Germany Cloud Computing Compliance Criteria Catalogue (C5)
Introduction
The Cloud Computing Compliance Controls Catalogue (C5) is a cloud security certification prescribed by the German Federal Office of Information Security (BSI). The certification describes the security controls and processes implemented by cloud service providers to secure customer workloads and the infrastructure supporting the cloud platform.
Purpose
While Omnissa Workspace ONE® cloud services are yet to undergo the certification for C5, this whitepaper intends to show the controls and processes Workspace ONE cloud services have in place to address the control requirements in C5 certification. To complement this whitepaper, customers can also utilize the mapping document published by BSI, which shows how C5 standards map to various international compliance certifications. The mapping document is available in Referencing Cloud Computing Compliance Criteria Catalogue (C5) to International Standards. For the latest updates on Workspace ONE compliance certifications, see the Omnissa Trust Center.
Audience
This document is intended for Workspace ONE commercial cloud administrators. It assumes at least intermediate knowledge of Workspace ONE cloud services and focuses on the policies, processes, and controls supporting the cloud-delivered services. Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP), on-premises, and third-party offerings are not in scope for this document.
Note: You can find the definitions for acronyms used in this document in Acronyms used in the Workspace ONE Security Series.
Structure of C5:2020 Framework
The control requirements in C5 are based on some of the leading international standards such as ISO27001/17/18, SOC, Cloud Security Alliance ANSSI Référentiel Secure Cloud 2.0, IDW, and BSI IT-Grundschutz Catalogues. The image below shows the 17 key control areas prescribed in the C5 framework (revised version 2020):
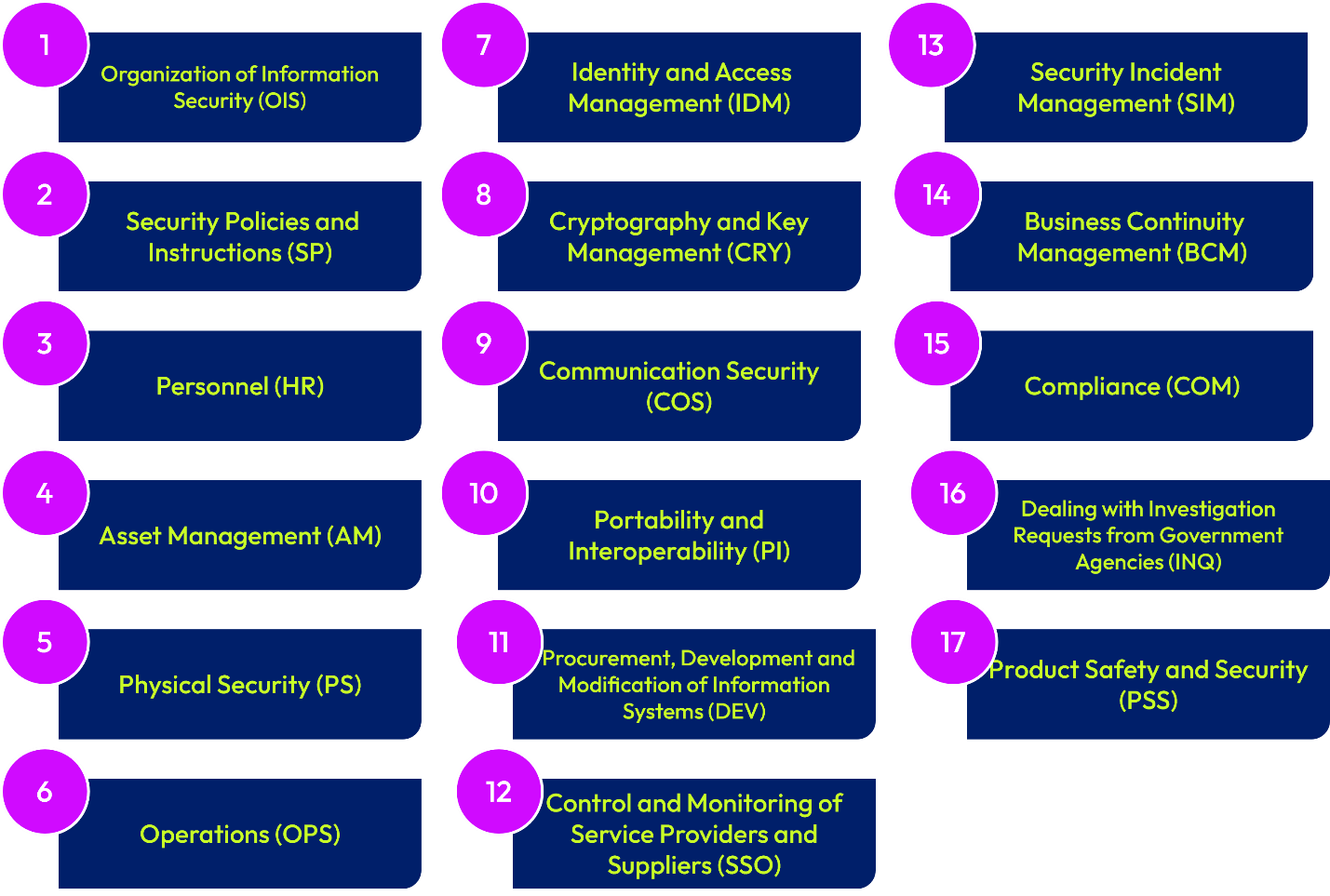
Figure 1: Control Areas of the Cloud Computing Compliance Criteria Catalogue (C5)
Workspace ONE Cloud Services Alignment with the C5 Areas
The following sections provide a general overview of how Workspace ONE cloud security controls are aligned with the C5 control area objectives and the applicable ISO 27001 reference mapping.
1. Organization of Information Security (OIS)
Table 1: C5 Area – Organization of Information Security (OIS)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
1 |
Organization of Information Security (OIS) |
Plan, implement, maintain, and continuously improve the information security framework within the organization. |
A.5 Information Security Policies A.6 Organization of Information Security A.8. Asset Management |
Workspace ONE cloud services have established an Information Security Management System (ISMS) based on ISO 27001 standards to manage risks relating to confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. Internal and external audits are performed annually under the Omnissa information security management system (ISMS) program. Omnissa has established information security policies in line with the ISO 27001 framework. The policies are published on the intranet, and the name of the person responsible for the policy is shown. Policies are reviewed at least annually.
Omnissa has considered significant interactions between itself and relevant external parties and risks that could affect the company’s ability to provide reliable service to its user entities.
Risks identified during the risk assessment process are ranked and formally documented, along with mitigation strategies. A formal process is documented to guide personnel when performing a risk assessment.
Omnissa maintains an ISMS framework to manage information security risks. Omnissa performs annual risk assessments as part of the Omnissa ISMS program to support security and compliance programs.
The framework security requirements have been designed and implemented to address industry standards around security and privacy. This effort requires the identification of applicable regulatory and contractual requirements, technical compliance with information security policies, protection of records, protection of information systems audit tools, and audit controls and reporting. This policy also requires Omnissa to adhere to the applicable legal, statutory, regulatory, or contractual obligations related to information security and security requirements.
Omnissa has a dedicated Security, Governance, Risk and Compliance team that oversees risk management and compliance across the organization. Where needed, the team liaises with relevant regulatory authorities to address specific regulatory concerns.
Figure 2: Comprehensive Security Framework
2. Security Policies and Instructions (SP)
Table 2: C5 Area - Security Policies and Instructions (SP)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
2 |
Security Policies and Instructions (SP) |
Provide policies and instructions regarding security requirements and to support business requirements. |
A.5 Information Security Policies
|
Omnissa has documented policies, standards, and system and network diagrams supporting Workspace ONE cloud services. Omnissa documents, updates, and maintains baseline configurations for software and hardware installed in the production environment; changes are governed by a defined change management policy, and baseline configurations are securely managed. Security baselines are documented to guide personnel to help ensure appropriate configurations are in place to protect sensitive information.
Omnissa uses various internal tools for the communication of Omnissa policies. These policies are published on the intranet, version controlled, reviewed, and updated on an annual basis. Managers are responsible for addressing known compliance issues with information security policies. Compliance issues are corrected, and if a compliance issue cannot be corrected, then managers must seek approval for an Information Security policy exception.
3. Personnel (HR)
Table 3: C5 Area - Personnel (HR)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
3 |
Personnel (HR) |
Ensure that employees understand their responsibilities, are aware of their responsibilities regarding information security, and that the organization’s assets are protected in the event of changes in responsibilities or termination. |
A.7 Human Resource Security A.13 Communications Security |
Omnissa has organizational charts in place to communicate the defined key areas of authority, responsibility, and lines of reporting to personnel related to the design, development, implementation, operation, maintenance, and monitoring of the system. These charts are communicated to employees via the company intranet and updated as needed.
Omnissa has established screening procedures where allowed by local laws. Omnissa performs background checks for new hires. The results are evaluated to determine employment eligibility. New hires are required to attend orientation meetings to review corporate security policies and obligations.
In alignment with the ISO 27001 standard, Omnissa personnel are required to complete annual security awareness training. Personnel supporting Omnissa managed services receive additional role-based security training to perform their job functions in a secure manner. Compliance audits are periodically performed to validate that employees understand and follow the established policies. Formal procedures are in place for granting and revocation of access for employees, and these procedures are validated by external auditors as part of compliance audits.
Omnissa has also documented terms and conditions for maintaining confidentiality as part of the Omnissa Terms of Service and Data Processing Addendum. Abuse of policies may result in disciplinary action, including possible termination and civil and/or criminal liability. Employees are made aware of their responsibilities for these terms and conditions at the time of employment and through annual training.
4. Asset Management (AM)
Table 4: C5 Area - Asset Management (AM)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
4 |
Asset Management (AM) |
Identify the organization’s own assets and ensure an appropriate level of protection throughout their lifecycle. |
A.8 Asset Management |
Omnissa has an established Asset Management policy that outlines the management of assets at Omnissa, including creation, processing, storage, transmission, deletion, and destruction. Omnissa maintains inventories of critical assets, including asset ownership and location.
Omnissa also maintains an acceptable use policy that dictates employee responsibility toward protecting and managing the company’s assets. Omnissa Corporate Human Resources has an established policy for employee termination processes and provides procedures for management to help ensure that company-owned assets are returned within the specified timeframe.
It is important to note that Omnissa uses Amazon Web Services (AWS) data centers to support the backend infrastructure for hosting Workspace ONE cloud services in Germany. Media storage devices used to store customer data are classified by AWS as critical and treated accordingly, as high impact, throughout their lifecycles. AWS has exacting standards on how to install, service, and eventually destroy the devices when they are no longer useful. When a storage device has reached the end of its useful life, AWS decommissions media using techniques detailed in NIST 800-88. Media that stored customer data is not removed from AWS control until it has been securely decommissioned.
5. Physical Security (PS)
Table 5: C5 Area – Physical Security (PS)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
5 |
Physical Security (PS) |
Prevent unauthorized physical access and protect against theft, damage, loss. |
A.11 Physical and Environmental Security A.17 Information Security Aspects of Business Continuity Management A.9 Access Control |
Omnissa uses AWS data centers to host Workspace ONE cloud services in Germany. AWS security management standards follow industry standards such as ISO 27001. AWS manages physical access to data centers as defined in the AWS Data Center Physical Security Policy. Physical access is strictly controlled both at the perimeter and at building ingress/egress points and includes, but is not limited to, fencing, walls, video surveillance, intrusion detection systems, and other electronic biometric access controls and alarm monitoring systems managed by a 24x7x365 professional security staff. See this article for more information on AWS controls. Furthermore, AWS performs regular audits of their physical infrastructure. Visit Amazon’s compliance page for more information on AWS data center security controls and compliance reports.
AWS data center electrical power systems are designed to be fully redundant and maintainable without impact to operations, 24 hours a day. AWS data centers are equipped with back-up power supply to ensure power is available to maintain operations in the event of an electrical failure for critical and essential loads in the facility.
Critical system components are backed up across multiple isolated locations known as Availability Zones (AZs). Each AZ is engineered to operate independently with high reliability, and Availability Zones are connected easily to architect applications that automatically fail-over between availability zones without interruption. Workspace ONE cloud services employ a highly redundant design with multiple best-in-class redundancy technologies combined with data replication strategies. The infrastructure is designed to help ensure that customers will typically not notice a disruption during a component or system failure inside a primary data center.
AWS monitors and performs preventive maintenance of electrical and mechanical equipment to maintain the continued operability of systems within AWS data centers. Equipment maintenance procedures are carried out by qualified persons and completed according to a documented maintenance schedule. AWS monitors electrical and mechanical systems and equipment to enable immediate identification of issues. Preventive maintenance is performed to maintain the continued operability of equipment.
6. Operations (OPS)
Table 6: C5 Area – Operations (OPS)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
6 |
Operations (OPS) |
Ensure proper and regular operation, including appropriate measures for planning and monitoring capacity, protection against malware, logging and monitoring events, and dealing with vulnerabilities, malfunctions and failures. |
A.12 Operational Security A.17 Information Security Aspects of Business Continuity Management A.9 Access Control A.13 Communications Security A.18 Compliance A.14 System Acquisition, Development and Maintenance |
Omnissa has a defined Information Security Program that includes Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery strategies for data and hardware redundancy, network configuration redundancy and backups, and regular testing exercises. This program implements appropriate security controls to protect its employees and assets against natural and manmade disasters. As a part of the program, an automated runbook system is engaged to help ensure policies and procedures are reviewed and made available to appropriate individuals.
Omnissa implements security mechanisms and redundancies to protect equipment from utility service outages. Omnissa facilitates the determination of the impact of any disruption to the organization through defined documents that identify dependencies, critical products, and services. The real-time status of the Workspace ONE cloud services, along with past incidents, is publicly available at https://status.workspaceone.com/
Omnissa maintains the systems it uses to deliver Workspace ONE services, including the application of patches deemed critical for the target systems. Our policy is to patch or upgrade network, utility, and security equipment after analyzing the severity and impact of potential vulnerabilities. Critical vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner, and changes are made using industry best practices. Testing is conducted by the QE department to ensure compatibility with the production environment. If required, rollback procedures are conducted by the QE team.
See our whitepaper for details on our CI/CD pipeline for patching each Workspace ONE service.
Omnissa continuously collects and monitors service operation logs using security information event management (SIEM) technologies. The 24x7x365 Omnissa Security Operations Center uses the SIEM to correlate information with public and private threat feeds to identify suspicious and unusual activities. The Omnissa Security Operations Center (SOC) team takes reported security events and escalates to the Omnissa Security Incident Response Team for security incident management as appropriate based on defined criteria. Logs are stored separately and securely. Access to logs is monitored.
7. Identity and Access Management (IDM)
Table 7: C5 Area – Identity and Access Management (IDM)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
7 |
Identity and Access Management (IDM) |
Secure the authorization and authentication of users of the Cloud Service Provider (typically privileged users) to prevent unauthorized access. |
A.6 Organization of Information Security A.9 Access Control A.12 Operational Security |
Omnissa has established an authentication and password policy that outlines the password requirements for our information assets, such as minimum password configurations, password restrictions, secure logon procedures, criteria for strong passwords, and password administration.
Access privileges to Workspace ONE cloud-hosted systems are controlled based on the principle of least privilege – only the minimum level of access required shall be granted. Access is based on an individual’s “need to know” as determined by job functions and requirements. Managing access to information systems is implemented and controlled through centralized identity stores and directory services.
A quarterly review is performed to help ensure service access is still appropriate. Controls are in place confirming the timely removal of systems access that is no longer required for business purposes. Entitlement actions are recorded via the systems used to grant/revoke access and provide evidence to support compliance programs.
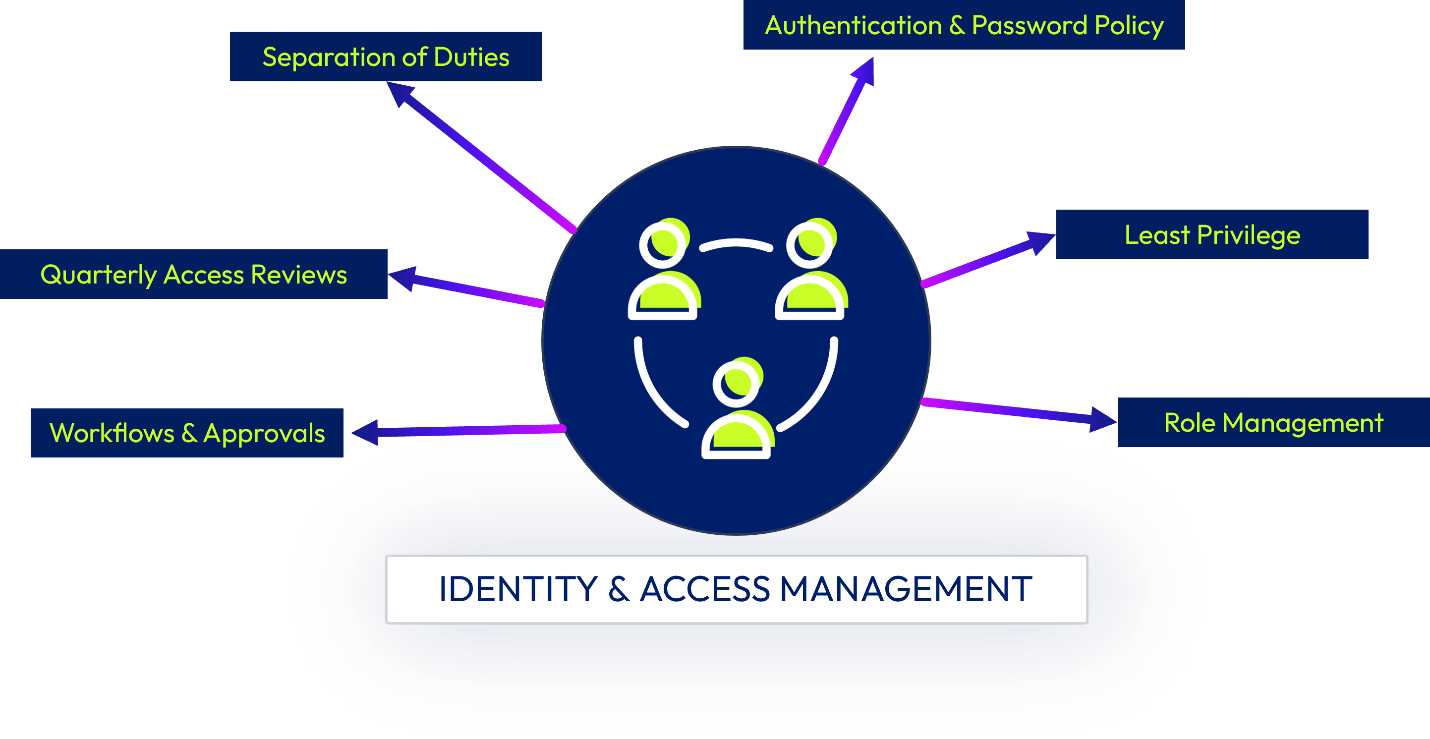
Figure 3: Omnissa Identity and Access Management Controls
8. Cryptography and Key Management (CRY)
Table 8: C5 Area – Cryptography and Key Management (CRY)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
8 |
Cryptography and Key Management (CRY) |
Ensure appropriate and effective use of cryptography to protect the confidentiality, authenticity, or integrity of information. |
A.10 Cryptography A.13 Communications Security A.18 Compliance |
Omnissa has an encryption policy that provides guidelines on the use of cryptographic controls and key management. The policy is reviewed on an annual basis. Cryptographic keys for Omnissa Workspace ONE® UEM and Omnissa Workspace® ONE Assist are stored securely on protected servers (such as access controls and encryption). For Omnissa Access and Omnissa Intelligence, the service uses the AWS Key Management Service (KMS) key generated and stored by KMS. Keys are managed in alignment with PCI-DSS
Workspace ONE services do not support the use of customer-managed keys in the hosted environment. As part of the shared responsibility model, customers can manage their own encryption keys for on-premises hosted resources, such as establishing and managing certificates for any on-premises integration connectors.
9. Communication Security (COS)
Table 9: C5 Area - Communication Security (COS)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
9 |
Communication Security (COS) |
Ensure the protection of information in networks and the corresponding information processing systems. |
A.13 Communications Security A.14 System Acquisition, Development and Maintenance |
Omnissa provides 24/7 monitoring for Workspace ONE cloud environments. Omnissa closely monitors network performance in addition to network security perimeter controls.
All access is technically enforced, logged, and monitored; access to the production environment requires a secure connection (VPN, SSH, and so on.). Firewalls are configured to deny-all settings to prevent intrusion into our production and corporate environments. Additionally, Omnissa deploys anti-virus/malware suites on servers commonly impacted by malware in our production environment that operate independently of our redundant firewalls. Networks are separated into tiers, and microsegmentation is used (where applicable) to protect against unauthorized access.
Omnissa has full auditing capabilities on all environments to enable the reconstruction of security incidents and events (such as Syslog, firewall logs, alerting tools, and access control lists) and deploys several mechanisms to detect intrusions and help protect against distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. These mechanisms range from real-time firewalls, Intrusion Detection System (IDS) technologies, internal logs and tools, and external intelligence (OSINT) data sources. Omnissa monitors for security events involving the underlying infrastructure servers, storage, networks, information systems, and upstream providers used in service delivery.
As part of our SDLC, Workspace ONE applications are also assessed against the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top Ten to identify potential application code to identify and remediate potential errors that could lead to unauthorized access and DDoS. In alignment with PCI-DSS, Workspace ONE services use file integrity monitoring to detect malicious behavior or changes in system files or libraries. In addition, Omnissa Access and Omnissa Intelligence use a web application firewall (WAF), which provides application layer protection against common web exploits.
Audits are performed at least annually that include controls for internal and external network penetration testing. Evidence of these third-party penetration tests is verified by third-party assessors, and this verification is published in customer-available compliance reports and executive summaries.
10. Portability and Interoperability (PI)
Table 10: C5 Area – Portability and Interoperability (PI)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
10 |
Portability and Interoperability (PI) |
Enable the ability to access the cloud service via other cloud services or IT systems of the cloud customers, to obtain the stored data at the end of the contractual relationship and to securely delete it from the Cloud Service Provider. |
A.11 Physical and Environmental Security |
Workspace ONE customers can access solution data at any time via the Workspace ONE administrative consoles. Additionally, administrators can export data from Workspace ONE consoles in various formats: XLS, PDF, and CSV prior to contract termination. Information on post-contract data deletion can be found in the Cloud Services Guide available on the Omnissa Legal Center.
11. Procurement, Development and Modification of Information Systems (DEV)
Table 11: C5 Area – Procurement, Development and Modification of Information Systems (DEV)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
11 |
Procurement, Development and Modification of Information Systems (DEV) |
Ensure information security in the development cycle of cloud service system components. |
A.12 Operational Security A.14 System Acquisition, Development and Maintenance A.8 Asset Management A.7 Human Resource Security A.9 Access Control |
Omnissa has a security development lifecycle process and a security organization that focuses on implementing robust operational and security controls. Omnissa identifies security defects using multiple methods, which can include automated and manual source-code analysis. Software releases go through a security architectural review, security audits, manual & automated code analysis, vulnerability scans, and additional reviews necessary to meet industry-leading security standards. Omnissa security personnel approve releases to validate internal processes and mitigate software security risks to customers. The Omnissa product security and product development groups apply the methodology as an end-to-end set of processes to use at specific times in the development group’s software development lifecycle, with the goal of helping teams to remediate security issues early in the lifecycle.
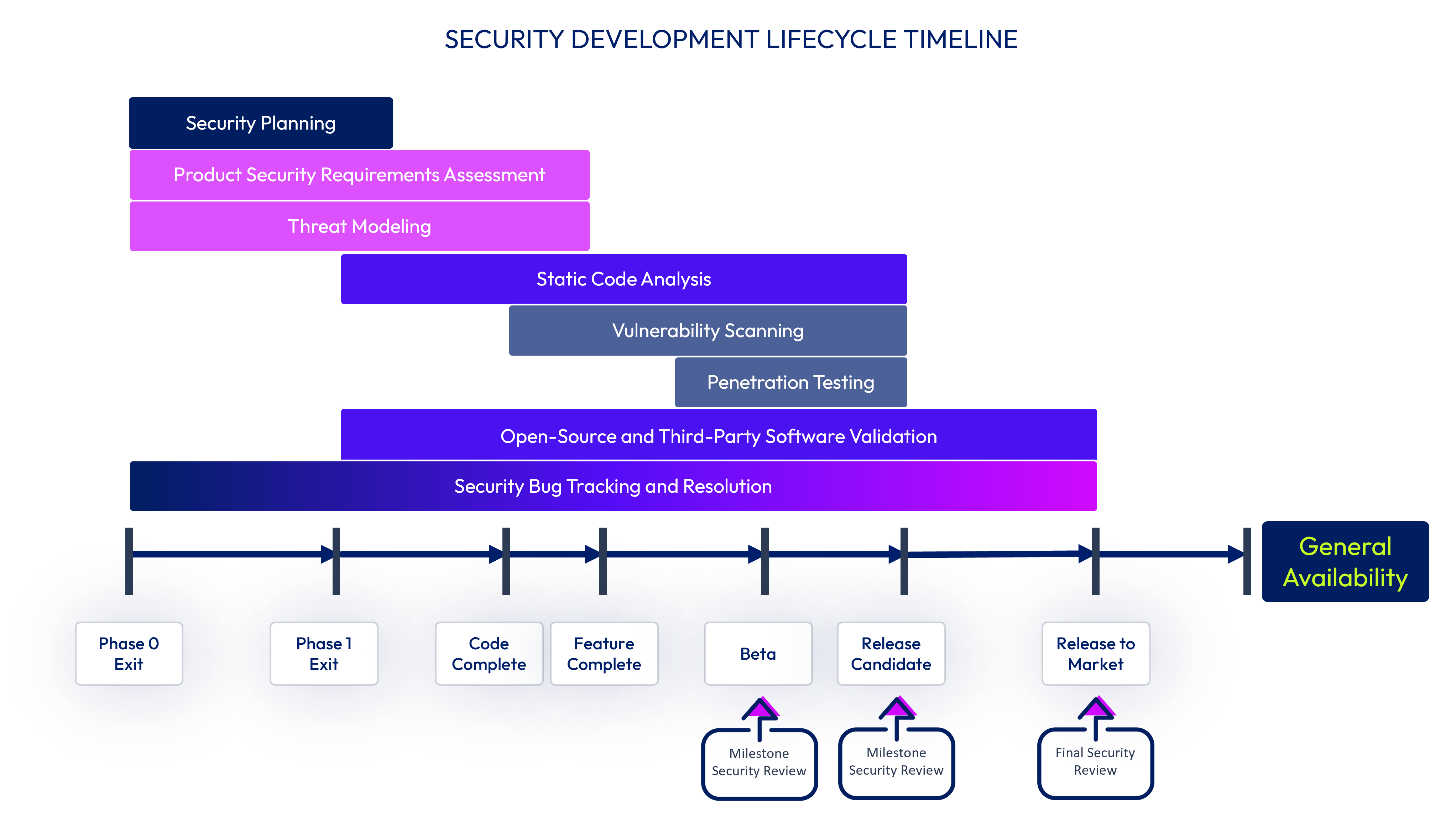
Figure 4: Omnissa SDLC Timeline
Omnissa security development lifecycle and change management processes guide personnel to conduct appropriate reviews and authorizations prior to implementing any new technologies or changes within the production environment. Change management policies and processes are also in place to guide management authorization of changes applied to the production environment. Internal audits of these processes are performed under the Omnissa Information Security Management System (ISMS) program and are essential to the Omnissa continuous improvement programs. Omnissa uses various change management tools to document and record change management artifacts and approvals. Respective documentation is retained within these tools throughout the change management cycle.
Production, development, and quality assurance environments and systems are separate and are adequately protected with physical, administrative, and technical safeguards. Access permissions are technically enforced, and access is monitored. No customer content is used for testing and development purposes.
12. Control and Monitoring of Service Providers and Suppliers (SSO)
Table 12: C5 Area – Control and Monitoring of Service Providers and Suppliers (SSO)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
12 |
Control and Monitoring of Service Providers and Suppliers (SSO) |
Ensure the protection of information that service providers or suppliers of the Cloud Service Provider (subservice provider) can access and monitor the agreed services and security requirements. |
A.15 Supplier Relationships A.7 Human Resource Security
|
Omnissa has an established Third-Party IT Risk Management policy. The policy applies to our management and oversight of third parties (vendors/suppliers) accessing or processing company data facilities, information, and/or information systems. It defines the requirements for assessments to be performed as part of negotiating and reviewing third-party agreements in line with Omnissa information security objectives and ongoing monitoring of such third parties for compliance.
Sourcing and business teams collaborate with the information security risk team to assure a risk-based approach is taken with respect to third parties to safeguard the security of information assets. Omnissa also maintains a list of third-party vendors and has a defined procurement process for vendors and contractors that involves multiple levels of due diligence and approvals to affirm that any vendors are selected in line with the purpose and desired scope.
Omnissa evaluates the service risk based on the type of service and type of data hosted by the supplier and implements appropriate processes to address specific risks. Omnissa also maintains a data processing addendum that covers the requirements for managing and processing personal data in line with applicable data processing regulations.
Workspace ONE UEM is currently hosted in cloud-hosted data centers and supports portability and interoperability; we do not use proprietary encryption mechanisms, and we use industry-standard technology such as Microsoft and Linux. Workspace ONE services are hosted in AWS, which does use some proprietary Amazon technologies and industry-standard Linux technology; however, Omnissa considers this vendor lock-in as low risk.
13. Security Incident Management (SIM)
Table 13: C5 Area – Security Incident Management (SIM)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
13 |
Security Incident Management (SIM) |
Ensure a consistent and comprehensive approach to the capturing, evaluation, communication, and handling of security incidents. |
A.16 Information Security Incident Management A.6 Organization of Information Security |
Omnissa has a documented security incident management policy, which is reviewed at least annually. Omnissa has an incident response program, plans, and procedures, which are documented and implemented.
Omnissa maintains an incident response plan, which includes evidence preservation and customer notification processes. Omnissa provides incident and problem management services (for example, detection, severity classification, recording, escalation, and return to service) for the infrastructure over which Omnissa has direct administrative access and control, including servers and services used to provide Workspace ONE cloud services. Customers are responsible for incident and problem management (for example, detection, severity, classification, recording, escalation, and return to service) for anything not under our direct control and administration, such as on-premises cloud connectors.
The Omnissa SOC uses log capture and SIEM tools, security monitoring technologies, and intrusion detection tools in real-time to identify unauthorized access attempts, any behaviors that would indicate abnormal activity, or any Omnissa personnel accessing customer data.
The Omnissa Security Incident Response team is notified by the SOC of any potential breach and participates in any investigation. If Omnissa becomes aware of a security incident in Workspace ONE cloud services that leads to the unauthorized disclosure or access to personal information provided to Omnissa as a processor, we will notify customers without undue delay and will provide information relating to a data breach as reasonably requested by our customers. Omnissa will use reasonable endeavors to assist customers in mitigating, where possible, the adverse effects of any personal data breach.

Figure 5: Omnissa Incident Response Cycle
14. Business Continuity Management (BCM)
Table 14: C5 Area – Business Continuity Management (BCM)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
14 |
Business Continuity Management (BCM) |
Plan, implement, maintain, and test procedures and measures for business continuity and emergency management. |
A.17 Information Security Aspects of Business Continuity Management |
Omnissa has a defined Information Security Program that includes Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery strategies for data and hardware redundancy, network configuration redundancy and backups, and regular testing exercises. This program implements appropriate security controls to protect its employees and assets against natural and manmade disasters. Where applicable, Omnissa implements security mechanisms and redundancies to protect equipment from utility service outages. As a part of the program, an automated runbook system is engaged to ensure policies and procedures are reviewed and made available to appropriate individuals. Additionally, these policies and procedures include defined roles and responsibilities supported by regular workforce training.
Omnissa follows frameworks that specify requirements to plan, establish, implement, operate, monitor, review, maintain, and continually improve a documented management system to protect against, reduce the likelihood of occurrence, prepare for, respond to, and recover from disruptive incidents when they arise. Additionally, Omnissa follows information security standards in the context of a business continuity program. Omnissa is adequately prepared for a critical business disruption so that its people, processes, systems, facilities, and other assets can respond, recover, and resume operations safely and efficiently and make sure that there is effective communication with stakeholders, thus minimizing financial, customer, brand, and operational impact to the company.
Omnissa has implemented backup and redundancy mechanisms to help ensure compliance with regulatory, statutory, and contractual obligations. The Omnissa business continuity plans and documentation are reviewed annually as part of the enterprise independent attestation in third-party compliance audits.
15. Compliance (COM)
Table 15: C5 Area – Compliance (COM)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
15 |
Compliance (COM) |
Avoid noncompliance with legal, regulatory, self-imposed or contractual information security and compliance requirements. |
A.18 Compliance A.9 Access Control A.12 Operational Security |
Omnissa has a compliance program in place that is designed after several industry standards and frameworks, including ISO 27001. Omnissa regularly conducts internal and external audits that include results from security and compliance assessments. The program utilizes internal/external audits to measure the effectiveness of the controls applied to reduce risks associated with safeguarding information and to identify areas of improvement.
Security is of the utmost importance to us. Our programs are continually evolving based on our own experiences, changes in the threat landscape, and our learnings based on industry observation and collaboration. For more information about Omnissa Compliance initiatives and Security programs, visit the Omnissa Trust Center.
16. Dealing with Investigation Requests from Government Agencies (INQ)
Table 16: C5 Area – Dealing with investigation requests from government agencies (INQ)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
16 |
Dealing with investigation requests from government agencies (INQ) |
Ensure appropriate handling of government investigation requests for legal review, information to cloud customers, and limitation of access to or disclosure of data. |
None |
Omnissa may, on occasion, receive a request from a government agency or law enforcement authority seeking access to content belonging to a customer. Regardless of where a request comes from or who the customer is, Omnissa is vigilant about protecting Customer Content. Omnissa will not disclose Customer Content unless required to do so to comply with a legally valid and binding obligation or order. Omnissa reviews each request to determine that it complies with applicable laws. See Required Disclosures in our General Terms available in the Omnissa Legal Center for details.
17. Product Safety and Security (PSS)
|
No |
Area |
Objective |
Applicable ISO Reference |
|
16 |
Product Safety and Security (PSS) |
Provide up-to-date information on the secure configuration and known vulnerabilities of the cloud service for cloud customers, |
A.12 Operational Security A.9 Access Control A.10 Cryptography A.18 Compliance A.13 Communications Security A.12 Operational Security A.14 System Acquisition, Development and Maintenance |
Omnissa has an industry-leading Security Development Lifecycle process and an Omnissa organization that focuses on implementing industry-standard operational and security controls.
Omnissa identifies security defects using multiple methods, which can include automated and manual source-code analysis. Workspace ONE releases go through a security architectural review, security audits, manual and automated code analysis, vulnerability scans, and additional reviews necessary to meet industry-leading security standards. Omnissa security personnel approve releases to validate internal processes and mitigate software security risks to customers. The Omnissa Product Security and product development groups apply the methodology as an end-to-end set of processes to use at specific times in the development group’s software development lifecycle, with the goal of helping teams to remediate security issues early in the lifecycle.
Omnissa security programs and practices establish requirements “by design” to evolve methodologies of protection against new “in-the-wild threats.” This approach is followed throughout the development process. Products are tested for vulnerabilities prior to full release or version update.
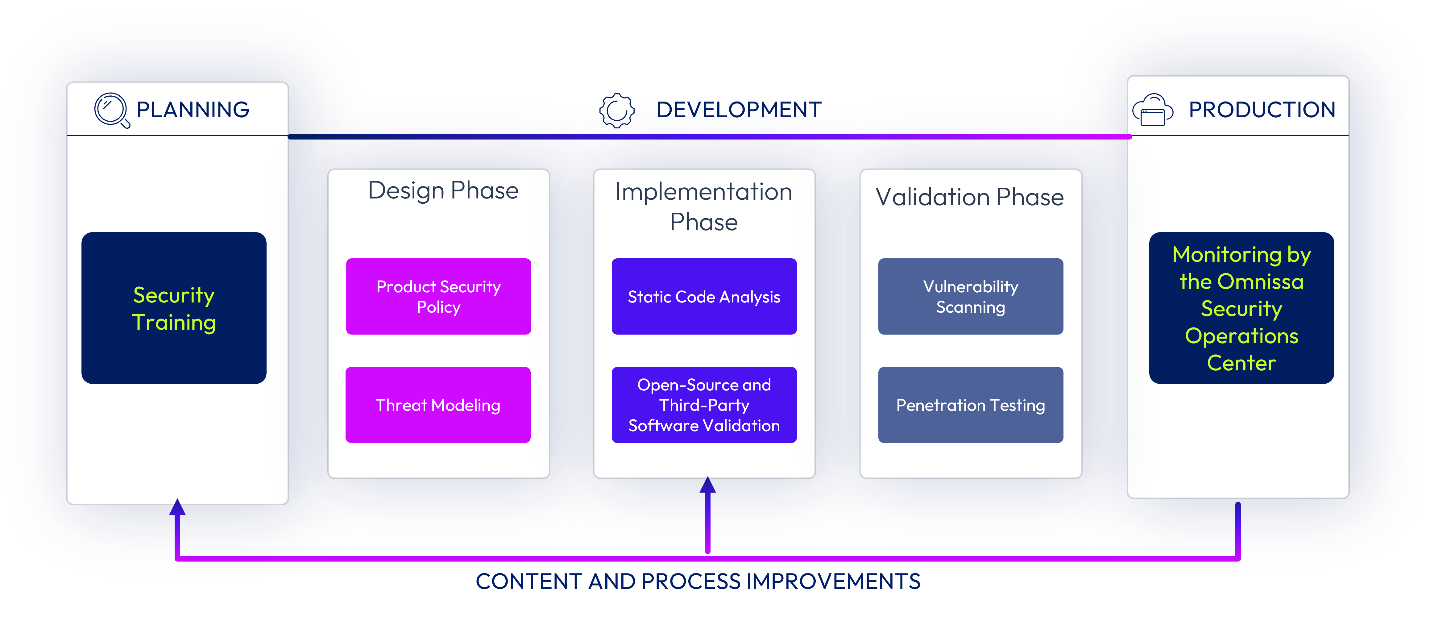
Summary and Additional Resources
Workspace ONE has undergone independent third-party audits on a regular basis to provide assurance to our customers that Omnissa has implemented industry-leading controls. Workspace ONE cloud services are not currently certified for C5. Information contained in this document is solely for the use of evaluating Workspace ONE security controls and does not represent an official endorsement by the BSI or a C5:2020 attestation.
Additional Resources
For more information about Workspace ONE cloud services, you can explore the following resources:
Changelog
The following updates were made to this guide:
Date | Description of Changes |
10/03/2024 |
|
About the Author and Contributors
The following people contributed their knowledge and assistance with this document:
- Andrea Smith, Sr. Program Manager, Customer Security Assurance.
- Andrew Osborn, Omnissa alumni.
Feedback
Your feedback is valuable.
To comment on this paper, contact Omnissa Technical Marketing at tech_content_feedback@omnissa.com.