.
Guidelines for Cryptography
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen aligns cryptographic to Payment Card Industry-Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) standards, including AES-256 for encrypting Data-at-Rest (DaR) and TLS 1.2 for encrypting Data-in-Transit (DiT). Omnissa manages Edge appliances and relevant security updates and patches while customers determine the level of encryption configured for their desktops.
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen enforces strong TLS encryption in-Transit to and from the Omnissa cloud environments over the public Internet to protect data against Machine-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks. In transit encryption includes traffic between end-user devices and the service, between the service and other services (such as Horizon Edge appliances and customer systems), and internally within the service, where applicable. Firewalls, managed perimeter devices, and strong physical and logical access controls provide layered security within the Horizon Control Plane hosted environments.
Customers manage encryption of their workload capacities, which include VDI Desktop VMs, multi-session VMs, images and user data. Customers can also optionally configure the Horizon Cloud Next-Gen to communicate to the on-premises, corporate network via a VPN or ExpressRoute connection.
Guidelines for Gateways
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for gateways, including firewalls, web proxies, web content filters and filtering. No controls have been developed for cross-domain solutions, diodes, and peripheral switches as Horizon Cloud Next-Gen will only contain PROTECTED data and these controls are not applicable.
Gateways, Firewalls, Web Proxies, Web Content Filters, Content filtering
Omnissa-managed Horizon Cloud Next-Gen leverages a robust, centralized SIEM infrastructure per PCI-DSS requirements. All critical systems and privileged access, firewall, and IDS logs are logged and monitored. Omnissa System Security logs and events are centrally aggregated and monitored in real-time 7x24x365 by the Omnissa SOC. Logs forwarded to the Omnissa SOC are retained for one year, and up to five years in archive.
Importantly, Omnissa and customers share ownership of, and responsibility for, various aspects of the service, which are outlined in the Cloud Services Guide on the Omnissa Legal Center. Omnissa will protect the information systems used to deliver Horizon Cloud Next-Gen over which Omnissa (as between Omnissa and a customer) has sole administrative level control. Customers are responsible for the security of the networks over which they have administrative level control. This includes, but is not limited to, maintaining effective firewall rules in all software-defined data centers (“SDDCs”) that a customer deploys when using Horizon Cloud Next-Gen.
Cross Domain Solutions, Diodes, Peripheral Switches
Horizon Cloud Next-Gen is offered as a public cloud service and so it will only be used for unclassified information or for information classified PROTECTED. Cross Domain Solutions and Diodes are not applicable. Controls related to peripheral switches are only applicable for Microsoft Azure as part of the shared responsibility model.
Guidelines for Data Transfers
Omnissa has developed controls and processes for data transfers and the protection of data exports.
Data Transfers
Omnissa employees are prohibited from manually transferring customer data from the production environment (for example, removal and storage of customer data on removable media). To help ensure accountability, full auditing capabilities are enabled on all Omnissa cloud environments.
Customers can import and export their data using manual techniques and are responsible for developing and implementing data transfer policies and procedures, including accountability, scanning, auditing, and logging.
Summary and Additional Resources
Introduction
This document addresses the security for Horizon Cloud Next-Gen in relation to the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) Information Security Manual (ISM). Information contained in this document is solely for the use of evaluating Horizon Cloud Next-Gen software and services and does not represent an official Infosec Registered Assessors Program (IRAP) certification or endorsement of Horizon Cloud Next-Gen by the ACSC.
Additional Resources
- Workspace ONE UEM Cloud Service Alignment with the ACSC Information Security Manual (ISM)
- Horizon Cloud Next-Gen Architecture
- Horizon Cloud Next-Gen technical documentation
Changelog
The following updates were made to this guide:
| Date | Description of Changes |
| 21 November 2024 | Rebranded and updated for Omnissa |
| 30 September 2024 | Document Published |
About the Author and Contributors
The following people contributed their knowledge and assistance with this document:
- Andrea Smith, Sr. Program Manager, Customer Security Assurance.
- Andrew Osborn, Omnissa alumni.
Feedback
Your feedback is valuable.
To comment on this paper, contact Omnissa at tech_content_feedback@omnissa.com.