Empower Frontline Workers Solution: Stage
Overview
Introduction
Frontline workers deliver the essential goods and services we rely on every day. Unlike desk-based knowledge workers, frontline workers are not tied to a desk and instead report to a jobsite or are in the field. Frontline workers make up most of the global workforce and can be found across a variety of essential and nonessential industries, including retail, healthcare, manufacturing, and supply chain logistics. Example frontline worker occupations include delivery drivers, warehouse workers, store associates, nurses, and flight attendants.
When it comes to mobility, frontline workers are unique in that they rely on mission-critical devices to complete the task or operation at hand. These devices are considered mission-critical because if they fail, the worker can’t do their job, immediately impacting the bottom line. It is estimated that device downtime can cost organizations millions of dollars a year in reduced productivity, financial loss, and customer dissatisfaction.
Mission-critical devices come in a variety of form factors, including desktop terminals, rugged handheld computers and tablets, ruggedized consumer devices, mobile point-of-sale or point-of-care devices, mobile printers, head-mounted wearables, interactive or self-service kiosks, and digital signage. They are typically corporate-owned, shared by multiple workers, and are optimized to access line-of-business (LOB) applications to complete a well-defined task or set of tasks.
Corporate-owned mission-critical technologies have unique management requirements. Because devices used by frontline workers are typically deployed outside the office in environments with limited connectivity, enrollment and configuration must be low touch. Organizations must also mitigate downtime by proactively managing devices and having the ability to quickly deploy a fix remotely when inevitable technological issues arise. Most importantly, because frontline worker occupations have a notoriously high turnover rate (with some industries experiencing 50-100% turnover), IT must deliver an exceptional, consumer-like digital experience to keep workers happy and engaged.
Scope of This Document
Workspace ONE provides a comprehensive set of tools across the three primary pillars of mission-critical device management: Stage, Manage, and Support. Each pillar contains technologies to simplify operations for IT teams responsible for mission-critical devices.
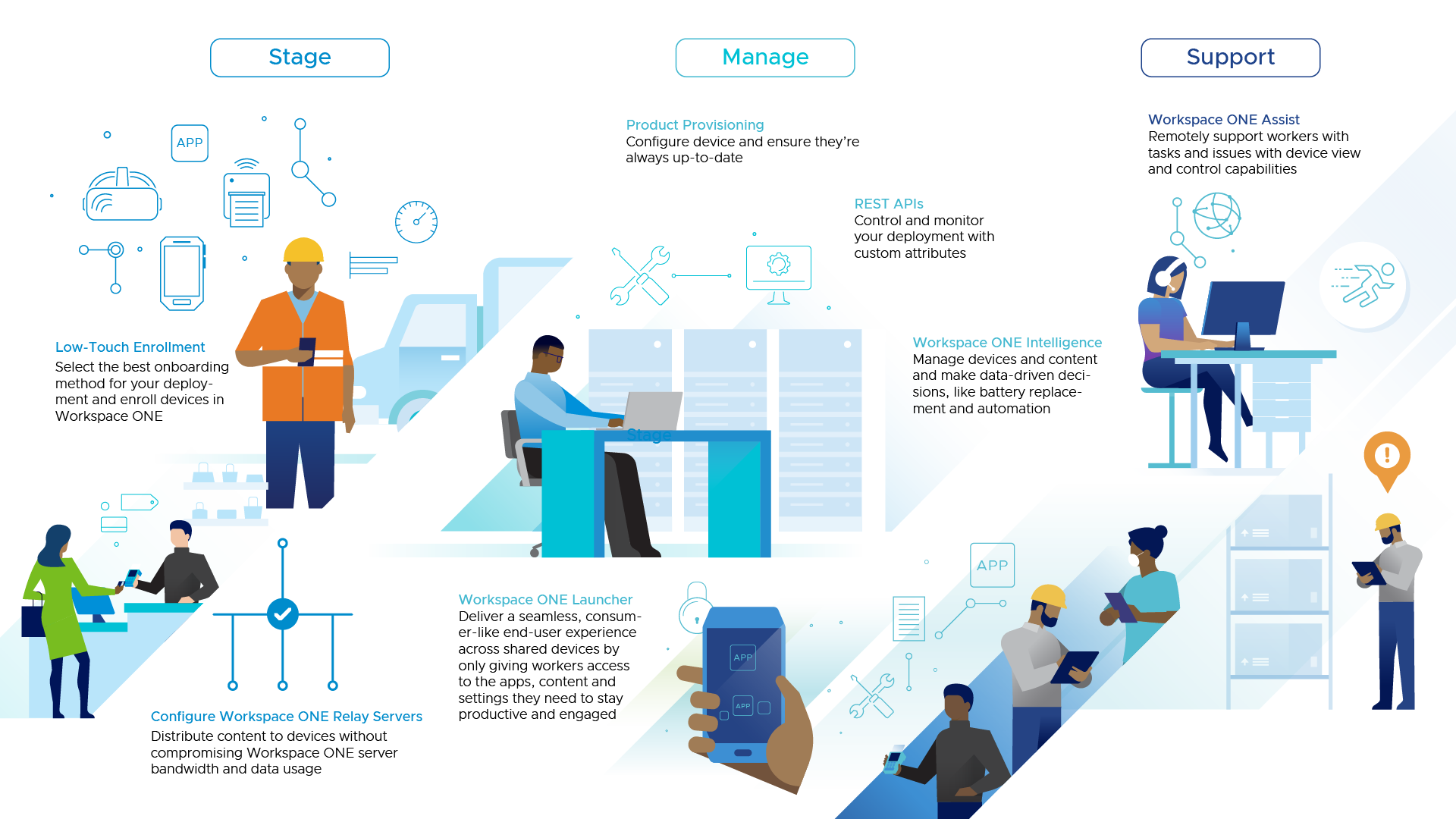
Figure 1: Three pillars of mission-critical device management: Stage, Manage and Support
This deployment considerations document provides an overview of the Stage component of the Empower Frontline Workers solution and is the first document in a three-part series.
Due to the prevalence of the Android operating system in frontline use cases, this document primarily addresses these types of devices.
Audience
This document is intended for prospective and current IT administrators of Workspace ONE and anyone who uses the Workspace ONE platform. Familiarity with mobile device management, security, networking, Active Directory, identity management, and directory services is assumed. Knowledge of Workspace ONE® UEM (Unified Endpoint Management), Workspace ONE® Access, and Horizon® is also helpful.
Stage
Introduction
To Manage and Support your device, it must first be enrolled into the Workspace ONE UEM console. This process is known as Staging. “Stage” is the first step towards preparing your device for production deployment and involves the installation of the Workspace ONE® Intelligent Hub application, configured with the necessary Workspace ONE UEM server information, group ID, username, and password information. A successful Stage process results in device enrollment into the Workspace ONE UEM console, where the device can then be prepared for production deployment.
Figure 2 provides a general overview of the available staging methods for Android Enterprise Enrollment without considering the make and model of the device.
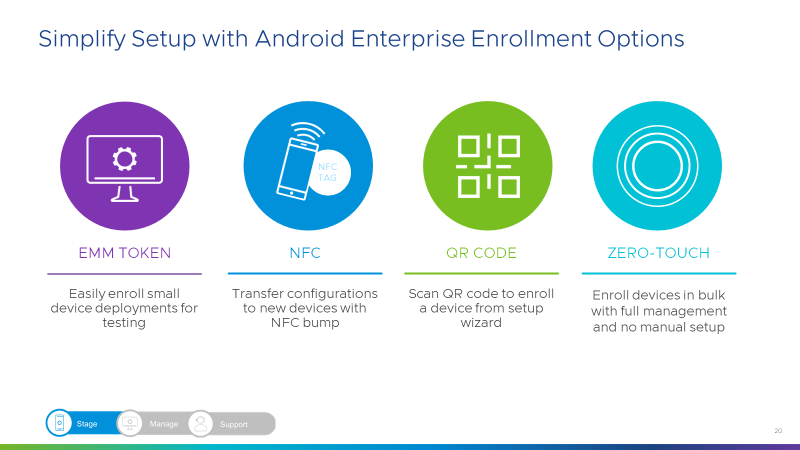
Figure 2: Common Device Staging Options
EMM Token
This method is the most manual, key-intensive approach, typically used for one-off enrollments, but rarely used for Production Staging projects. The “token” referred to here, is represented by an EMM (Enterprise Mobile Management) specific value. For Workspace ONE, the “Token” value is “afw#hub”. This information would need to be provided in place of Personal Google Registration information to start the enrollment process.
Using this method, an IT administrator enters an EMM specific token value in the setup wizard:
- Turn on a new or factory-reset device. Follow the setup wizard.
- Enter Wi-Fi login details to connect the device to the Internet.
- When prompted to sign in, enter the token provided by your EMM.
- Follow the instructions to complete setup.
Which Android devices are supported?
Android Marshmallow (6.0) or later devices.
Which management sets can you deploy with this setup method?
- Full device management
- Dedicated device management
- Work profiles (company-owned, Android 8.0+ devices only)
NFC Bump
This method takes advantage of the NFC radio embedded within many Android devices, which facilitates the automatic transfer of setup information between the host device or NFC tag and the child device to be enrolled into Workspace ONE UEM.
Which Android devices are supported?
Any Android Marshmallow (6.0) or later device with NFC capabilities.
Which management sets can you deploy with this setup method?
- Full device management
- Dedicated device management
QR Code
One of the most common methods used today, a QR code is generated by the Workspace ONE UEM console and intended to be scanned by the device(s) to be enrolled. The QR code contains all the necessary information to provide to the device for enrollment, including the URL download link to the server hosting the Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub app, the URL of the Workspace ONE UEM console, the group ID, username, and password. The device user simply prepares the device to scan the QR code, then scans it to start the enrollment process.
Which Android devices are supported?
New or factory-reset Android Nougat (7.0) or later devices with a QR code reader.
Which management sets can you deploy with this setup method?
- Full device management
- Dedicated device management
- Work profiles (company-owned, Android 8.0+ devices only)
Zero-Touch
Perhaps the most automated approach, and the most secure, is the zero-touch method. If a device is pre-registered to the Google zero-touch portal by an authorized zero-touch reseller partner, that device, upon factory reset boot up, will automatically contact the zero-touch portal and check for an assigned profile. The profile provides instruction to the device as to where to automatically download the Workspace ONE Intelligent Hub and provides the necessary information such as the Workspace ONE UEM console URL, group ID, username, and password information to configure the enrollment.
Which Android devices are supported?
A device running Android Pie (9.0) or later*, compatible devices running Android Oreo (8.0) or later, or Pixel phone with Android Nougat (7.0), purchased from a zero-touch reseller partner.
*Initially via selected resellers only
Which management sets can you deploy with this setup method?
- Full device management
- Dedicated device management
- Work profiles
Out of these Google-provided methods, QR code and zero-touch enrollment are the most popular selections for enrolling a device. As noted in the descriptions for each of these methods, different requirements need to be considered.
OEM Specific Enrollment Methods
Besides the standard Google-provided methods mentioned previously, many device manufacturers have developed their own techniques for enrolling a device into the Workspace ONE UEM console.
Samsung Corporation
Knox Mobile Enrollment (KME) is a Samsung-developed portal, similar to the Google Zero Touch Portal, where resellers can pre-register Samsung devices, and associate a profile that provides instructions to the device for enrollment. KME is designed for bulk enrollments and is a free IT solution offered by Samsung.
Zebra Technologies
StageNow is a utility developed by Zebra Technologies, for Zebra devices, that can be used as a standalone staging solution for simple profile creation and device deployments. StageNow capabilities have been integrated within the Workspace ONE UEM console for enrolling Zebra devices. Using the StageNow menu option within the Workspace ONE UEM console, a StageNow bar code enrollment sheet can be created for an administrator or user to scan and start the enrollment process. See Enroll Zebra Devices with Stage Now Barcode, Android for more information.
Honeywell Corporation
Honeywell’s Enterprise Provisioner utility is a Windows-based software tool used to create provisioning tasks for Honeywell Android devices. Omnissa has worked with Honeywell to integrate enrollment capabilities with this tool into the Workspace ONE UEM console. See Enroll Honeywell Devices with Staging Barcode, Android for more information.
Panasonic Corporation
Panasonic’s Rapid Configuration (PaRC) Tool enables easy setup and configuration of multiple settings profiles across Android-based devices via a central PaRC console. Users can generate a configuration file or QR code using this tool on a Windows PC and apply it to target Android devices. Up to 40 functions can be configured, including Wi-Fi settings, barcode reader setup, app installation, and application allow/deny list. The PaRC tool supports the following Android models: Android 5.1.1, Android 6.0.1, Android 8.1, Android 9.0.
Summary and Additional Resources
Introduction
This deployment considerations document is the first of a three-part series and provided an overview of the Stage component of mission-critical device management, powered by Workspace ONE UEM.
Additional Resources
Visit the Empower Frontline Workers Solution Architecture page on Tech Zone for more technical resources.
Changelog
The following updates were made to this guide:
| Date | Description of Changes |
| 2024/9/12 |
|
| 2023/12/20 |
|
| 2021/09/16 |
|
About the Author and Contributors
This document was written by:
- David Dwyer, Staff Solution Engineer, Solution Engineer and Subject Matter Expert for Mission Critical (Rugged) and IoT Deployments, Omnissa
With contributions from:
- Christina Minihan, Staff Architect, Workspace ONE Technical Marketing, Omnissa
- Jessie Stoks, Group Product Line Marketing Manager, Omnissa
Feedback
Your feedback is valuable.
To comment on this paper, contact Omnissa Technical Marketing at tech_content_feedback@omnissa.com